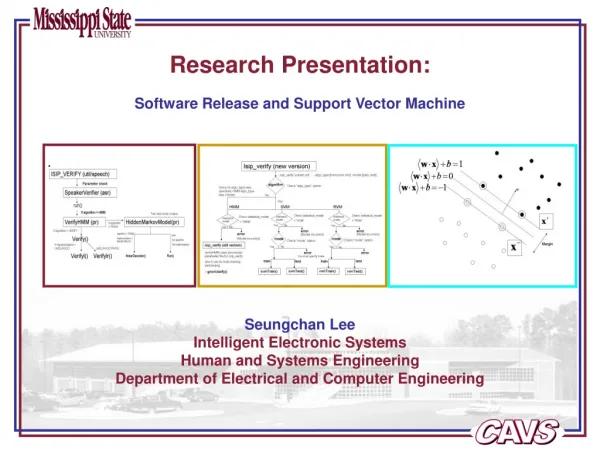
Research Presentation
400 likes | 829 Vues
Otorhinolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery at PENN Excellence in Patient Care, Education and Research since 1870. Research Presentation. Jason M. Leibowitz, MD June 25, 2009 Preceptor: Marcia S. Brose, MD PhD . Overview. Background Hypothesis Methods Results Discussion

Research Presentation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Otorhinolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery at PENN Excellence in Patient Care, Education and Research since 1870 Research Presentation Jason M. Leibowitz, MD June 25, 2009 Preceptor: Marcia S. Brose, MD PhD
Overview • Background • Hypothesis • Methods • Results • Discussion • Conclusions & Future Directions
Thyroid cancer is themost commonendocrine neoplasm. Thyroid cancer will be diagnosed in 33,550 individuals (8070 men and 25,480 women) this year. From 1997-2004 incidence of thyroid cancer increased by 6.2% mostly due to increased detection. From 1985 to 2004 mortality rate increased by 0.3% a year. Thyroid Cancer in the United States
RAI-Refractory Disease • 25-50% of metastatic thyroid cancers lose ability to take up Iodine. • Iodine Uptake inversely correlates with survival. • This is attributed to down regulation of the Na+/I- Symporter (NIS). • Limited treatment options for unresectable thyroid cancer refractory to RAI.
Molecular Pathway involved in Thyroid Cancer • Activation of MAPK pathway • Oncogenic activation of this pathway in 70% of all thyroid cancers. • BRAF is a serine threonine kinase Xing, 2007.
2003: The BRAF V600E mutation is the most common genetic alteration in thyroid cancer, occurring in about 45% of sporadic papillary thyroid cancers (PTCs). V600E BRAF V600E in Thyroid Cancer
BRAF V600E • Point mutation in 40-45% of PTC • Upregulation of MMP, VEGF --> invasion, angiogenesis • Silencing of tumor suppressive genes, genes involved in iodine transport • BRAF mutation associated with multiple negative prognostic indicators.
RAS • Family of small G-proteins involved in transduction of cellular signals from the cell membrane. • Mutations in RAS gene lead to inappropriate activation with constitutively activated downstream pathways and also promote chromosomal instability. • 20% FTC contain a RAS mutation RAS mutations may correlate with aggressive behavior (tumor dedifferentiation and poorer prognosis).
Targeted Therapy in Thyroid cancer • Loss of differentiation (inability to trap RAI), unresectable lesion, leads to poor prognosis • BRAF inhibitors • BAY 43-9006 (Sorafenib) • Multikinase inhibitor
Sorafenib • Orally active multikinase inhibitor (study dose 400mg BID). • Monoclonal antibody with multiple targets including BRAF, VEGFR1, VEGFR2. • Blocks tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis. • FDA approved for treatment of RCC and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Targeted Therapy and Genotype • K-RAS gene mutation and metastatic colorectal carcinoma. • Recent results from Phase II & III clinical trials demonstrate that patients with metastatic colorectal cancer benefit from anti-EGFR therapy. • Patients with K-RAS mutation in codon 12 & 13 should not receive anti-EGFR therapy since they do not receive any benefit. • EGFR and non-small cell lung cancer: • Epithelial growth factor receptor • 10% mutated in NSCLC • EGFR mutations are predictors of TKIs responsiveness and may show a long lasting response to TKIs • EXON 19 Deletion respond better to TKIs.
Prior Data 84 weeks N=43 WDTC N= 52
Papillary vs. Follicular FTC = 19 PTC= 24 P<0.095
Prior Data • Conclusions from prior data: • Improved PFS with Sorafenib. • Improved PFS of FTC treated with Sorafenib when compared to PTC.
