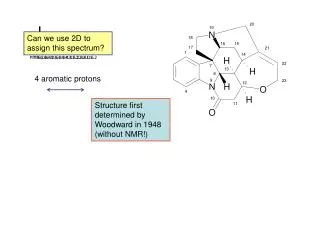
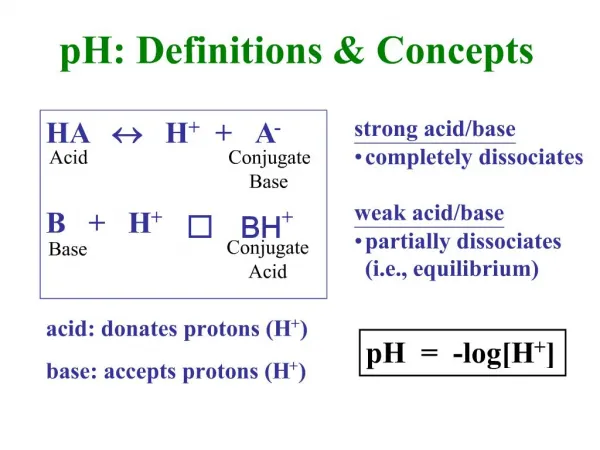
PROTONS
161 likes | 612 Vues
A proton is a subatomic particle with an electric charge of one positive fundamental unit. PROTONS. Protons are much larger and heavier than electrons. It is about 1836 times the mass of an electron. What are their properties?. Protons are found in the nucleus of atoms.

PROTONS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A proton is a subatomic particle with an electric charge of one positive fundamental unit PROTONS Protons are much larger and heavier than electrons It is about 1836 times the mass of an electron What are their properties? Protons are found in the nucleus of atoms quark structure of the proton The number of protons in the nucleus determines the chemical properties of the atom Protons are observed to be stable and their theoretical minimum half-life is 1×1036 year
NEUTRONS What are their properties? Neutrons are subatomic particles with no net electric charge They are also found in the nucleus of an atom Quark structure of the neutron The number of neutrons determines the isotope of an element Neutrons consist of two down quarks and one up quark
ELECTRONS What are their properties? An electron is a fundamental subatomic particle that carries a negative electric charge Electrons are found outside the nucleus of an atom Together with the atomic nuclei (protons and neutrons), electrons make up atoms An electron’s mass is approximately 1 / 1836 of the proton Electron mean lifetime is >4.6x10^26 years Electrons can also act as waves
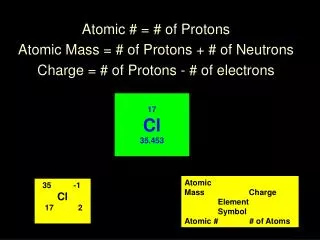
Hyphen Notation • Hyphen notation is the written name of the element plus its mass number.
Examples • Hydrogen-1 • Helium-3 • Uranium - 235
Nuclear Notation • Uses the first letter of the element plus it’s mass number and atomic number
Examples atomic number 1H 3 Mass number
Why does it matter? • Nuclear and hyphen notation allow us to express different forms of the same isotope • For example, there are more than one hydrogen so simply writing “hydrogen “ does not mean one specific isotope • So by using hyphen notation, we are able to express a single isotope of hydrogen by showing it’s mass number or using nuclear notation to show hydrogen’s mass number AND atomic number
For more information • http://teachers.popejohn.org/Mrs_Olsen/Ch3Atom/Ch.3-Atom%2005.ppt
Elemental Identities! Q: What gives an element its identity? A: The atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) provides a unique identity for elements because each element contains a different number of protons. Example: Atomic # is 6….. It must be Carbon!!!!