Aromatic Substitution
480 likes | 833 Vues
Aromatic Substitution . Chapter 22. Sections to skip!!. Skip sections 22.1 (most), 22.3, 22.4, and 2.13 through 22.15 Keep 22.16 (review from c. 351, for some of you) Keep 22.17. Problems. In text: 4 - 6 8 - 13 20 - 29 End of Chapter: 1 - 5 9 - 13 . Sect. 22.1 Nomenclature.

Aromatic Substitution
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Aromatic Substitution Chapter 22 WWU-Chemistry
Sections to skip!! Skip sections 22.1 (most), 22.3, 22.4, and 2.13 through 22.15 Keep 22.16 (review from c. 351, for some of you) Keep 22.17 WWU-Chemistry
Problems • In text: 4 - 6 8 - 13 20 - 29 • End of Chapter: 1 - 5 9 - 13 WWU-Chemistry
Sect. 22.1 Nomenclature WWU-Chemistry
Catechols WWU-Chemistry
Nomenclature-- examples WWU-Chemistry
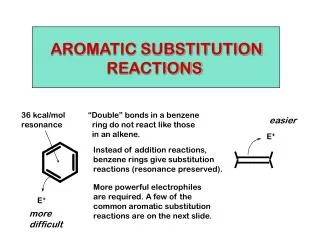
Chapter 22: Aromatic Substitutions, Monosubstitution reactions on benzene Sect. 22.2 Electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism Sect. 22.5 Nitration Sect. 22.6. Halogenation Sect. 22.7 Friedel-Crafts Reactions Sect. 22.8 Sulfonation Reactions (skip fall 2006) WWU-Chemistry
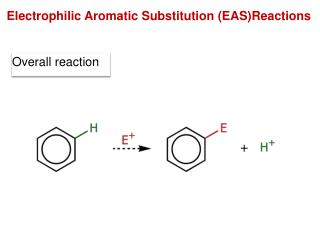
Sect. 22.2 Electrophilic aromatic substitution. WWU-Chemistry
Sect. 22.5: Nitration • conc. HNO3 and H2SO4 react to make electrophile, NO2+ • nitro aromatics are important intermediates • reduction of nitro groups give anilines WWU-Chemistry
Mechanism of Aromatic NitrationStep 1: Where does the electrophile come from? Nitronium ion (NO2+) is the electrophile that reacts with the benzene ring. WWU-Chemistry
Mechanism of Aromatic Nitration (Step 2) WWU-Chemistry
Mechanism of Aromatic Nitration (Step 3) WWU-Chemistry
Sect. 22.6: Halogenation • active electrophile is a bromonium or chloronium ion • need Lewis acid catalyst ( FeX3 ) to activate X2 WWU-Chemistry
Sect. 22.7: Friedel-Crafts Alkylation • alkyl halide + AlCl3 -->carbocation + AlCl3X- • watch out for carbocation rearrangements! • more than one alkylation can occur --> mixtures! WWU-Chemistry
Friedel-Crafts Acylation • acid chloride + AlCl3 --> acylium ion + AlCl4- • cation rearrangements are NOT observed! • acylation will only occur ONCE... • reaction VERY sensitive to substituents-- an acyl group prevents further reaction WWU-Chemistry
Aromatic substitution on Benzene • Sect. 22.8: Sulfonation (skip, fall 06) • Sect. 22.9: Summary WWU-Chemistry
Sect. 22.10 and 22.11: Directing effects • methoxy group releases electrons by resonance effect: ortho and para director • nitro group withdraws electrons by inductive and resonance effect: meta director WWU-Chemistry
These are ortho and para directors! All are electron releasing!! WWU-Chemistry
All ortho/para directing groups have pairs of electrons next to the benzene ring! The only exception are alkyl groups. They are also ortho/para directors. WWU-Chemistry
Why do ortho/para groups direct as they do? Resonance!! WWU-Chemistry
These are meta directors! All are electron withdrawing!! WWU-Chemistry
Now let’s look at a meta directing group This is an example of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS). WWU-Chemistry
Why does the nitration reaction take place preferentially at the meta position? Let’s ask a “what if” question. WWU-Chemistry
ortho BAD! meta para BAD! WWU-Chemistry
meta substitution preferred because the + charge is never next to the CO2R group WWU-Chemistry
Activation during substitution All ortho and para directing groups are activating relative to benzene, except halogen substituents. Halogens are weakly deactivating but are still o, p- directors. WWU-Chemistry
Deactivation during substitution • All meta directors arestrongly deactivating relative to benzene. WWU-Chemistry
Sect. 22.12 and 22.17: Some synthetic examples involving aromatic substitution WWU-Chemistry
ortho/para directors can work together with meta directors. They reinforce each other. WWU-Chemistry
Strong o/ p directors win over weak o, p and meta directors. WWU-Chemistry
Substitution RARELY occurs in-between two substituents--too hindered! WWU-Chemistry
Some groups can be modified to change their directing effects. WWU-Chemistry
Good stuff! Order of reaction is critical! WWU-Chemistry
Some more good stuff! WWU-Chemistry
An explosive! WWU-Chemistry
2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene = TNT WWU-Chemistry
Some miscellaneous examples • Nitration of 3-nitrobenzoic acid • Acylation of 1,3-dimethylbenzene • Acylation of 1,4-dimethylbenzene • Make 2-methyl-1-phenylpropane WWU-Chemistry
Sect. 22.16 Aromaticity and Huckel’s Rule Aromatic compounds 4n + 2 pi electrons n = 1 6 pi electrons systems : WWU-Chemistry
Other n = 1 aromatics : : : : : 6 electrons, one pair not involved! 6 electrons, one pair not involved! 6 electrons All are aromatic! WWU-Chemistry
n = 0 aromatic: 2 pi electrons WWU-Chemistry
Some Antiaromatic compounds : Not aromatic! WWU-Chemistry
Diazonium ions, Azo Dyes and the Sandmeyer Reaction- from Chapter 23 (not covered 06) Sect 23.16: Diazonium ion formation Sect 23.17: Sandmeyer reaction Sect 23.19: Azo dyes WWU-Chemistry