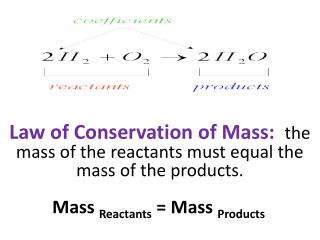Understanding Chemical Equations: Reactants and Products Explained
40 likes | 157 Vues
A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction, showcasing the transformation of reactants into products. For instance, in the equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O, glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2) are the reactants that yield carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) as products. The large numbers before molecules are coefficients that indicate the quantity, while the small numbers (subscripts) specify the number of atoms present. Reactants are always found on the left side and products on the right side of the equation.

Understanding Chemical Equations: Reactants and Products Explained
E N D
Presentation Transcript
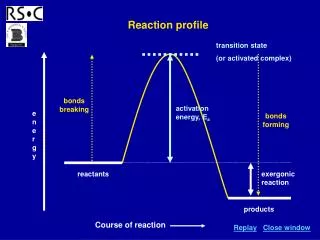
Chemical Equations • A chemical equation is a set of chemicals that are involved in a chemical reaction (chemical change). • For example • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • The big numbers in front tell us how many of the whole molecule, these are called coefficients. • The little numbers to the right of an atom tell us how many there are of that atom in the whole molecule, these are called subscripts.
Reactants • In the equation • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • The C6H12O6 + 6O2 • C6H12O6 is a type of sugar called glucose AND • 6O2 is the oxygen in the air we breath. • Both the oxygen and the sugar are called the reactants. • You can always find the reactants on the left side of the arrow in a chemical equation.
Products • In the equation • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • The 6CO2 + 6H2O are the products. • The 6CO2 is 6 carbon dioxide molecules AND • The 6H2O is 6 water molecules. • These are called the products because when you put the reactants together you produce 6 water molecules and 6 carbon dioxide molecules. • Products are ALWAYS on the right in a chemical equation.