Projectile Motion
100 likes | 385 Vues
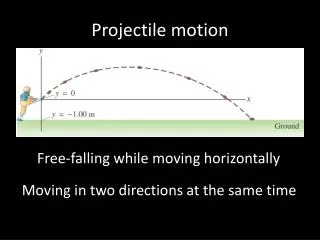
Projectile Motion. Also known as two dimensional motion or trajectory problems. Projectile Motion. Projectile motion occurs when objects are launched at an angle so they are moving in both the horizontal and vertical directions. Projectile Motion.

Projectile Motion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Projectile Motion Also known as two dimensional motion or trajectory problems
Projectile Motion • Projectile motion occurs when objects are launched at an angle so they are moving in both the horizontal and vertical directions
Projectile Motion • Key Idea: Because gravity only acts vertically, the way to solve these problems is to separate the problem into a vertical part and a horizontal part and solve them separately.
Projectile Motion • Typically the place to start is to resolve the velocity vector (which is at an angle) into a vertical velocity and horizontal velocity.
Projectile Motion • Solve the problem by keeping the vertical and horizontal components in separate tables • VerticalHorizontal • The variable which is common to both is time.
Projectile Motion • Example: launch a cat at 50m/s at an angle of 30 degrees w/the horizontal • Find the maximum height, horizontal distance, and time in the air • V(horizontal) = 50 x cos(30) = 43.3 m/s • V(vertical) = 50 x sin(30) = 25 m/s
Projectile Motion • Vertical • V(vertical) = 25m/s • Time (to peak) = 2.5 seconds so total time up and down is 5.0 seconds • Distance (up) = ½ a t2 = 31.2m
Projectile Motion • Horizontal • We found the total time in the air = 5 seconds (from the vertical part) • The distance travelled horizontally is the horizontal velocity x time = 43.3m/s x 5s = 220m
Projectile Motion • Nice visual
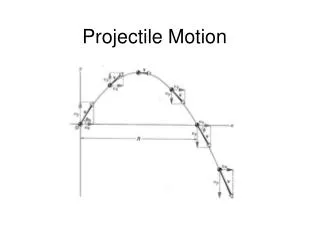
Projectile Motion • Nicer visual