Photosynthesis
350 likes | 703 Vues
Photosynthesis. All organisms use energy to carry out the functions of life. Agenda. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? What are the colors of the visible light spectrum? In what cellular organelle does photosynthesis take place? Why is photosynthesis important?

Photosynthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Photosynthesis All organisms use energy to carry out the functions of life.
Agenda • What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? • What are the colors of the visible light spectrum? • In what cellular organelle does photosynthesis take place? • Why is photosynthesis important? How is the process of photosynthesis in C4, C3, and CAM plants different? • Go over Vocabulary Definitions • Photosynthesis Web Activity • Notes: Photosynthesis-light & pigments • Worksheet: Absorption of Chlorophyll
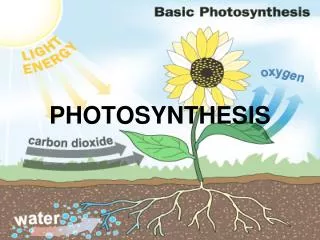
Importance of Photosynthesis • Transforms sunlight energy into chemical energy stored in molecules (bonds) • Bond energy within triose phosphate formed in photosynthesis is transferred between organisms within the food pyramid (more energy at bottom than top) • Triose phosphate (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate) is converted to carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids • Photosynthesis releases oxygen to atmosphere
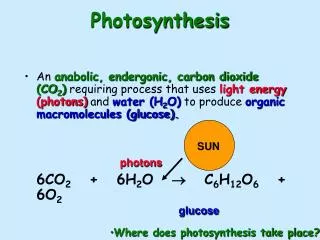
Biochemical Reaction Reactants Products • Triose phosphate (Glucose) • Oxygen • Sunlight • Water • Carbon dioxide H2O + CO2 + light energy (C6H12O6)+ O2
Capturing the Light • “Light dependent reactions” take place in chloroplast found in mesophyll of leaf. • Grana within thylakoid membrane • Stroma-solution Surrounding grana
Light and Pigments • Sun light appears white, but it is actually composed of a variety of colors called the Visible Spectrum. • Light can be reflected, absorbed or transmitted by an object. • Pigment absorb light, therefore the light reflected or transmitted no longer appears white
Peaks indicate Light absorbed Trough where light is reflected
The color you see is what is reflected. • Ex. Chlorophyll (a,b) absorbs blue and red light, but reflects green light
Review What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? What are the colors of the visible light spectrum? In what cellular organelle does photosynthesis take place? Why is photosynthesis important? • Complete the Absorption of Chlorophyll Worksheet
Agenda How does the structure of a chloroplast lead to light absorption? What are the variety of pigments found in the thylakoid of a chloroplast? • Review Light Absorption • Review Vocabulary • Notes: Structure of Leaf & pigment • Complete Pigments & Light Absorption PSSA Worksheet
Structure of Leaf • Leaves are a plant's main photosynthetic organs. • Gases and water vapor come in and out of a leaf through its stoma.
Epidermis • Outer layer which produces a waxy waterproof coating. • undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores (stomata) which control the loss of water vapor (transpiration) and the entry of carbon dioxide. • Mesophyll • contain the photosynthetic cells of the leaf. • long columnar cells nearer the surface (palisade parenchyma) • looser irregular cells beneath (the spongy mesophyll parenchyma).
Log onto: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/photosynth/intro.html Select: #4 Structure of a Leaf #6 Chloroplast Structure
Chloroplast Pigments • Within the thylakoid are a variety of pigments. • Chlorophyll a- yellow/green • Chlorophyll b- blue/green • Carotenoids - orange • Each pigment absorbs a different wavelength of light.
Chlorophyll a is directly involved in the light reactions of photosynthesis • Chlorophyll b and carotenoids are considered to be accessory pigments, assisting Chlorophyll a in capturing light energy.
Review How does the structure of a chloroplast lead to light absorption? What are the variety of pigments found in the thylakoid of a chloroplast? • Complete Pigments & Light Absorption PSSA Worksheet
Agenda What occurs during photolysis? How does the structure of a photosystem lead to it function? What is the main purpose of the light dependent phase of photosynthesis? • Vocabulary Quiz • Notes: Photolysis & light Reaction • Complete Section 6-1 Review Worksheet & Photosynthesis PSSA Worksheet
Photolysis • Splitting of water molecules • Oxygen is released through stomata • H+ picked up by NADP and pumped through thylakoid to stroma for Calvin cycle • Carbon Dioxide is absorbed through stomata and used in the Calvin cycle
Light Dependent Phase-thylakoid • Groups of chlorophyll and carotenoid pigment molecules are found in the thylakoid membrane • Photosystem I • Photosystem II • Accessory pigment molecules in both photosystems absorb light energy causing electrons to become excited. • Energy is passed within the photosystem through pigment molecules to chlorophyll a
Electron Transport Chain • Aided by enzymes, therefore affected by temperature • Excited electrons leave chlorophyll a molecules to a primary electron acceptor in the stroma of the chloroplast • Electron acceptor donates electrons to a series of molecules located in the thylakoid allowing protons(H+) to move into the thylakoid
Electron Transport Chain cont. • Photosystem I electrons are replaced by electrons from Photosystem II • Photosystem II gets the electrons from splitting water, for every 2 water split, 4 electrons are available • If this did not happen, photosynthesis would stop
Chemiosmosis/ATP Synthase Relies on a concentration gradient of protons across the thylakoid membrane. Protons are pushed through ATP Synthase in the thylaloid membrane Adds a phosphate group to ADP making ATP
Review What occurs during photolysis? How does the structure of a photosystem lead to it function? What is the main purpose of the light dependent phase of photosynthesis? • Complete Section 6-1 Review Worksheet • Complete Photosynthesis & Light Absorption PSSA Worksheet
Agenda What is the main purpose of the light independent phase of photosynthesis? How is the process of photosynthesis in C4, C3, and CAM plants different? • Review • Lab: Plant Stoma • Notes: Light Independent Phase & Alternative Pathways • Complete Biochemistry of Photosynthesis PSSA Worksheet
Light Independent Phase • Also called the Calvin Cycle • Produces organic compounds, using the energy stored in ATP and NADPH in the light reactions and carbon dioxide • Steps • CO2 diffuses into stroma combining with an enzyme (RuBP), the molecule is split and becomes 3-PGA • Each PGA is converted to another molecule(3-phosphate) in a 2 part step • One receives a P from ATP, and the other receives a Proton (H+) from NADPH • One G3P leaves to make carbohydrates • One is converted back to RuBP to be used again
Carried out by Plants • C3 plants. • because the CO2 is first incorporated into a 3-carbon compound. • Stomata are open during the day. • Photosynthesis takes place throughout the leaf. • Most plants are C3. • C4 plants. • because the CO2 is first incorporated into a 4-carbon compound. • Stomata are partially open during hottest part of the day. • into the plant very quickly, and then it "delivers" the CO2 directly to RUBISCO for photosynthesis. • Photosynthesis takes place in inner cells • Ex. Corn, Sugar Cane, Crab grass • CAM plants. CAM stands for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism • because the CO2 is stored in the form of an acid before use in photosynthesis. • Stomata open at night (when evaporation rates are usually lower) and are usually closed during the day. CAM plants include many succulents such as cactus, agaves, bromeliads and also some orchids
Review • What is the main purpose of the calvin cycle of photosynthesis? • Complete Biochemistry of Photosynthesis PSSA Worksheet