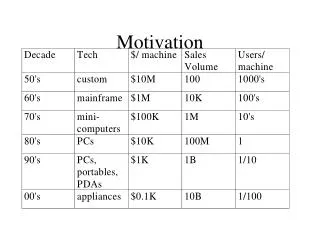
Research Motivation
450 likes | 912 Vues
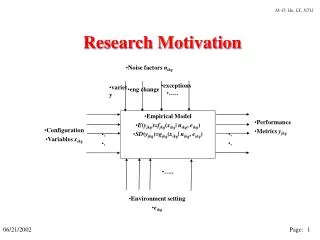
Noise factors n ikq. exceptions. variety. eng change. …. Empirical Model E ( y jkq )= f jkq ( x ikq | n ikq , e ikq ) SD ( y jkq )= g jkq ( x ikq | n ikq , e ikq ). Performance Metrics y jkq. Configuration Variables x ikq. …. Environment setting e ikq. Research Motivation.

Research Motivation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Noise factors nikq exceptions variety eng change ….. Empirical Model E(yjkq)=fjkq(xikq| nikq, eikq) SD(yjkq)=gjkq(xikq| nikq, eikq) Performance Metrics yjkq Configuration Variables xikq . . . . ….. Environment setting eikq Research Motivation Page:
晶圓廠產出目標轉換成分散式產流控制規範之研究晶圓廠產出目標轉換成分散式產流控制規範之研究 胡 明 德 M.-D. Hu, S.-C. Chang, “Translating Overall Production Goals into Distributed Flow Control Parameters for Semiconductor Manufacturing,” Journal of ManufacturingSystems, Vol. 22, No. 1, 46-63, 2003. NSC-89-2212-E-002-040 中華民國九十一年六月二十一日 Page:
Outlines • Research Motivation • OQN Modeling • Decomposition-Based OQN Analysis • Translation Problem Solution: BQNA • Numerical Experiments • Conclusions & Future Research Page:
Noise factors nikq exceptions variety eng change ….. Empirical Model E(yjkq)=fjkq(xikq| nikq, eikq) SD(yjkq)=gjkq(xikq| nikq, eikq) Performance Metrics yjkq Configuration Variables xikq . . . . ….. Environment setting eikq Research Motivation Page:
Mask Clean Oxidation Lithography Wafer Oxide Photoresist Photoresist strip Etching Wafer Fabrication • Process Flow Highly Re-entrant • Fabricate an Oxide Layer • Machine Unreliable • High Capital Investment • High Product Add-on Value / Short Life Cycle Page:
PFC Activities in a Fab Page:
Overall Production Goals Manufactuing Execution System (on-line measurements) Production Flow Control Parameter Extraction Wafer Fabrication Shop Floor PFC Schemes (release/dispatching) PFC Process Logic in a Fab Modeling Performance Analysis Control Page:
Overall Production Goals • System Output Rate :d • System Cycle Time :T • Inter-Departure Time Variability : translating PFC Control Requirements • Wafer Release Control : • Dispatching Decision Reference : -Nodal WIP, Nodal CT Need : Translation Methodology Page:
Given • Fab production Goals • Process Routing Information • Service Node Parameters • By Assuming • FCFS Discipline for Each Node • To Solve • External Arrival Parameters • Internal Arrival Parameters of Each Node Define Generic Translation Problem Page:
OQN Modeling Page:
OQN Model of a Re-entrant Line Node : Group of Identical Failure Prone Machines Queue : Infinite Buffer for each Step Job Class : Part Type Arrival : General Independent Processes Service : General Time Distribution Routing : Deterministic with Feedback Discipline : First-Come-First-Serve Page:
OQN Modeling Summary • Considered Features • Multiple Part types • Multi-Server Node • Re-entrant Deterministic Routing • Failure Prone Machine • Batch Server/ Batch Arrival • Not Modeled • Scrap • Rework • Process Yield • Stability Lot Size Change Probabilistic routing Page:
Arrival Parameters Nodal Performance Measures Service Parameters Decomposition Approximation • Each Network Node as an IndependentGI/G/m Queue • Two Notions • Two Parameters, Mean & SCV, to Characterize Arrival & Service Processes Page:
Merging j i Splitting i j Flow Through a Queue Departure Rated = l Inter-departure Time SCV Input Output i Approximated by 3 Basic Operations Page:
Traffic Rate Performance Measures : WIP, Cycle Time, ... Traffic Variability Interaction among Nodes Two Traffic Equations Page:
Give • Wafer Release Parameters • Service Node Parameters • Process Routing Information • FCFS Discipline for Each Node ( , ) ( , ) • Solve • Internal Arrival Parameters of Each Node • Derive • Nodal Level Performance • System Level Performance Decomposition Analysis Summary Page:
