Bacterial genomes
340 likes | 1.37k Vues
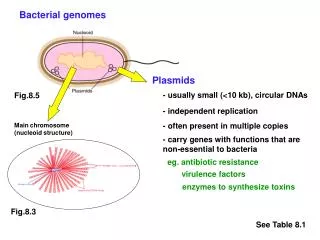
Bacterial genomes. Plasmids. - usually small (<10 kb), circular DNAs. Fig.8.5. - independent replication. - often present in multiple copies. Main chromosome (nucleoid structure). - carry genes with functions that are non-essential to bacteria. eg . antibiotic resistance.

Bacterial genomes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bacterial genomes Plasmids - usually small (<10 kb), circular DNAs Fig.8.5 - independent replication - often present in multiple copies Main chromosome (nucleoid structure) - carry genes with functions that are non-essential to bacteria eg. antibiotic resistance virulence factors enzymes to synthesize toxins Fig.8.3 See Table 8.1
Not all bacteria have single, circular chromosomes… Table 8.2 Deinococcusradiodurans 2 circular chromosomes (2.6 & 0.4 Mbp), megaplasmid (177 kb) & plasmid (46 kb) Borrelia burgdorfei (Lyme disease) ~1.0 Mb linear plus 14-21 small linear & circular plasmids (ranging in size from ~ 5 – 60 kb, NCBI site) White Science 286:1571, 1999 … so difficult to define a “bacterial genome” etc. GironsMicrobiol140:1803, 1994 If a plasmid carries essential gene(s), consider it part of genome
First bacterial genome sequenced July 1995: Haemophilus influenza 1.8 Mbp Small segment of H. influenza genome: Energy metabolism Replication Amino acid biosynthesis
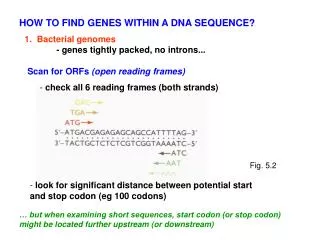
GENOME OF E.coli K12 - coloured blocks above or below line denote orientation of genes (ie. direction of transcription) 4639 kb Further blowup: Genes on opposite strands are close, but not at exactly same location Fig.8.6 - usually single, circular genomes in bacteria - tightly packed with genes (rarely introns in bacteria) - short intergenic spacers (expressed as single polycistronic RNA) - genes sometimes organized as operons ~ 600 operons in E.coli, often encode proteins for related function or pathway (eg lac operon for lactose utilization) - DNA transposons (IS elements) ~ 20 in E.coli genome
CATEGORIES OF BACTERIAL GENES Table 8.4
RANGE OF BACTERIAL GENOME SIZES “Native” genes Foreign DNA eg. transposons, IS elements (insertion sequences) Fig.8.10
DNA transposons in bacteria Transposons can mediate horizontal gene transfer between bacteria Fig. 9.17
LATERAL GENE TRANSFER - movement of genes horizontally from one species to another (vs. vertical transmission from parent to progeny) Mediated by bacteriophages, plasmids, transposons ... Brown 2d ed Fig. 2.23
And some bacteria have large number of pseudogenes… Mycobacterium leprae vs. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Nature 409: 1007, 2001 Massive gene decay in M. leprae “reductive evolution” in obligate parasites during colonization of new niche?
Welch PNAS 99:17020, 2002 3 strains of E.coli compared Venn diagram All three are very different from each other in gene content! - recently acquired pathogenicity genes on “islands” in genome (enable specialized niches?) - genomic data useful in developing effective drugs?
News release Nov. 13, 2012: “An outbreak of the hospital superbug MRSA has been brought to an end by UK doctors cracking the bacterium's genetic code” Lancet Infect Diseases (published on-line Nov. 14, 2012) Patient Hiramatsu Trends Microbiol 9:486,2001 SCBU= special care baby unit Black boxes: how long in hospital “After two months without a case and deep cleaning the ward, another case appeared. Analysing the DNA showed that it was again part of the outbreak and attention turned to a carrier.” “Tests on 154 members of staff showed that one [red H in figure] was also carrying MRSA, which may have been spread to babies in the unit. They were treated to remove the infection.”
Bacteriophage genomes Table 9.1 - use as tools in molecular biology (vectors) - vehicle for movement of genes between bacteria Genes are tightly packed in bacteriophage & viral genomes ... with some cases of overlapping genes Gene D (capsid morphogenesis) Gene E (cell lysis) - different reading frames are used Fig. 9.2
Mitochondria (and chloroplasts) originated from endosymbiotic bacterial ancestors and many genes were transferred to the host nucleus But the organelles retained a small number of genes essential for respiration (mito) and photosynthesis (chl) see Fig.8.11-813 Timmis Nature Rev Genet 5:123, 2004