The Medieval Church
160 likes | 335 Vues
The Medieval Church. Cross- ing the line between religion and politics. Conversion. In the Middle Ages (500-1300 AD), the church was on a mission- to convert all of Europe to Christianity By the late Middle ages, western Europe had become a Christian civilization

The Medieval Church
E N D
Presentation Transcript
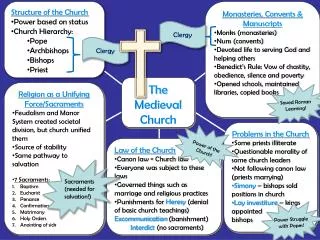
The Medieval Church Cross-ing the line between religion and politics
Conversion • In the Middle Ages (500-1300 AD), the church was on a mission- to convert all of Europe to Christianity • By the late Middle ages, western Europe had become a Christian civilization • Anyone who did not belong to the church community was viewed with suspicion • I didn’t see you at church…..
Church life • The church was the center of daily life • Not only was it often the largest public building in a village, but it central because of the role it played in lives of the people • Some roles may be:
Church life • The church was where you were after your birth, when you got married, and when you died • Daily life revolved around the Christian calendar, featuring many holidays and feasts of saints • Many churches had relics- the remains of, or things formerly belonging to, saints
Church life • The church asked for a tithe • Tithe- a tax for the church equal to 10% of your income • This money went to support the local church • Eventually, more and more of this money found its way to Rome
Church life • The Church had a conflicting view on women • Women were viewed as equal before God • The church protected women from serious injury from their husbands, set a minimum age for marriage • However, women were viewed as weak on Earth and needed guidance from men • Women often punished more harshly for same crimes
Monasteries and convents • Men and women who wished to devote their lives to the church entirely became monks and nuns and lived in monasteries and convents, respectively • In 530 AD, a monk named Benedict developed rules to govern life in these religious places • Became known as the Benedictine Rule
Monasteries and convents • Under Benedictine rule, monks and nuns took three vows: • 1) Obedience to head of monastery or convent • 2) Poverty • 3) Chastity
Monasteries and convents • Monasteries and convents served many purposes • They took care of the sick and gave rest to tired travelers • They provided opportunities for learning, teaching classics in Latin • Many monks copied books by hand; others wrote books.
Church as a secular force • Secular-worldly, not spiritual • Secular holidays- • Spiritual holidays
Church as a secular force • The pope claimed papal supremacy • Papal supremacy- the belief that since the Pope is God’s representative, he has authority over all leaders (kings, emperors)
Church as a secular force • Church leaders, such as bishop, were usually also nobles, with vast territories and even armies under their control • Monasteries had large amounts of land • The pope himself controlled an area in Italy known as the papal states • Secular leaders were often related to church leaders
Church as a secular force • The Church was able to influence the population with the threat of excommunication • Those who were excommunicated were cut off from church, not allowed to receive Christian burial, and therefore condemned to hell • Could threaten nobles with interdict- an order excommunicating an entire region
Church as a secular force • This power led to Church corruption • Vows of poverty were forgotten, some church members lived in luxury • Priesthood sometimes became inherited, ignored priest duties
Church as a secular force • Church also a force for peace • Demanded fighting between nobles stop between Friday and Sunday • May have led to reduction in violence
Treatment of Jews • As Europe became more and more Christian, suspicion of Jews increased • Because they were not a part of Church life, they became mysterious to people • Natural disasters were blamed on them • Church eventually banned them from holding property or some jobs • Jews fled to Eastern Europe, where they flourished until modern times