UNIT 8 SOUTH ASIA
1.57k likes | 1.75k Vues
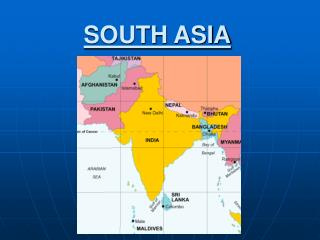
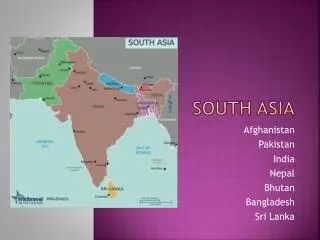
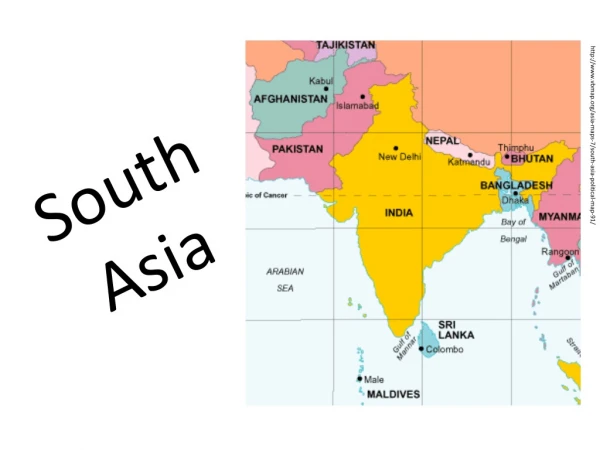
UNIT 8 SOUTH ASIA. Subcontinent: A landmass that is like a continent, only smaller, such as South Asia, which is called the Indian subcontinent. Archipelago – a set up of closely grouped islands. Atoll – a ring-like coral or string of small islands surrounding a lagoon.

UNIT 8 SOUTH ASIA
E N D
Presentation Transcript
UNIT 8 SOUTH ASIA
Subcontinent: A landmass that is like a continent, only smaller, such as South Asia, which is called the Indian subcontinent.
Atoll – a ring-like coral or string of small islands surrounding a lagoon.
*Highest mountain range in the world *Formed as a result of the collision of the Indian subcontinent with Asia
Himalaya Mountains *Extend along northern borders of Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Burma *They contain the 3 highest mountains on earth
Mount Everest *Highest mountain in the world *Located on the Nepal-China border *Climbers bring a significant source of revenue – up to $25,000 per permit to climb *Youngest person to climb was 13 years old – May, 2010
Ganges River: *1557 miles long *Begins in an ice cave on the southern slopes of the Himalayas
Bathing in the Ganges Sacred to the people – holiest river in India
Belief that the river came down from heaven to purify the Earth and wash away the sins of mankind.
Ganges River Information • The Ganges Basin is 200 – 400 miles wide • Empties into the Bay of Bengal • The delta is mainly in Bangladesh – largest delta in the world • Directly and indirectly affects the largest population in the world with over 420 million people relying on it for food, water, bathing, and agriculture.
Ganges Pollution Troubles • The amount of toxins and chemicals and other dangerous bacteria found in the water are now 3000 times over the limit suggested as safe. • Approximately 1 billion liters of untreated sewage are dumped in the rive each day • Rapid population explosion in the past 25 years along with lax regulations on industry has put a huge strain on the river.
Thousands of bodies are cremated on the banks of the river yearly with many being released into the river. • Hundreds of unwanted or illegitimate babies, cattle, and other animal carcasses are dumped into the river. • Hindus do not want to accept that their “mother Ganges”, nectar of God, can be responsible for bringing them illness and misery. • River is now the leading cause of infant and child mortality rates, skin problems, and some more serious disabilities.
Delta – a fan-like landform as the river flows into the ocean
Indus River: *Most important river in Pakistan *Begins in Tibet and flows into the Arabian Sea *River system is fed mainly by snow and glaciers of the Himalayas *Indus River Valley Civilization was located here
Indus Valley Civilization *Largest of the world’s 1st civilizations *Located in Pakistan *Was a highly developed urban civilization
Sultan – a ruler of a Muslim country Mandalas – geometric designs that are symbols of the universe and aid in meditation. Used in a Tibetan style of Buddhism
Hinduism: *3rd largest religion in the world *Largest religion in India *Oldest religion in the world *It is a way of life *referred to as Santana Dharma – eternal law
Hinduism Beliefs and Themes: *Dharma – ethics and duties *Samsara – rebirth (reincarnation) *Karma – right action *Moksha – liberation from the cycle of Samsara
Believe in: *Truth *Honesty *Non-violence *Celibacy *Cleanliness *Contentment *Prayers *Poverty *Perseverance *Penance
Hinduism • Scriptures are referred to as “Shastras” – collection of spiritual laws • Sruti – revealed • Smriti - remembered • Also worship spirits, trees, animals, and planets • Believe in 1 supreme Absolute called “Brahman” • The gods and goddesses of Hinduism represent the many aspects of Brahman
*System of social classes in India *One of the cornerstones of Hinduism *Each person is born into a caste and can only move into a different caste through reincarnation *Each caste has a separate political status