Longest Palindromic Substring
630 likes | 1.37k Vues
Longest Palindromic Substring. Yang Liu. Problem. Given a string S Find the longest palindromic substring in S. Example: S=“ abcbcbb ”. The longest palindromic substring is “ bcbcb ”. Simple Idea(Brute Force). S=“ abcbcbb ”. Length= n(6) substring: “ abcbcbb ”---not palindromic.

Longest Palindromic Substring
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Longest Palindromic Substring Yang Liu
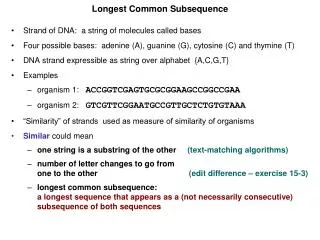
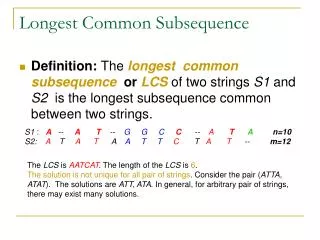
Problem • Given a string S • Find the longest palindromic substring in S. Example: S=“abcbcbb”. The longest palindromic substring is “bcbcb”.
Simple Idea(Brute Force) S=“abcbcbb” Length=n(6) substring: “abcbcbb”---notpalindromic Length=n-1(5) substring: start=0, end=n-2(4): “abcbc”---notpalindromic start=1, end=n-1(5): “bcbcb”---palindromic Longest palindromic substring: “bcbcb”
Simple Idea(Brute Force) For len=n to 2 for start=0 to n-len end= start+len-1 if substring(start,end) is palindromic return substring(start,end) Return first character Complexity
Dynamic Programming(DP) • If substring(i,j) is palindromic, then substring(i+1,j-1) is palindormic • P[i,j]=1 if substring(I,j) is palindormic =0 otherwise • When j-i is small(=0, 1), easy to know: P[i,i]=1 and P[i,i+1]=(S[i]==S[j]) (base) • Computer P[i,j] from small j-i to big j-i: P[i,j]=P[i+1,j-1] && S[i]==S[j]
Example of DP S=“abcbcbb” P[i,i]
Example of DP S=“abcbcbb” P[i,i] P[i,i+1]
Example of DP S=“abcbcbb” P[i,i] P[i,i+1] P[i,i+2] P[i,i+3]
Example of DP S=“abcbcbb” P[i,i] P[i,i+1] P[i,i+2] P[i,i+3] . . .
Example of DP S=“abcbcbb” Max palindromic substring? P[i,i] for(len=n to 1) for(i=0 to n-len) if (P[i,i+len-1]) return S[i..i+len-1] P[i,i+1] P[i,i+2] P[i,i+3] . . .
DP Algorithm for(i=0 to n-1) P[i,i]=1; P[i,i+1]=(S[i]==S[i+1])?1:0; for(len=3 to n) for(i=1 to n-len+1) P[i,i+len-1]=(P[i+1,i+len-2] && S[i]==S[i+len])?1:0 for(len=n to 1) for(i=0 to n-len) if (P[i,i+len-1]) return S[i..i+len-1] O(n2) time and space
Algorithm of O(1) Space and O(n2) time • Given the center of a palindrome, easy to find the maximum substring with that center • center at i: check S[i-dist]==S[i+dist] S=“abcbcbb” center at 2(c) S[2-1]=S[2++1]=b continue S[2-2]!=S[2+2] stop • center at i,i+1: check S[i-dist]==S[i+1+dist] • Do this for all possible centers(n+n-1=2n-1)
Linear Time Algorithm • The previous algorithm simply computes: • an array P[1..n-1] where P[i] is the length of maximum substring centered at i. • an array Q[1..n-2] where Q[i] is the length of maximum substring centered at i and i+1. • Can we reduce the time to compute P[i] & Q[i] by using already computed P[j] & Q[j] (j<i)?
Compute P[i] & Q[i] Efficiently S=“abbabbabbabbabbaba” • “abbabbabbabbabbaba” P[6]=12 • “abbabbabbabbabbaba” Q[7]=16 • P[7]? Q[7]? • “abbabbabbabbababa” Shall we compare S[8] & S[10]? • “abbabbabbabbababa” No! its image P[2] W.R.T S[7] and the rightmost edge of P[7] provide a lower bound. • Similarly, “abbabbabbabbabbaba” implies a lower bound from P[6] and the rightmost edge of Q[7]
Lower Bound of P[i] • Depends on the rightmost edge of paralindromic substrings and the image of S[i] in the substring. • Rightmost edge: rEdge • Image: depends on the length of the substring • can we make the length of paralindromic substrings to be always odd?
Length Change of Paralindromic Substrings • Insert a special character between any adjacent characters in the input string • S =“abcbcbb” S=“#a#b#c#b#c#b#b” • S=“abccbab” S=“#a#b#c#c#b#a#b”
Center, Image, and Rightmost Edge • “abbabbabbabbabbaba” P[19]=? center rEdge=26 =13 • “#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#a” image=2*13-19=7 P[7]=13 P[19]>=P[7]=13
Center, Image, and Rightmost Edge • “aababbabbabaaaba” P[19]=? center rEdge=28 =15 • “#a#a#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#a#a#a#b#a” image=2*15-19=7 P[7]=7 P[21]>=P[7]=7
Center, Image, and Rightmost Edge • “babbabbabbabbaaaba” P[21]=12 center rEdge=28 =15 • “#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#a#b#a#b#a” image=2*15-21=9 P[9]=19 P[21]>=2(rEdge-i)-1 =2(28-21)-1=13
Center, Image, and Rightmost Edge • “babbabbabbabbaaaba” P[21]=12 center rEdge=28 =15 • “#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#a#b#a#b#a” In general, paralindromic substring centered at i can be extended to one side at least min(P[i], rEdge-i) (P[i] now refers to the maximum characters in one side including the center character at i)
Center, Image, and Rightmost Edge • “abbabbabbabbabbaba” P[19]=? center rEdge=26 =13 • “#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#a” image=2*13-19=7 P[7]=7 P[19]>=min(P[7],26-19)=7
Center, Image, and Rightmost Edge • “aababbabbabaaaba” P[19]=? center rEdge=28 =13 • “#a#a#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#a#a#a#b#a” image=2*13-19=7 P[7]=3 P[21]>=min(P[7],28-)=
Center, Image, and Rightmost Edge • “babbabbabbabbaaaba” P[21]=12 center rEdge=28 =15 • “#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#b#b#a#a#b#a#b#a” image=2*15-21=9 P[9]=10 P[21]>=min(P[9],28-21+1)=8
O(n) Algorithm For(i=1 to n-1) insert special character before A[i] center=0; rEdge=0; For(i=1 to 2n-1) image=2*center-i; P[i]=min(P[image],rEdge-i+1); extend P[i] to its maximum; if(P[i]+i>rEdge) rEdge=P[i]+I; center=i; Find the maximum P[i] for i in 1, 3, …, 2n-1. Return the substring centered at i with 2P[i]-1 characters. Why the complexity is O(n)?
Exercise 1 • Find one of the longest paralindromic subsequences. Example: S=“abbbcccabaa” Longest paralindormicsubsequenc: “abccba” from “abbbcccabaa”
Exercise 2 Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. Do this without extra space.
Research Reference “A New Linear-Time ‘On-Line’ Algorithm for finding the smallest initial palindrome of a string”, G. Manacher, JACM 22(3):346-351, 1975.