Viruses and Viral Diseases in Plants and Animals
100 likes | 193 Vues
Explore the impact of plant and animal viruses, including viral diseases affecting brain health and immune systems, with insights into prions and vaccine protection strategies.

Viruses and Viral Diseases in Plants and Animals
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Výukový materiál MB 04 - 102 Tvůrce: Mgr. Šárka Vopěnková Tvůrce anglické verze: ThMgr. Ing. Jiří Foller Projekt: S anglickým jazykem do dalších předmětů Registrační číslo: CZ.1.07/1.1.36/03.0005 Tento projekt je spolufinancován ESF a SR ČR 2014 VIRUSES - DISEASES
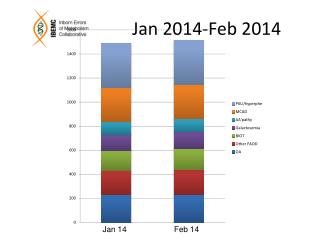
plant viruses can stop the growth of plants • mostly RNA – viruses • virus of tobacco mosaic • transfer from a plant to another plant by insects, seeds, vegetative reproduction • symptoms: • formation of spots on the leaves • rolling up the leaves • abortive growth VIRAL DISEASES OF PLANTS
proteins cause infectious diseases of brain • slow degeneration of nervous system • incubation period – several years • scarpie – by sheep • BSE by cattle „mad cows´ disease“ • 1986 first diagnosed in Great Britain • brain > sponge form • CJD – human form of prion infection PRIONS
faulty shape variant of particular protein in brain cells> degeneration • resistant against higher temperatures, enzymes • Nobel prize in 1997 - Stanley Prusiner PRIONS
viruses penetrate into organisms: • through injured skin • through mucous membranes of respiratory ways • through mucous membranes of digestive system • they reproduce at the place of entering > virus of common cold • they reproduce in the target cells > they spread through lymph and blood • viruses are excreted: • through the mucus from nose, larynx • salivas • through peeled off skin • through blood, urine, excrements VIRAL DISEASES OF ANIMALS AND HUMAN
common cold virus > influenza • it belongs to RNA – viruses • fever • ague • headache, pain in muscles • various tribes of viruses > they cross over > new genetic combinations – human do not have antibodies • > pandemic VIRAL DISEASES OF ANIMALS AND HUMAN
smallpox (variola) • foot-and-mouth disease > animals • viral hepatitis B • verrucas • adenoviruses > catarrhs of upper respiratory ways • herpes simplex • herpes zoster DNA VIRUSES
polio • HIV • viral hepatitis A • common cold • influenza • mumps • measles • rabies • rubella • encephalitis DNA VIRUSES
immune system • vaccination based on the ability of the immune system to produce antibodies • vaccine: • weakened originator of disease > stimulation of the immune system • vaccines against: • polio • measles • rubella PROTECTION AGAINST INFECTION
JELÍNEK, Jan a Vladimír ZICHÁČEK. Biologie pro gymnázia: teoretická a praktická část. 2. dopl. a rozš. vyd. Olomouc: Nakladatelství Olomouc, 1998. ISBN 80-718-2050-4 • KUBIŠTA, Václav. Obecná biologie. Praha: Fortuna, 2000, ISBN 80-7168-714-6. • CHALUPOVÁ - KARLOVÁ, Vlastimila. Obecná biologie. Olomouc: Nakladatelství Olomouc, 2010, ISBN 978-80-7182-282-0. • ZÁVODSKÁ, Radka. Biologie buněk. Praha: Scientia, 2006, ISBN 80-86960-15-3. • ROSYPAL, Stanislav. Nový přehled biologie. 1. vyd. Praha: Scientia, 2003, 797 s. ISBN 80-718-3268-5 SOURCES