Understanding Organic Compounds: The Building Blocks of Life
100 likes | 272 Vues
Organic compounds, primarily characterized by carbon and hydrogen, are essential to life. Scientists once believed all carbon compounds originated from living organisms, hence the term "organic." Now, we recognize that carbon is present in many nonliving substances. Organic compounds include vital nutrient molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. These compounds involve carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen and may contain elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Understanding these compounds is key to grasping the chemistry of life.

Understanding Organic Compounds: The Building Blocks of Life
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Greetings! Carbon Based Life Forms
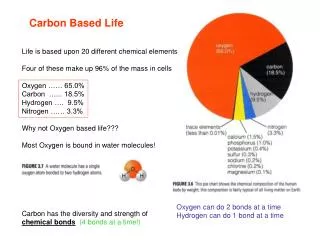
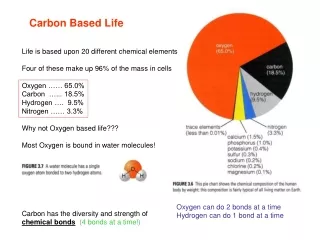
Organic Compounds • Scientists once thought that all carbon compounds came from living or once-living organisms, and they called these compounds organic. Scientists now know that carbon is also in many nonliving things. • Today, scientists define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains carbon atoms usually bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. • Organic compounds can also contain other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, or sulfur.
CHONPS • The different elements that are included in organic compounds are: C – carbon H – hydrogen O – oxygen N – nitrogen P – phosphorous S – sulfur chomps with an ‘n’!
Not Organic • Compounds such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) are not organic because they do not have a carbon-hydrogen bond. Don’t confuse organic compounds with organic food.
Nutrient Organic Molecules • The nutrient organic molecules that are important for life are carbohydrates (sugar), protein, and lipids (fat).
Organic Molecules are made of chains of carbon atoms • There is energy in the bonds between the atoms in the molecules. • The more bonds, the more energy the molecule has.
Glucose (a simple Carbohydrate) • Carbon (the black colored atom) is the backbone for the glucose molecule.
Lipids - Fat • A fat molecule is made of a long chain of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms attached to them. There are many bonds, which means high energy!
Protein • Carbon is colored light blue in this model of a section of a protein molecule. Again, carbon is the backbone.