From Gene to Protein
370 likes | 652 Vues
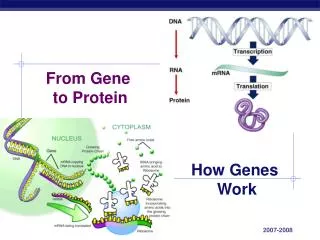
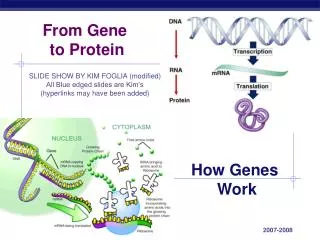
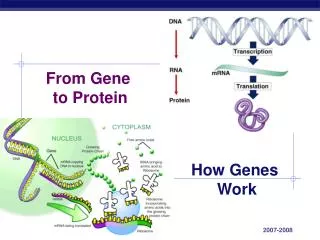
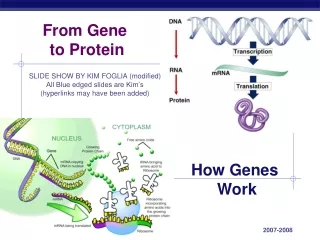
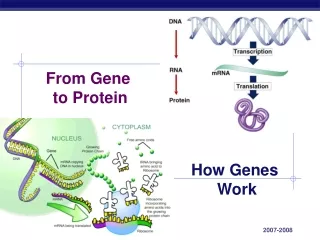
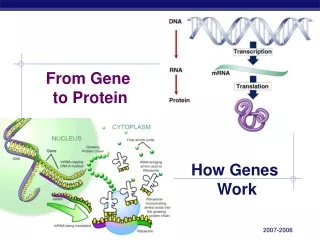
From Gene to Protein. How Genes Work. What do genes code for?. How does DNA code for cells & bodies? how are cells and bodies made from the instructions in DNA. DNA. proteins. cells. bodies. Gene to Protein. Flow of genetic information in a cell

From Gene to Protein
E N D
Presentation Transcript
From Gene to Protein How Genes Work
What do genes code for? • How does DNA code for cells & bodies? • how are cells and bodies made from the instructions in DNA DNA proteins cells bodies
Gene to Protein • Flow of genetic information in a cell • How do we move information from DNA to proteins? transcription translation RNA DNA protein trait DNA gets all the glory, but proteins do all the work! replication
aa aa aa aa aa ribosome aa aa aa aa aa aa From gene to protein nucleus cytoplasm transcription translation DNA mRNA protein trait
RNA • ribose sugar • N-bases • uracil instead of thymine • U : A • C : G • single stranded • lots of RNAs • mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, sRNA… transcription DNA RNA
The Big Picture • Video
Transcription fromDNA nucleic acid languagetoRNA nucleic acid language Transcription Video
Transcription • Making mRNA • transcribed DNA strand = template strand • untranscribed DNA strand = coding strand • same sequence as RNA • synthesis of complementary RNA strand • transcription bubble • enzyme • RNA polymerase coding strand 3 A G C A T C G T 5 A G A A A C G T T T T C A T C G A C T DNA 3 C T G A A 5 T G G C A U C G U T C unwinding 3 G T A G C A rewinding mRNA template strand RNA polymerase 5 build RNA 53
Which gene is read? • Promoter region • binding site before beginning of gene • TATA box binding site • binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors
Transcription Factors • Initiation complex • transcription factors bind to promoter region • suite of proteins which bind to DNA • turn on or off transcription • trigger the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA 1 2
RNA polymerase Matching bases of DNA & RNA A • RNA poymerase unwinds double helix and matchsRNA bases to DNA bases • RNA polymerase added to the 3’ end • Transcription continues until termination sequence is read C U G A 3 4 5 G G U C U U G C A C A U A G A C U A 5' 3' G C C A T G G T A C A G C T A G T C A T C G T A C C G T
3' poly-A tail 3' A A A A A mRNA 50-250 A’s 5' cap P P P 5' G Post-transcriptional processing • Need to protect mRNA on its trip from nucleus to cytoplasm • enzymes in cytoplasm attack mRNA • protect the ends of the molecule • add 5 GTP cap • add poly-A tail • longer tail, mRNA lasts longer: produces more protein 6
intron = noncoding (inbetween) sequence exon = coding (expressed) sequence Eukaryotic genes have junk! • Eukaryotic genes are not continuous • exons = the real gene • expressed / coding DNA • introns = the junk • inbetween sequence intronscome out! eukaryotic DNA
intron = noncoding (inbetween) sequence exon = coding (expressed) sequence mRNA splicing • Post-transcriptional processing • eukaryotic mRNA needs work after transcription • primary transcript = pre-mRNA • mRNA splicing • edit out introns • make mature mRNA transcript ~10,000 bases eukaryotic DNA pre-mRNA primary mRNA transcript ~1,000 bases mature mRNA transcript spliced mRNA
