Biology 3A - respiration
330 likes | 526 Vues
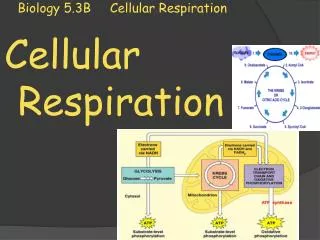
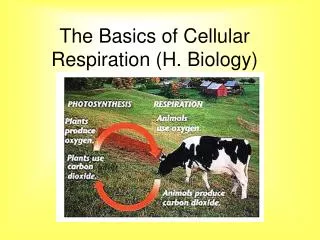
Biology 3A - respiration. Cellular respiration. Provides energy for the cell Occurs in _________ cells Net equation: Occurs as a series of reactions, involving many different enzymes Involves ____________ and ___________ reactions. Cellular respiration. Provides energy for the cell

Biology 3A - respiration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cellular respiration Provides energy for the cell Occurs in _________ cells Net equation: Occurs as a series of reactions, involving many different enzymes Involves ____________ and ___________ reactions
Cellular respiration Provides energy for the cell Occurs in all cells Net equation: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy (ATP) Occurs as a series of reactions, involving many different enzymes Involves anaerobic and aerobic reactions
ATP and ADP • Act as chemical batteries • Carry and release small amounts of energy ATP adenosine adenosine phosphate ADP energy
Carrier proteins Carry hydrogen ions to electron transport chains NAD NADH + H+ FAD FADH2 + H+
Anaerobic respiration • Occurs in the c_________ • Does not need o__________ • Involves 2 processes – g_________ and f_____________
Anaerobic respiration • Occurs in the cytoplasm • Does not need oxygen • Involves 2 processes – glycolysis and fermentation
Glycolysis • Glucose is broken down into 2 p________ (pyruvic acid) molecules • Reactions use 2 ________ • Reactions make ___ ATP • Net ATP = _____/glucose molecule
Glycolysis • Glucose is broken down into 2 pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules • Reactions use 2 ATP • Reactions make 4 ATP • Net ATP = 2/glucose molecule
Fermentation In animals: Pyruvate is converted to l________ a_____ In plants and fungi: Pyruvate is converted to e_________ and _______
Fermentation In animals: Pyruvate is converted to lactic acid In plants and fungi: Pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide
Aerobic respiration • Occurs in the _________________ • Needs _____________ • Involves T___________ reaction, K______ cycle and E__________ transport chain • Involves many reactions and enzymes • Produces ____ ATP • Waste products are
Aerobic respiration • Occurs in the mitochondrion • Needs oxygen • Involves Transition reaction, Krebs cycle and Electron transport chain • Involves many reactions and enzymes • Produces 36 ATP • Waste products are carbon dioxide and water
Transition reaction • Pyruvate attaches to Coenzyme A to form Acetyl Coenzyme A • Acetyl Coenzyme A enters mitochondrion and releases the pyruvate into the Krebs cycle • Coenzyme A can also pick up fatty acids and take them into the Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle • Occurs in the m_________ of the mitochondrion • A cycle of reactions generates ATP and hydrogen ions (carried by NAD and FAD carriers to electron transport chain) • Waste product is • Produces _____ ATP/glucose molecule
Krebs cycle • Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion • A cycle of reactions generates ATP and hydrogen ions (carried by NAD and FAD carriers to electron transport chain) • Waste product is carbon dioxide • Produces 2 ATP/glucose molecule
Electron transport chain • Found in the ____________ (inner membranes) of the mitochondrion • ATP is generated as hydrogen ions are passed down the chain • Oxygen is • Waste product is • Produces ______ ATP/glucose molecule
Electron transport chain • Found in the cristae (inner membranes) of the mitochondrion • ATP is generated as hydrogen ions are passed down the chain • Oxygen is used up • Waste product is water • Produces 34 ATP/glucose molecule
Factors affecting rate of respiration • Temperature • Concentration of glucose • Concentration of oxygen • Concentration of wastes (CO2 or alcohol)
Factors affecting rate of respiration • Temperature as temperature increases, respiration increases, until temperature gets too high enzymes denature • Concentration of glucose as glucose increases, respiration increases, until maximum level reached • Concentration of oxygen as oxygen increases, respiration increases, until maximum level reached • Concentration of wastes (CO2 or alcohol) as wastes increase, respiration decreases
Factors affecting rate of respiration Carbon dioxide concentration Carbon dioxide concentration Oxygen concentration Glucose concentration Carbon dioxide concentration Carbon dioxide concentration Temperature Waste concentration
Factors affecting rate of respiration Carbon dioxide concentration Carbon dioxide concentration Oxygen concentration Glucose concentration Carbon dioxide concentration Carbon dioxide concentration Temperature Waste concentration