Environmental Problem and Location
190 likes | 370 Vues
Environmental Problem and Location. My Name GEOG 4450 Environment & Society Interaction Project 1. Problem Definition. Select an environmental problem or issue that concerns you Define the problem specifically- do not be vague. Study Area Selection.

Environmental Problem and Location
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Environmental Problem and Location My Name GEOG 4450 Environment & Society Interaction Project 1
Problem Definition • Select an environmental problem or issue that concerns you • Define the problem specifically- do not be vague
Study Area Selection • Define a geographical location or small region where the problem or issue is occurring. It should be a city, county, or small region. • Maps • Photos
Processes • Identify and describe the various natural and artificial processes that are affecting the issue • Physical geography • Ecological/biological • Historical • Demographic • Social/political • Economic
Examination • Examine the important interrelationships between the various processes • Diagram the linkages and attribute some weight to those that are most crucial for understanding the problems
Examples • Provide examples of people and/or groups who are working on the issue • Give their story and links to their web site or books
Forest Plantation Conversion in Southern Chile Doug R. Oetter GEOG 4450 Environment & Society Interaction Project 1
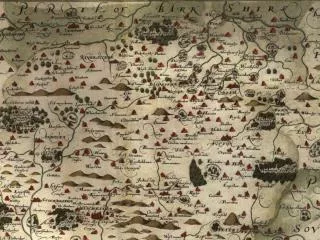
Forest Conversion in the Bio Bío Watershed, Southern Chile • Biobío River located in the central region of Chile • Supports a complex ecosystem comprised of a multitude of threatened plant and animal species • Home to over a million native people • Population = 1.85 million • Area = 37,000 km2 • Increasing dependence on global forestry • Wood exports tripled in five years to $3.4 billion • Heavy reliance on multi-national corporations to participate in timber extraction • 4.5 million acres of native forests cleared from 1985-1995 Native Forests Agro-Forest Plantations
The Biobío River Basin Chile- Central Region
Agro-Forest Plantations • Eucalyptus spp. • Pinus radiata
Historical • Once the land of the Mapuche • Mapu = land • Che = people • Finally defeated by Chilean military in 1885 and opened for settlement • “Pacification of the Araucanian” • Conversion to agriculture, pasture, dairy operations
Demographic • Overall 9.5% rise in population from 1992 to 2002 • 913,306 in 1992 • 999,758 in 2002 • Several rural comunas lost population • Urban centers gained at a higher rate
Chile’s Turbulent Political Economy • 1970: Election of Allende • Economic crisis • 1973: Military coup under Pinochet • Neo-liberal economic policies encourage export growth • 1989: Return to democratic government • International influence of globalization • Export dependency: copper, grapes, wood
National Debt • $43.15 billion (2004) • Pressure from creditors such as the World Bank is increasing • Loans have supported many projects that lead to deforestation • Road construction • Clearing for agriculture • Hydro-electric projects Region VIII. Plantations by species for selected years in thousands of hectares. (INFOR 2004)
Documented Impacts of Forest Removal • Increases in soil erosion and siltation • Loss of biodiversity • Water quality impacts • Fisheries decline • Disruption of animal habitat
Historical Conversion from Native Forest to Agriculture following European Settlement Examination of Linkages Continued population increase in rural settings Political decision to promote Neo-liberal economic solution: subsidies for forest plantations and export Continued decimation of native forests and forced relocation of population to urban centers Reliance on global economic patterns drive up national debt and require continued expansion of resource sector
Examples • Global Forest Watch • Good news: 45% of current forest is mature native • Bad news: only 2% of native forests in Region VIII remain as frontier forests, and 80% of that is unprotected! • Native stands are highly fragmented, which threatens migration of endangered mammals and birds, along with the genetic diversity from their endemic environments • “Chile's Frontier Forests: Conserving a Global Treasure” Ruth Noguerón Program Coordinator - North and South America