Steady-State Performance Measures: • Throughput Rate d = l • Mean Cycle Time Arrival Parameters Performance Measures Estimate Performance Measures Page:
control Intuitive Solution : Derived Flow Control Requirements Desired Target Mean Rate : =d Required Bound on SCV : Translation Problem Solution: BQNA Flow Control Parameters Production Goals (d, T) How to Achieve the Goals (d, T)? Page:
General BQNA Results • Desired Arrival Rate (1st order) • Bounds on Inter-Arrival Time SCV (2nd order) Page:
BQNA Summary • Translation Problem Solution • External Arrival Parameters • Internal Arrival Parameters • PFC Application • External Arrival Parameters • Internal Arrival Parameters • Wafer Release Control • Nodal Level WIP/CT Measures • Dispatching Decision Reference • Apply to Existing PFC Schemes Page:
Numerical Experiments Page:
BQNA Local & System Performance Estimation Discrete Event Simulator Distributed PFC Parameters Analysis Results Simulation Results COMPARE Numerical Validation Flow Overall System Production Goals Page:
FAB1 Experiment Example • Overall Production Goals • Desired Output Rate = 0.52 lots/hr • Target Mean CT = 383.25 hours • Model Characteristics • Lu, Ramaswamy and Kumar (1994) • Single Product Type • 12 Machine Groups • Total 40 Failure Prone Machines • 60 Steps for a Complete Process • Exponential Time Distribution • Average Loading Intensity over 90% Page:
FAB1 Machine Group Data Page:
Mean Cycle Time Hours Cycle Time Standard Deviation BQNA BQNA Hours Simulation Simulation 35 35 30 30 25 25 20 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Machine Group Index Machine Group Index FAB1 - Nodal Cycle Time Results Page:
WIP Standard Deviation Mean WIP BQNA BQNA Lots Lots 18 Simulation 20 Simulation 16 14 15 12 10 10 8 6 5 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Machine Group Index Machine Group Index FAB1 - Nodal WIP Results Page:
FAB2 Experiment Example • Overall Production Goals • Desired Output Rate = 10 lots/hr • Target Mean CT = 40.64 hours • Model Characteristics • Bitran and Tirupati (1988) • 10-Product Fab Model • 13 Machine Groups • Different Processing Time Distribution Page:
FAB2 Machine Group Data Page:
Mean Cycle Time BQNA Hours Simulation 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Machine Group Index FAB2 Mean Cycle Time Results Page:
Cycle Time Standard Deviation BQNA Hours Simulation 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 Machine Group Index FAB2 Cycle Time Standard Deviation Page:
Experiments Summary • In the Simulation • Wafer Release follows the derived external parameters. • FCFS is the service discipline of each node. • Discussions • WIP & CT mostly within 95% of accuracy at both node & system • Less than one millisecond of CPU time to apply BQNA to the FAB Model • Dimension of the linear equations depends only on the number of different MGs performance of individual nodes may serve as guiding references for real applications Page:
Conclusions • Proposed a Generic Definition of the Translation Problem • Constructed an OQN Model for Failure Prone Re-entrant Lines • Established a Decomposition-Based Analysis Procedure for OQN Models • Developed BQNA for Translating Overall Production Goals into Local Control Parameters • Conducted Numerical Experiments on Two Full-Scale Fab Models to Demonstrate the Application Potential Page:
Future Research • Enhance the Applicability of BQNA to Include • Lot Size Change • Scrapts • Reworks • Statistical Production Flow Control • Statistical Process Control Concept Based • Developing SPFC Theory • Developing SPFC Application Methods (SPFC Control Charts) WIP Upper Bound Target Level (m) Lower Bound Machine Page: