Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
320 likes | 1.39k Vues
Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA). Alexis Popkow H191 - Neutron Physics - 4/7/10. What is NAA?. Determine the chemical composition of a sample Lunar samples, artifacts, forensics Can identify up to 74 different elements in gases, liquids, solids, and mixtures

Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA) Alexis Popkow H191 - Neutron Physics - 4/7/10
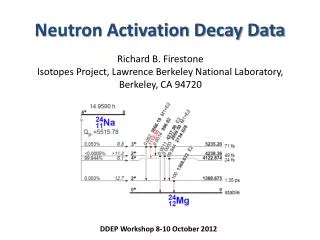
What is NAA? • Determine the chemical composition of a sample • Lunar samples, artifacts, forensics • Can identify up to 74 different elements in gases, liquids, solids, and mixtures • Can also determine the concentration of the elements of interest:
Requires Neutrons • A nuclear reactor • A source that emits neutrons by fission (e.g. Californium) • Alpha Source (like Radium) with Beryllium • D-T fusion
Some elements of interest • Arsenic • Chromium • Selenium • Chlorine • Mercury • Magnesium
Used to Find: • Impurities in industrial products and foods • Poisons in human hair • Hazardous material at dumps • Trace elements in archaeological remains • Testing for elements in air filters
How? • Hit source with neutrons • Sources become radioactive • Then decay in predictable ways
How? • Detect the gamma-rays (prompt and delayed) - with gas detector, scintillators, semiconductors • Bin number of counts at each energy
Gamma-ray Spectroscopy • Gamma spectrum is characteristic of the nuclides in the source (or elements that are activated in NAA) • Equipment: • Detector (NaI, HPGe) - voltage pulse • Amplifiers or multi-channel analyzers - shape the pulse • ADCs - collects data, produces spectrum
Benefits • Small sample sizes (.1mL or .001gm) • Non-destructive • Can analyze multiple element samples • Doesn’t need chemical treatment • High sensitivity, high precision
Resources • N.C. State University Reactor Program • University of Wisconsin Nuclear Reactor • Wikipedia • Reed Research Reactor • University of Missouri Research Reactor