Bone Development & Bone Growth
230 likes | 618 Vues
Bone Development & Bone Growth . Osteogenesis /ossification : The process of bone tissue formation In the embryo formation of the bony skeleton Bone growth continues into early adulthood as we increase in size Later in life bone can grow in thickness. Formation of the Bony Skeleton .

Bone Development & Bone Growth
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Osteogenesis/ossification: The process of bone tissue formation • In the embryo formation of the bony skeleton • Bone growth continues into early adulthood as we increase in size • Later in life bone can grow in thickness
Formation of the Bony Skeleton • Week 8 – fibrous membranes and hyaline cartilage begin to ossify. • Intramembranous ossification: development from fibrous membrane • Endochondral ossification: development from hyaline cartilage
Intramembranous Ossification • Forms most bones of the skull and clavicles • All bones formed via this route flat bones • Fibrous CT from mesenchymal cells is framework on which ossification begins
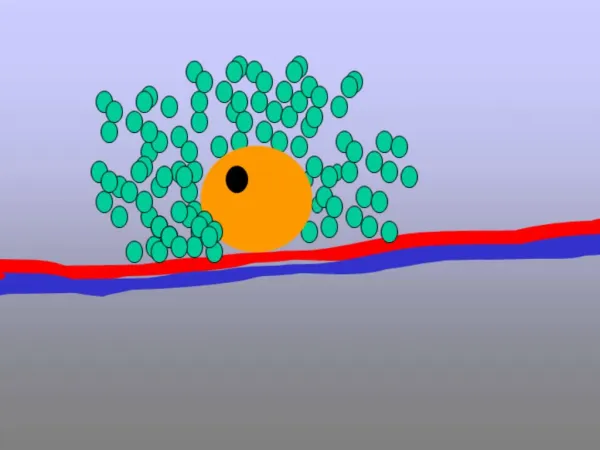
Four Major Steps: STEP ONE An ossification center appears in the fibrous CT membrane Mesenchymal cells cluster and become OSTEOBLASTS forming ossification center
Step Two Bone matrix (osteoid) is secreted within the fibrous membrane -osteoblasts secrete osteoid -trapped osteoblasts become osteocytes
STEP THREE Woven bone and periosteum form -accumulating osteoid is laid down between embryonic blood, forming random network -result is a network of trabeculae. -vascularizedmesenchyme condenses on the external surface of the bone and forms periosteum
Step Four • Bone collar of compact bone forms and red marrow appears • -Trabeculae just deep to the periosteum thicken, forming a bone collar that will later be replaced by mature bone • -Spongy bone (diploe), persist internally and its vascular tissue becomes red marrow
Endochondral Ossification From the skull down, minus the clavicle!
Begins in the second month of development. • More complex than intramembranous ossification • Begins in the center of long bone primary ossification center • Perichondrium becomes infiltrated with blood vessels • As a result osteoprogenitor cells become OSTEOBLASTS
1 • A BONE COLLAR FORMS AROUND THE DIAPHYSIS OF THE HYALINE CARTILAGE MODEL
2 • Cartilage in the center of the diaphysis calcifies and then cavitates
3 • The periosteal bud invades the internal cavity and spongy bone forms
4 • The diaphysis elongates and a medullary cavity forms
5 • The epiphyses ossify
Postnatal Bone Growth • Infancy/youth long bones lengthen entirely by interstitial growth of the epiphyseal growth • Grow in thickness appositional growth