Exploring the Cultural and Geographic Diversity of South Asia
390 likes | 508 Vues
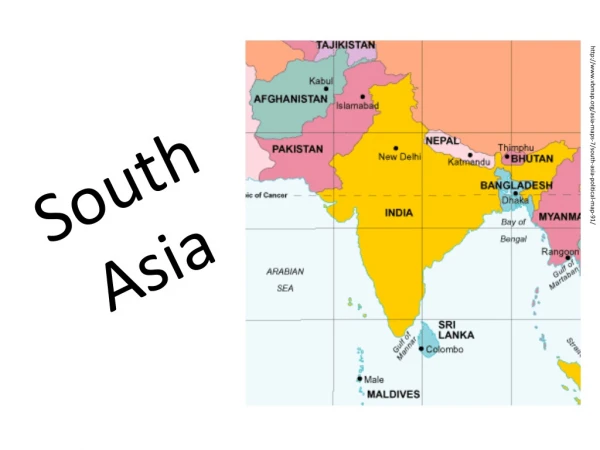
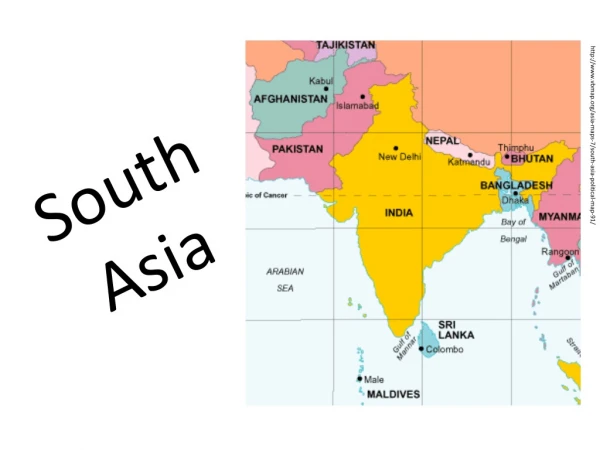
South Asia, comprising India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, the mountainous north, and the southern islands, is a region defined by its complex geography and rich cultural heritage. Home to over 1.2 billion people, it remains one of the world's most populous areas, characterized by subsistence agriculture and low-income economies. The region is known for the distinctive monsoon season that influences life and agriculture. Major religions such as Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, and Sikhism intertwine within its diverse cultural tapestry, reflecting deep historical roots, ancient traditions, and ongoing social dynamics.

Exploring the Cultural and Geographic Diversity of South Asia
E N D
Presentation Transcript
THE REALM Five Regions • India • Pakistan • Bangladesh • Mountainous North • Southern Islands
MAJOR GEOGRAPHIC QUALITIES OF SOUTH ASIA • Well defined physiographically • The world’s second largest population cluster • Low income economies • Population concentrated in villages - subsistence agriculture • Boundary problems - Kashmir • FEDERAL SYSTEM • ADOPTED BY INDIA IN 1947 • PROVIDES REGIONS AND PEOPLES WITH SOME AUTONOMY AND IDENTITY
Monsoons --“To know India and her people, one has to know the monsoon.” --To the people of India, the monsoons are a source of life, but it also causes destruction. -- Very distinctive seasonal precipitation regime
CULTURE • A culturally fragmented realm • Religious and linguistic diversity • Religious Patterns: • Islam is predominant in Pakistan and Bangladesh. • Hinduism is predominant in India, generally. • Sikhism thrives in northern India. • Buddhism is predominant in Sri Lanka.
CULTURE HEARTHThe Indus River • Where an early culture emerged and developed • Arts and trade routes emerged from isolated ethnic groups and villages to towns and beyond. • Hinduism emerged from the beliefs and practices brought to India by the Aryans (6th century BC) • Buddhism born of discontent; made the state religion of India in 3rd century BC • Islam swept through central India from the 8th -10th centuries AD
One of the world’s oldest religions Diffused south and east down the Ganges River (see text for holy site). Absorbed and eventually supplanted earlier native religions and customs HINDUISM
HINDUISM • Not just a religion; an intricate web of religious, philosophical, social, economic, and artistic elements • No common creed, no single doctrine • No direct divine revelation • No rigid narrow moral code
MAJOR TENETS OF HINDUISM • Three main ideas are important in understanding the Hindu religion and the Caste System • Reincarnation • Karma • Dharma
REINCARNATION • Every living thing has a soul. • When a living thing dies, its soul moves into another living creature. • Souls are reborn in a newly created life.
KARMA • Every action brings about certain results. • There is no escaping the consequences of one’s actions. • Good behavior is rewarded when the soul is reborn into a higher ranking living creature; bad behavior is punished when the soul is reborn into a lower ranking living creature.
DHARMA • A set of rules that must be followed by all living things if they wish to work their way up the ladder of reincarnation. • Each person’s dharma is different.
THREE BASIC PRACTICES • Puja or worship (also, Hindus do not eat beef) • Cremation of the dead • Regulations of the caste system (note video)
E. J. PALKA ORIGINS AND SPREAD OF BUDDHISM • Siddhartha Gautama (563 - 483 B.C.) – a.k.a Buddha. Born in Nepal. • Buddhism came from Hinduism (just as Christianity came from Judaism). • Emperor Asoka adopted it as the state religion (3rd Century B.C.) • Adherents object to harsher features of Hinduism (e.g. Caste System) • Focuses on knowledge, especially self-knowledge • Elimination of worldly desires, determination not to hurt or kill people or animals
FOUR “NOBLE TRUTHS” OF BUDDHISM • Sorrow and suffering are part of all life. • People suffer because they desire things they cannot have. • The way to escape suffering is to end desire, to stop wanting, and to reach a stage of not wanting. • To end desire, follow the “middle path,” i.e., the path that avoids the extremes of too much pleasure and desire.
