RSA Cryptosystem
140 likes | 641 Vues
RSA Cryptosystem. What is RSA ?. RSA is a public-key cryptosystem . It was developed by Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman in 1977. The security of the RSA system is based on the hard problem of factoring a large integer. Public-key cryptosystem.

RSA Cryptosystem
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is RSA ? • RSA is a public-key cryptosystem. • It was developed by Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman in 1977. • The security of the RSA system is based on the hard problem of factoring a large integer.
Public-key cryptosystem • Encrypt messages with private(public) key and decrypt with public(private) key. • It’s computationally infeasible to determine dk given ek and cryptographic algorithm. • RSA , ElGamal , Elliptic Curve are well-known public-key cryptosystems.
C = ESK(M) M = DSK(C) Bob Alice Secret-key cryptosystem CA= E(MA ,PKB) MA = D(CA ,PRB) Alice Bob Public-key cryptosystem
Why public-key? • Key distribution Conventional encryption require to share key in advance . • Digital signature Secret-key cryptosystem can’t provide authentication.
Secrecy and Authentication KRa KUb y x Source A Message source Encryption Algorithm Encryption Algorithm network Decryption Algorithm Decryption Algorithm Message dest. Destination B KUa KRb
RSA algorithm Key Generation Select p,q p and q both prime Calculate Calculate Select integer e Calculate d Public key KU = {e,n} Private key KR = {d,n}
RSA algorithm (continue) Encryption Plaintext : M < n Ciphertext : C = Me ( mod n ) Decryption Plaintext : C Ciphertext : M = Cd ( mod n )
The Security of RSA • Possible approaches to attack RSA: Brute Force Try all possible keys Mathematical attacks Equivalent to factor n Timing attacks Depending on the Running time of decryption.
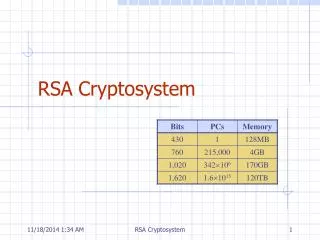
The Security of RSA Mathematical attacks: Factoring a 130 decimal digits (431 bits) has been done. Key size: 1024 ~ 2048 bits will be reasonable in the future.
Application of RSA • E-bank • VPN • Secure telephones • Palm • Wireless Devices ex. Ericsson R380s ,Nokia 9210 • Reference: www.rsasecurity.com