The Autonomic nervous system
220 likes | 602 Vues
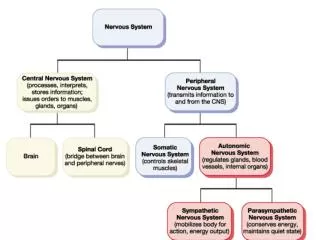
Honors Anatomy & Physiology. The Autonomic nervous system. in PNS operates via reflex arcs includes: autonomic sensory neurons integrating centers in CNS autonomic motor neurons. ANS. Autonomic reflex arc.

The Autonomic nervous system
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Honors Anatomy & Physiology The Autonomic nervous system
in PNS • operates via reflex arcs • includes: • autonomic sensory neurons • integrating centers in CNS • autonomic motor neurons ANS
when somatic motor neurons sends impulse to a muscle the effect always excitatory…if they stop sending impulses that muscle atrophies autonomic motor neurons regulate visceral activities by either increasing (exciting) or decreasing (inhibiting) ongoing activities in their effector tissues (cardiac or smooth muscle, glands) Autonomic Motor Neurons
source of most input to ANS via sensory receptors called interoceptors • not consciously perceived most of time • located in: • blood vessels • visceral organs • muscles • in nervous system Autonomic sensory neurons
most cannot be altered to any great degree making some responses ideally suited for lie detector tests Autonomic responses
most consist of 3 motor neurons in series 1st neuron has cell body in CNS myelinated axon synapses in autonomic ganglion with 2nd motor neuron cell body: its unmyelinated axon effector except Autonomic Motor Pathways
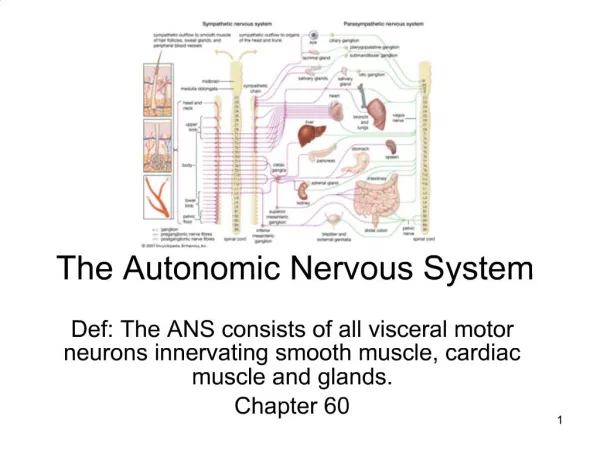
Sympathetic Division Parasympathetic Division • preganglionic axons from thoracolumbar nerves • ganglia far from visceral effector in: • sympathetic chain or collateral ganglia • neurotransmitter used: • ACh in ganglia • NE in effector organ • preganglionic axons from craniosacral nerves • ganglia near or w/in visceral effector organs • neurotransmitter used: • ACh in ganglia • ACh in effector organ 2 Branches of Motor part of ANS
most organs have dual innervation nerve impulses from 1 will increase activity (excitation) & impulses from other decrease activity (inhibition) Motor part of ANS
2 groups: • sympathetic trunk ganglia • lie in vertical row, either side of vertebrae • prevertebral ganglia • lie anterior to vertebral column close to large abdominal arteries Sympathetic ganglia
Parasympathetic ganglia • most close to or w/in effector organ
Effects of sympathetic & parasympathetic divisions of the ans
Raynaud’s phenomenon: • due to excessive sympathetic stimulation of smooth muscles in arterioles of digits • digits become ischemic (lack of blood) after exposure to cold or with emotional stress Homeostatic Imbalances of the ans
autonomic nerve neuropathy: often caused by long-standing diabetes, neuropathy affects 1 or more autonomic nerves, can interfere with reflexes hyperhydrosis: profuse sweating due to intense stimulation of sweat glands vagotomy: cutting vagus nerve; often done to decrease production of HCl in patients with severe ulcers Medical terminology