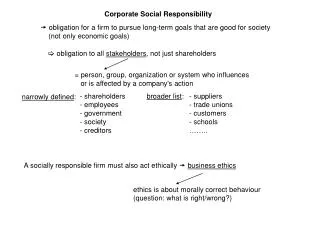
Corporate Social Responsibility
110 likes | 407 Vues
Corporate Social Responsibility. LECTURE 13 Corporate Social Responsibility MGT 610. Corporate Social Responsibility. Chapter 4 Roles of Various Institutions in CSR. Corporate Social Responsibility. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand that CSR is integral to the development process

Corporate Social Responsibility
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Corporate Social Responsibility LECTURE 13 Corporate Social Responsibility MGT 610
Corporate Social Responsibility Chapter 4Roles of Various Institutions in CSR
Corporate Social Responsibility LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Understand that CSR is integral to the development process • Understand the role of the major institutions of the civil society in CSR • Create awareness of certain institutional initiatives in progress and the need for further contribution in the field
Corporate Social Responsibility • The concept of virtue of the market has faded when we are faced with consequences of progress • Question is WHY HAS THE MARKET FAILED TO DELIVER? • All human are basically good and believe in collectivist living • Question is WHY THE DIVIDE BETWEEN THE RICH AND THE POOOR IS INCREASING • Have our own mechanism failed us by creating unethical negative emotions like greed, hatred and jealousy • The answer may be found when we analyze the different markets in which business operates • The three major markets are • Capital markets • Labor markets • Consumer markets
Corporate Social Responsibility • Capital markets • Provides basic necessities for production i.e. land, finances, technology, raw material • While participating in this markets are the firms operating with CSR? • Reason • Search for cheaper, quicker sources rather than ethical sources • Quality of inputs is compromised • CSR Vs productivity • Short term Vs long term • Firms may use CSR to keep government regulations away
Corporate Social Responsibility • Labour markets • It is believed that education creates responsible, trustworthy dependable people. Also the need for highly specialized world of today • As we specialize the depth of knowledge increases but the width of knowledge decreases • This means we are more interdependent and for that one needs trust • If ask a class to identify their favorite company • It would relate back to pay package • And not about how responsible the company was or is • Therefore the company that offers the highest package gets the best brains • Our system of education sharpens the intellect more than the emotions, the labour markets also participates in exploitive behavior • Example Harvard Business School
Corporate Social Responsibility • Consumer markets • Not driven by CSR • Consumer not driven to bear the extra cost of CSR • Driven by advertising and not whether the company has been operating ethically • Companies say that since CSR does not sell we do not highlight it • Though business say that customer is the king but what powers does the king have • Veto power • Veto power can operate when there is equal sharing and transparency • Monopolies and oligopoly limit free choice of consumers thus limiting the virtue of the markets • Consumer at the mercy of the producers • Consumers have to come together collective bargaining power to ensure responsible behaviors
Corporate Social Responsibility • Looking at the above concerns it is important for the government to play a proactive roles to ensure that CSR is promoted • Limit to corporation efforts hence support is needed by government • Responsibility of the government to create safe environment for business investment, provide basic infrastructure, reasonable regulatory processes and public policies • Create a level playing field • Obstacles • MNCs may increase the standards of living but other factors nullify CSR • Vested interest of corporations may lead to unfair policies • Promote products behind the façade of CSR • Government engineering policies that may cater to party funds
Corporate Social Responsibility • Role of the government is to seek balance between authority and responsibility • Ensure that social responsibility is incorporated in their role, relationship and influence • Governance is • Enforcing laws with the objective of ensuring justice, peace • Proactive actions that reduces gaps between have and have not's • Ensure welfare of people • Government justify behavior based on utilitarianism • Problem is moderate benefits to large and severe discomfort to smaller groups • This discomfort may fester in to activities like terrorism and fundamentalist movements • Eat in the process of development
Corporate Social Responsibility • Government has to ensure distributive justice • It has to based on the absence of specific information • Advantage or disadvantaged based on social class and fortune • Government should ensure • Markets remain competitive • Equal opportunity • Resources are utilized efficiently • Outcome of business is distributed • Social capital has to be enhanced by developing human capital • Corruption has to be rooted out to ensure true competitiveness • The role of the government is to provide guidance to business about CSR • Unethical activities thrives best in Chaos • Expectations regarding welfare have to be clear with a proper chain of accountability laid out for monitoring