The Role of Phosphorus in the Environment and Its Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems
140 likes | 300 Vues
This presentation by Marjana Rudberg and Natalie Kautz explores the significance of phosphorus in the environment, highlighting both organic and inorganic sources. Key topics include phosphates from fertilizers, sewage, and industrial waste, and their detrimental effects on water bodies through eutrophication. It discusses the implications for ecosystems, particularly focusing on Lake Erie and the introduction of zebra mussels. The presentation also outlines control methods to mitigate phosphorus pollution through better agricultural practices and the importance of monitoring and treatment of water sources.

The Role of Phosphorus in the Environment and Its Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Phosphorus in the Environment Presented By: Marjana Rudberg and Natalie Kautz
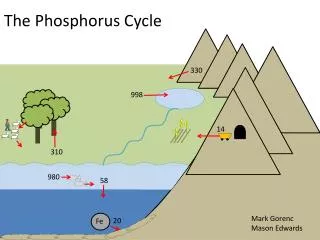
Organic Bound to plant or animal tissue Broken down from organic pesticides Inorganic Non-organic phosphorus Two types: Orthophosphate: “reactive phosphate” Polyphosphate: decomposes to orthophosphate Phosphorus
Sources of Phosphates • Fertilizer Runoff • Sewage and Industrial Waste • Car Emissions • Household Cleaners and Products • Runoff From Garbage Dumps
Air: Relatively harmless oxygen compounds formed within minutes Soil: Less harmful compounds formed within a few days With little oxygen, remains unchanged in deep soil for years Water: Oxygen: relatively harmless compounds in hours or days Low oxygen levels: degrades to highly toxic substance phosphine Later evaporates and changed to less harmful compounds Lifetime In Environment
Eutrophication • Lake has an overload of nutrients • Choke out other species -Algea Blooms * Keep out sunlight * Die use up oxygen
Phosphorous in Lake Erie • Declared dead in 1960s • Reduction of Phosphorous by 50% • The West is stable and on target but Central and East are not.
Phosphorous in Lake Erie • Zebra Mussels found in North America in 1988 • Mussels eat plankton and make the water cleaner • Reduction of desired fish • Fear that Increasing the phosphorous levels will increase zebra mussel population not the fish • Also Fear that increasing the phosphorous levels will also increase the algae along the shore line
Factors Water Movement/Flow Light Temperature Nitrogen Levels Algae and Plankton Growth General Guidelines Rivers and Streams 10-100 μg/L Lakes 5-50 μg/L Control Standards
Most common detection through spectrometry Biological Treatment: Phosphate intake by sludge microorganisms Chemical Treatment: Metal Salts Aluminum Sulfate Ferric Chloride Detection and Treatment
Control Methods • Decrease soil erosion • Reduce water runoff from fields • Use organic fertilizers • Proper farming techniques
References • ATSDR Homepage. <http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/tfacts103.html>. (accessed 12/7/04). • EPA Homepage. <http://www.epa.gov>. • <http://lakes.chebucto.org.> • FOCA Homepage.<http://www.foca.on.ca/Infobase/ Environment/Phosphorus/Effects.htm>. (accessed 12/7/04).