FALL OF BUDDHISM ON THE SUBCONTINENT • Hinduism was broad and tolerant, accepting many of the teachings of Buddha, so many stayed with Hinduism • Also, Buddhists in India were willing to compromise with the beliefs and customs of Hinduism • Final blow to Buddhism came in the 8th century, with the arrival of Islam, which: -- Destroyed the great Buddhist monasteries -- Burned libraries -- Killed monks • Today there are only 1 million Buddhists in India – in the region where it started!
ISLAM Monotheistic No idols One sacred book Uniform dogma - 5 pillars Intolerant (of other religions) Eat beef/Sacrifice cows Bury Dead Social Equality (in theory) Theocratic society (state religion encouraged) HINDUISM Polytheistic Many idols Various sacred writings Varying beliefs Absorbed other religions Don’t eat beef/Venerate cows Burn dead (cremation) Caste separation Having the religion as part of the “State” is of secondary importance RELIGIOUS CONTRASTS
INDIA • ENCOMPASSES 3/4s OF SOUTH ASIA’S TOTAL AREA • A FEDERATION OF 28 STATES, AND 1 National Capital Territory. • POPULATION OF 1.124 BILLION PEOPLE – the world’s largest democracy. • 28% URBANIZED • 14 MAJOR AND NUMEROUS MINOR LANGUAGES
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT (INDIA) • 38% LIVE BELOW THE POVERTY LINE • A MIXTURE OF TRADITIONAL VILLAGE FARMING AND MODERN AGRICULTURE • HANDICRAFTS, OLD AND NEW BRANCHES OF INDUSTRY; CLOTHING INDUSTRY (note video) • MULTITUDE OF SUPPORT SERVICES AND NUCLEAR POWER
E. J. PALKA E. J. PALKA
GREEN REVOLUTION • THE SUCCESSFUL DEVELOPMENT OF HIGHER YIELD, FAST-GROWING VARIETIES OF RICE AND OTHER CEREALS IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES • INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH PROGRAM-1960s • FOCUSED ON THE FOOD CRISES • INCREASED PRODUCTION PER UNIT AREA VIA: • MIRACLE CROPS • NEW IRRIGATION SYSTEMS • INTENSIVE USE OF FERTILIZERS
INDIA’S GREAT CITIES • MUMBAI(BOMBAY) - 18.9 MILLION • ACHIEVED “PRIMACY” BASED ON ITS SITUATION. It was the nearest Indian Port to Europe. • KOLKATA (CALCUTTA) - 14.6 MILLION • 500,000 HOMELESS • FORMER BRITISH COLONIAL CAPITAL (1772-1912) • DELHI (NEW AND OLD) - 16.2 MILLION • BRITISH AND INDIAN SEAT OF GOVERNMENT
PAKISTAN (AT PARTITION, 1947) India WestPakistan EastPakistan
PAKISTAN • ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF PAKISTAN • POPULATION OF 166.9 MILLION • 80% SUNNI MUSLIMS; 16% SHIA MINORITY • 34% URBANIZED
KASHMIR (Jammu and Kashmir) • Although its population is mainly Muslim, much of Jammu and Kashmir became part of India in 1947. India and Pakistan have fought two wars over the territory, and there has been a separatist insurgency in the area. • INDEPENDENCE & PARTITION • FACED WITH THE CHOICE OF JOINING EITHER HINDU INDIA OR MUSLIM PAKISTAN • HINDU MAHARAJA BUT MUSLIM POPULATION • JANUARY 1949 – U.N. CEASE FIRE • 1980 to 88 – Muslim extremists continue insurgency
BANGLADESH • INDEPENDENT SINCE 1971 • FORMERLY EAST PAKISTAN (see previous slides) • 85% MUSLIM, 12% HINDU • 147.3 MILLION PEOPLE • DENSITY = 3,914/sq mi • 2.1% ANNUAL GROWTH RATE • NATURAL HAZARDS – CYCLONES
THE SOUTHERN ISLANDS • MALDIVES • >1,000 ISLANDS • <115 SQ MI / 300 SQ KMS • POPULATION OF 300,000 • OVERWHELMINGLY MUSLIM • HIGHEST GNP IN THE REALM • SRI LANKA • FORMERLY CEYLON • INDEPENDENT SINCE 1948
SRI LANKA • 20.1 MILLION PEOPLE (70% BUDDHISTS) • PLANTATION AGRICULTURE: • TEA, RUBBER, COCONUTS • SOUTH (MAJORITY OF POPULATION) • ARYAN • BUDDHISTS • SPEAK SINHALA (INDO-EUROPEAN) • NORTH (18% OF THE POPULATION) • DRAVIDIAN • HINDU • TAMIL LANGUAGE
SRI LANKA • SINHALESE vs. TAMILS • TAMILS DEMAND EQUAL RIGHTS: -- EDUCATION -- EMPLOYMENT -- LAND OWNERSHIP -- LANGUAGE AND POLITICS • LTTE – LIBERATION TIGERS OF TAMIL EELAM
E. J. PALKA E. J. PALKA E. J. PALKA
E. J. PALKA E. J. PALKA