Mastering Literacy Concepts: EOG Test Strategies
980 likes | 1.09k Vues
Prepare for your EOG test with effective strategies for reading comprehension. Learn how to find main ideas, recall facts, understand sequence, and more. Get ready to ace your test with these helpful tips!

Mastering Literacy Concepts: EOG Test Strategies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
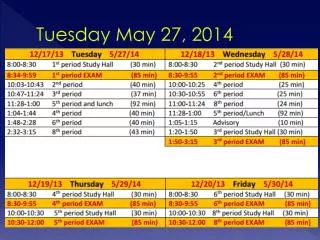
May 27, 2014 EOG Review Homework: Get a good night's sleep. Eat breakfast. Don't stress- YOU KNOW ALL OF THIS STUFF!!! Objective: I can show mastery of literacy concepts learned this year. I can ROCK tomorrow's EOG!!! Warm Up (in your composition book) Take out your comp book or paper to take notes on. http://www.really-learn-english.com/image-files/prepc-intro.png
Things to remember.... 1. All bookbags, pencil pouches, PHONES (turned off completely) etc. to be left in your locker. We will go to lockers once all students have finished testing. 2. Bring ONLY sharpened #2 or mechanical pencils with good erasers(make sure you have enough lead if using mechanical), a highlighter and a sweatshirt or jacket in case you get cold. 3. ABSOLUTELY NO CELL PHONES, GUM, WATER BOTTLES, FOOD, BOOKS, ETC. ALLOWED IN CLASSROOM.
Test taking strategies Use RUNNERS!!! Read and highlight key words in all questions and important information in the text. Read the entire passage and everything above, below, in sidebars, captions, etc. Reread the question, figure out what it is asking, and read ALL the answer choices! Eliminate wrong answers and be able to justify why they are incorrect. Look back into the passage to be able to justify your answer choice. Don't leave any questions blank. If you need to come back to a question, mark the question in your booklet, not on the answer sheet! Be sure that your question number in the booklet matches the question number on your answer sheet. If you change an answer, be sure to erase your first answer completely! http://rakadd.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/test-cartoon-picture20testanxiety1.gif
Understanding the questions Finding the main idea Recalling facts and details Understanding sequence Recongnizing cause and effect Comparing and contrasting Making predictions Finding word meaning in context Drawing conclusions and making inferences Distinguishing between fact and opinion Identifying author's purpose Interpreting figurative language Summarizing
Finding the main idea What is the main idea?
Finding the main idea The main idea of a reading passage is a sentence that tells what the passage is mostly about. Questions about the main idea ask you to find what a passage is mostly about or mainly about. The question might also ask you to choose the best title for a passage. When answering a question about the main idea, ask yourself, "What is the passage mostly about?"
Recalling facts and details Every reading passage contains facts and details. The facts and details tell more about the main idea. Questions about facts and details ask you about something that was stated in the passage. To answer a question about a fact or a detail , look back in the passage to find the answer.
Understanding sequence Sometimes a passage is told in order, or sequence. Different things happen at the beginning, in the middle or at the end of the passage. Questions about sequence ask you to remember and put events or details in order. Questions about sequence often contain key words such as first, then, last, after, before, etc.
Recognizing cause and effect What is a cause? What is an effect?
Recognizing cause and effect A cause is something that happens. An effect is something that happens because of the cause. Look at the example below: I forgot to set my alarm clock, so I was late for school. What is the cause? What is the effect? Questions about cause and effect usually begin with key words such as Why, what happened or because.
Comparing and contrasting What does it mean to compare? What does it mean to contrast?
Comparing and contrasting Some questions ask you to find how two things are alike (compare) or different (contrast). Questions that ask you to compare or contrast usually contain key words such as most like, different, alike, similar to, etc.
Making predictions What is a prediction?
Making predictions A prediction is something you think will happen in the future. You will not find the answers to these questions stated directly in the passage, but there are clues you can use from the passage to make a good guess about what might happen next. Questions about predictions ask What will probably happen or what is most likely to occur next.
Finding word meaning in context What are context clues?
Finding word meaning in context Sometimes when you read, you come across a word you do not know. You may be able to tell the meaning of the word by the way it is used in the sentence. This is called understanding the word meaning in context. Questions about meaning in context ask you to find the meaning of a word that may not be familiar to you based on clues in surrounding sentences. If you have trouble choosing an answer for a question like this, try each answer choice in the sentence where the word appears in the passage, and see which one makes the most sense.
Drawing conclusions and making inferences What is an inference?
Drawing conclusions and making inferences When you read, many times you must figure out things on your own. The author doesn't always tell you everything. Read the following sentences: The moon cast an eerie glow in Jake's room. Suddenly, he saw a shadow by the window. Jake sat up in bed, frozen with fear. From what the author has written, you can infer that it was nighttime, since the moon was out, and Jake was in bed. What else can you infer? Questions about drawing conclusions often contain the key words you can tell or probably.
Distinguishing between fact and opinion What is a fact? What is an opinion?
Distinguising between fact and opinion A fact is something that can be proven to be true, while an opinion is how someone feels about something. Statements that are opinions often contain key words such as best, most, nicest, greatest, etc.
Summarizing What is a summary?
Summarizing Questions about the best summary of a passage ask you about the main points or events of a passage. When you answer questions about a summary, first ask yourself What is the main idea of the passage? A good summary is closer to the main idea than to any single detail found in the passage.
Identifying author's purpose What is author's purpose?
Identifying author's purpose Questions about author's purpose ask you WHY an author wrote the passage. Most authors write for one of these reasons: to PERSUADE the reader to INFORM the reader to ENTERTAIN the reader
Elements of fiction What are elements that a story must / may have?
Elements of fiction Plot Characters Setting Point of view Theme Symbol
plot chart what is plot?
exposition introduces
characters the animal, people or things that take place in the action of a story
characterization the techniques a writer uses to ________________________
methods of characterization *think of a new kid walking into school...how will you get to know him /her? * appearance - how does the character look? thoughts - what does the character think? what do other characters say about him/her? dialogue - what does the character say? actions - what does the character do?
characterization one final way that a character might be revealed in a story is through comments from the narrator.
exposition introduces setting
setting the time and place where the action in a story occurs - there "where" and the "when" of a story
central conflict the main problem or struggle that drives the plot of a story
conflict the struggle between opposing forces within the plot of a story
rising action the plot builds in intensity as characters struggle internally and externally
climax the _____________________ of the story
falling action events __________________ and lead to the plot's _______________________
resolution the outcome of the _______________________; loose ends are tied up
theme the ______________________ of a work of literature. *Remember* Multiple texts can all have the same theme Think about the topic of the work, then ask what lesson does the author want me to know relating to this topic.
symbol a symbol is a person, place, object or activity that stands for something beyond itself.
elements of nonfiction Types of nonfiction biography autobiography essay informative article interview
biography The story of a person's life told by someone else
autobiography The story of a person's life told by ______________________ 4 types of autobiographical writing memoir journal diary letter
memoir a form of autobiographical writing that focuses on ________________________