snRNPs snRNA intron exon exon 5' 3' spliceosome 5' 3' lariat 5' 3' exon exon mature mRNA excised intron 5' 3' RNA splicing enzymes • snRNPs • small nuclear RNA • Attaches to introns • Spliceosome • several snRNPs • recognize splice site sequence • cut & paste gene 7 8
Gene to Protein Processed mRNA leaves the nucleus 9
Learning Check • Summarize the steps of transcription
Translation fromnucleic acid languagetoamino acid language
The Structure of Proteins • Proteins are made from subunits called amino acids • Hundreds of thousands of different proteins made by all living things are remarkably similar in their construction • All proteins in living things are assembled from only 20 different amino acids
TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGG DNA AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCC mRNA MetArgValAsnAlaCysAla protein ? How does mRNA code for proteins? How can you code for 20 amino acids with only 4 nucleotide bases (A,U,G,C)? 4 ATCG 4 AUCG 20
TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGG DNA AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCC mRNA AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCC mRNA codon MetArgValAsnAlaCysAla protein ? mRNA codes for proteins in triplets
The code • Code for ALL life! • strongest support for a common origin for all life • Code is redundant • several codons for each amino acid • Start codon • AUG • methionine • Stop codons • UGA, UAA, UAG
GCA UAC CAU Met Arg Val How are the codons matched to amino acids? 3 5 TACGCACATTTACGTACGCGG DNA 5 3 AUGCGUGUAAAUGCAUGCGCC mRNA codon 3 5 tRNA anti-codon aminoacid
aa aa aa aa aa ribosome aa aa aa aa aa aa From gene to protein nucleus cytoplasm transcription translation DNA mRNA protein trait
Transfer RNA structure • “Clover leaf” structure • anticodon on “clover leaf” end • amino acid attached on 3 end
Ribosomes • Facilitate coupling of tRNA anticodon to mRNA codon • Structure • ribosomal RNA (rRNA) & proteins • 2 subunits • large • small E P A
3 2 1 Building a polypeptide • Video • Initiation • brings together mRNA, ribosome subunits, initiator tRNA • Elongation • adding amino acids based on codon sequence • Termination • end codon release factor Leu Val Ser Met Met Ala Leu Met Met Leu Leu Trp tRNA C A G C G A C C C A A G A G C U A C C A U A U U A U G A A 5' 5' A A 5' C U U 5' A A G G A G U U G U C U U U G C A C U 3' G G U A A U A A C C mRNA 3' 3' 3' U G G U A A 3' E P A
RNA polymerase DNA Can you tell the story? aminoacids exon intron tRNA pre-mRNA 5' GTP cap mature mRNA aminoacyl tRNAsynthetase poly-A tail 3' large ribosomal subunit polypeptide 5' tRNA small ribosomal subunit E P A ribosome
Mutations Mutations are changes in DNA • Point mutations – single base pair change • Inheritable (if occurs in gametes)
Point mutation • Base pair substitution • Replacement of a pair of complementary nucleotides with another nucleotide pair • Some have little/no impact • Silent mutation • No observable effect on the phenotype • How is this possible?
Missense mutation • Amino acid swap • Some may have little effect, others can cause disease
Nonsense mutation • Amino acid changed to stop codon • Drastically alters the protein
Mutations • Frameshift mutations- involve the insertion or deletion of a base • They result in an entirely different sequence of amino acids because they change the _______________ Mutations are changes in DNA