Accounting Equation
300 likes | 942 Vues
Accounting Equation. Assets = Claims. Claims on the assets are from two sources: Creditors (liabilities) Investors or owners (equity). Assets = Liabilities + Equity. Accounting Equation. Assets = Liabilities + Equity. Common Stock + Retained Earnings. Accounting Equation.

Accounting Equation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
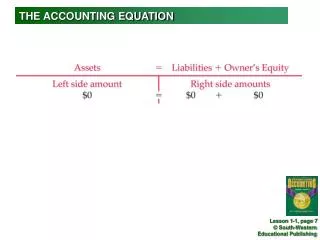
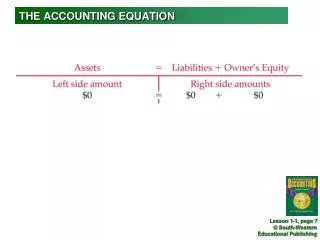
Accounting Equation Assets = Claims • Claims on the assets are from two sources: • Creditors (liabilities) • Investors or owners (equity). Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Common Stock + Retained Earnings Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity
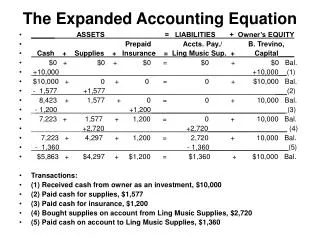
ACCOUNTING EQUATION Assets = Claims to Assets Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity Owners’ Equity = Common Stock AND R. E. Dividends Revenues Expenses (Net Income)
Transaction Analysis • What is a transaction? • a business event involving a transfer of something of value between entities • What is transaction analysis? • determining the effect of a business event on the financial statements • Where do you start? • First, UNDERSTAND THE BUSINESS EVENT • Second, determine the transaction’s effects on the accounting equation -- UNDERSTAND IT • Third, determine the effects on the financial statements – UNDERSTAND IT
Recording Business Events Under the Accounting Equation • Businesses obtain assets from three sources: • Owners • Creditors • Profitable Operations Now, let’s look at the effects of some transactions on the accounting equation—Notice that EVERY transaction in Ch. One involves Cash—that will NOT be true after this chapter.
Illustration – Rustic Camp Sites (RCS) Use the Transaction Worksheet that I Provided to Record RSC Transactions on the next several slides. The completed worksheet is available as an ‘avi’ file.
Event 1: Rustic Camp Sites (RCS) was formed on January 1, 2004, when it acquired $120,000 cash from issuing 35,000 shares of common stock. • RCS increases assets (Cash). • RCS increases stockholders’ equity (Common Stock). Record on our formatted transaction worksheet Double-Entry Bookkeeping
Event 2: RCS acquired an additional $400,000 of cash by borrowing from a creditor. • RCS increases assets (Cash). • RCS increases liabilities (Notes Payable). Record on our formatted transaction worksheet
Event 3: RCS paid $500,000 cash to purchase land. • RCS decreases assets (Cash). • RCS increases assets (Land). Record on our formatted transaction worksheet
Event 4: RCS obtained $85,000 cash by leasing campsites to customers. • RCS increases assets (Cash). • RCS increases stockholders’ equity (REVENUE EARNED—Increases Retained Earnings). Record on our formatted transaction worksheet
Event 5: RCS paid $50,000 cash for operating expenses such as salaries, rent, and interest. • RCS decreases assets (Cash). • RCS decreases stockholders’ equity (Expenses incurred that Decreases Retained Earnings). Record on our formatted transaction worksheet
Event 6: RCS paid $4,000 in cash dividends to its owners. • RCS decreases assets (Cash). • RCS decreases stockholders’ equity (Dividends declared Decreases Retained Earnings). Record on our formatted transaction worksheet
Event 7: The land that RCS paid $500,000 to purchase had an appraised market value of $525,000 on December 31, 2004. Historical Cost Concept Reliability Concept Requires that most assets be reported at the amount paid for them (their historical cost) regardless of increases in market value. Information is reliable if it can be independently verified. Appraised values are opinions and will vary from appraiser to appraiser.
Summary of Transactions—as presented in a “Transaction Worksheet” Color Code Legend Green = numbers used in the statement of cash flows Red = numbers used in the balance sheet Blue = numbers used in the income statement Now, let’s prepare the financial statements for RCS using the data presented above.