Limiting Reactants
160 likes | 342 Vues
Limiting Reactants . What Is a Limiting Reactant?. Many cooks follow a recipe when making a new dish. When a cook prepares to cook he/she needs to know that sufficient amounts of all the ingredients are available. Let’s look at a recipe for the formation of a S’more :. 2 Graham

Limiting Reactants
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What Is a Limiting Reactant? • Many cooks follow a recipe when making a new dish. • When a cook prepares to cook he/she needs to know that sufficient amounts of all the ingredients are available. • Let’s look at a recipe for the formation of a S’more:
2 Graham Crackers Halves 6 Chocolate Squares 1 Marshmallows
10 • How many Graham Cracker Halves do you need? • If you want to make 5 S’mores: • How many Chocolate Squares do you need? 30 • How many Marshmallows do you need? 5
2 Graham cracker halves, 6 chocolate squares, 1 marshmallow 1 • How many S’mores can you make if you start with: • 6 Graham cracker halves, 18 chocolate squares, 3 marshmallow 3 1 • 20 Graham cracker halves, 60 chocolate squares, 1 marshmallow
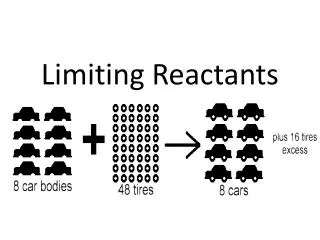
We can’t make anymore than 1 S’mores with our ingredients. • The marshmallows limits the number of S’mores we can make. • If one of our ingredients gets used up during our preparation it is called the limiting reactant (LR) • The LR limits the amount of product we can form; in this case S’mores.
It is equally impossible for a chemist to make a certain amount of a desired compound if there isn’t enough of one of the reactants. • A balanced chemical rxn is a chemist’s recipe. • Which allows the chemist to predict the amount of product formed from the amounts of ingredients available
Let’s look at the reaction equation for the formation of ammonia: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) • When 1 mole of N2 reacts with 3 moles of H2, 2 moles of NH3 are produced. • How much NH3 could be made if 2 moles of N2 were reacted with 3 moles of H2? 2 molsof ammonia
The amount of H2 limits the amount of NH3 that can be made. • From the amount of N2 available we can make 4 moles of NH3 • From the amount of H2 available we can only make 2 moles of NH3. • H2 is our limiting reactant here. • It runs out before the N2 is used up. • Therefore, at the end of the reaction there should be N2 left over. • When there is reactant left over it is said to be in excess.
How much N2 will be left over after the reaction? • In our rxn it takes 1 mol of N2 to react all of 3 mols of H2, so there must be 1 mol of N2 that remains unreacted. • We can use our new stoichiometry calculation skills to determine 3 possible types of LR type calculations. • Determine which of the reactants will run out first (limiting reactant) • Determine amount of product • Determine how much excess reactant is wasted
Limiting Reactant Problems: Given the following reaction: 2Cu + S Cu2S • What is the limiting reactant when 82.0 g of Cu reacts with 25.0 g S? • What is the maximum amount of Cu2S that can be formed? • How much of the other reactant is wasted?
Given the following reaction:2Cu + S Cu2S • What is the limiting reactant when 82.0 g of Cu reacts with 25.0 g S? • To do this you must convert the reactants to the same unit and substance. • Once they are the same unit and substance you can then compare the values. Which ever reactants is the smallest is the Limiting Reactant.
Given the following reaction:2Cu + S Cu2S • What is the maximum amount of Cu2S that can be formed? • Convert the Limiting Reactant to the product you are looking for.
Given the following reaction:2Cu + S Cu2S • How much of the other reactant is wasted? • Convert the Limiting Reactant to the Excess Reactant to find the amount of Excess Reactant used up. • Subtract the value found from how much Excess Reactant you began with.
Hydrogen gas can be produced in the lab by the rxn of Magnesium metal with HCl according to the following rxn equation: Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 • What is the LR when 5.0 g Mg reacts with 6.0 g HCl? • What is the maximum amount of H2 that can be formed? • And how much of the other reactant is wasted?