Overview • Background • Hypothesis • Methods • Results • Discussion • Conclusions & Future Directions
Hypothesis • There are specific genotypes (i.e. BRAF V600E, RAS mutations) that predict favorable response to targeted therapy (Sorafenib).
Null Hypothesis • Specific genetic mutations do not predict response to targeted therapy in thyroid cancer.
Overview • Background • Hypothesis • Methods • Results • Discussion • Conclusions & Future Directions
Research Plan • Tissue samples collected from patients with treatment-resistant thyroid cancer with long term follow-up (approximately 30 patients). • All patients received targeted therapy (Sorafenib). • Samples with WDTC analyzed for mutations in BRAF and RAS genes when available: • BRAF - V600E • RAS - Exon 12, 13, 61
Sequence Output Computer program interprets data and produces an electropherogram, (aka trace) Each peak represents a base: A = Adenosine T = Thymine C = Cytosine G = Guanine N = Reading cannot be determined
Overview • Background • Hypothesis • Methods • Results • Discussion • Conclusions & Future Directions
Results of Stage 1 Analysis • N= 30 • M = F = 15 • PTC=17, FTC= 9, Other (ATC/PD, MTC): 4 • Samples analyzed for BRAF mutation: • 23/30 (76.6%): samples analyzed for BRAF mutation • 4/30 (13%): definite genotype but questioned due to phenotype (ATC/PD, MTC) • 2/30 (6%): unable to amplify DNA despite multiple PCR attempts • 1/30 (3%): pending analysis • 18/30 samples analyzed for RAS mutation, all WT copies of the gene
Results of Stage 1 Analysis • N=22 (interim analysis) • 13 WT BRAF • 9 BRAF V600E • 16 PTC • 9 WT BRAF, 7 V600E • 6 FTC • 4 WT BRAF, 2 V600E
BRAF V600E P<0.02 N=13 (WT=8, V600E=5)
Updated genetics • In our expanded analysis to 22 pts with WDTC, the effect is no longer significant but the trend exists. • We are further investigating BRAF copy number in these patients N =22 WT = 13 BRAF V600E = 9 p=NS
Overview • Background • Hypothesis • Methods • Results • Discussion • Conclusions & Future Directions
BRAFV600E Correlates with worse Survival Elisei et. al, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, October 2008, 93(10):3943–3949
BRAFV600E Correlates with worse SurvivalState of the mutation in PTC, 10/2008
THE BRAF connection Ciampi et al. 2005
Updated genetics • In our expanded analysis to 22 pts with WDTC, the effect is no longer significant but the trend exists. • We are further investigating BRAF copy number in these patients N =22 WT = 13 BRAF V600E = 9 p=NS
BRAF (red) x 3 7 centromere (green) x 3
BRAF x4 7 centromere x4
4 copies each 3 copies each
THE BRAF connection! Positive Predictor! Ciampi et al, 2005.
Future Directions • Completion of genotyping analysis of all patients • Evaluation of copy number gains in WDTC • Hypothesis: Copy number gain accounts for improved survival in FTC treated with Sorafenib • Null: Copy number gain does not influence survival in FTC
Selected Sources • Ciampi R, Zhu Z, Nikiforov YE. BRAF copy number gain in thyroid tumors detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Endocrine Pathology 2005; 16(2): 99-105. • Ciampi R, Nikiforov YE. Alterations of the BRAF gene in thyroid tumors. Endocrine Pathology 2005; 16:3): 163-171. • Gupta-Abramson V, Troxel AB, Nellore A, et al. Phase II Trial of Sorafenib in Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Journal Clin Onc 2008; 26 (29): 4714-4719. • Kundra P, Burman KD. Thyroid Cancer Molecular Signaling Pathways and Use of Targeted Therapy. Endoc Metab Clin N Am 2007;36: 839-853 • Murer B. Targeted Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Arch Path Lab Med. 2008; 132: 1573-1575. • Nikiforov YE. Thyroid Carcinoma: Molecular Pathways and Therapeutic targets. Modern Pathology 2008; 21: S37-S43. • Vasko V, Ferrand M, Cristofaro JD et al. Specific Pattern of RAS Oncogene Mutations in Follicular Thyroid Tumors. J. Clin Endocrin. & Metab. 2003; 88(6):2745-2752. • Xing M. BRAF Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Pathogenic Role, Molecular Basis, and Clinical Implication. End Rev 2007; 28(7): 742-762.
Thanks • Marcia Brose, MD PhD • Cathy Ma MD, PhD • Kanchan Puttaswamy, MS