Efficient Data Handling in Visual Basic .NET: Saving and Reading Files
270 likes | 394 Vues
This chapter focuses on saving and accessing data in Visual Basic .NET using files instead of databases for small datasets. It illustrates essential file handling concepts, such as streams, records, and fields, defining the structure of data files. You'll learn to implement StreamWriter and StreamReader for writing and reading data, including using the Write and WriteLine methods for data output. Additionally, it covers file management, including how to specify file paths, error handling when files do not exist, and utilizing the File Common Dialog for user-friendly file access.

Efficient Data Handling in Visual Basic .NET: Saving and Reading Files
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Programming In Visual Basic .NET Chapter 3Saving Data and Objects In Files
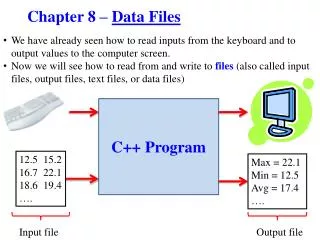
Data Files • To save data from one run of the application to the next • Use when there is only a small amount of data that would not warrant the use of a database • Use for Windows applications, the default security policy for the Internet and Intranets does not allow access to disk files
Data File Terminology • File ==> Entire collection of data • Records ==> Rows, one per entity • Fields ==> Columns, data elements within row
Sample Data File Last Name First Name Phone Maxwell Harry 909-555-1234 Helm Jennifer 818-555-2222 Colton Craig 909-555-3333 Records Fields
File Handling Using Streams • A Stream is designed to transfer a seriesof bytes from one location to another • Streams are objects that have methods and properties • Found in the System.IO.namespace • File handling projects must contain an Imports statement before the statement declaring the form's class
Form Form Read Input Write Output Data File File I/O • Reading and writing data in a disk file • Writing = Output • Reading = Input
Writing Data in a File • User inputs data into text boxes • Declare a new StreamWriterobject • Also declares the name of the data file • Use StreamWriter's WriteLine method • Copies data to a buffer in memory • Call StreamWriter's Close method • Transfers data from buffer to the file and releases system resources used by the stream
Writing Data in a File (continued) • Declaring a new StreamWriter object opens the file • If the file does not exist, a new one is created • Declare the StreamWriter object either in the declarations section of your program or in a procedure
Instantiating a StreamWriter Object • General Form • Default location for file is the bin directory beneath the folder for the current project • Can specify the complete path of the file Dim ObjectName As New StreamWriter("FileName") Dim ObjectName As New StreamWriter("FileName", BooleanAppend)
Declaring a StreamWriter Object - Examples Dim phoneStreamWriter As New StreamWriter("Phone.txt") Dim namesStreamWriter As New StreamWriter("C:\MyFiles\Names.txt") Dim logFileStreamWriter As New StreamWriter("C:\MyFiles\LogFile.txt", True) True = Append data to this existing file
Write and WriteLine Methods • Write Method • Places items consecutively in the file with no delimiter (separator) • WriteLine Method • Places an enter (carriage return) between items • Used in this chapter
The WriteLine Method - General Form • DataToWrite argument may be string or numeric • Converts any numeric data to string and writes string data in the file ObjectName.WriteLine(DataToWrite)
The WriteLine Method - Examples phoneStreamWriter.WriteLine(nameTextBox.Text) phoneStreamWriter.WriteLine(phoneTextBox.Text) namesStreamWriter.WriteLine("Sammy") bankBalanceStreamWriter.WriteLine(balanceDecimal.ToString( ))
Closing a File • Use StreamWriter'sClose method • Finishes writing all data from the stream's buffer to the disk and releases system resources • Commonly coded in form’s closing event procedure
Closing a File - Example Private Sub exitButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles exitButton.Click ' Close the file and the form. phoneStreamWriter.Close( ) Me.Close( ) End Sub
Viewing the Contents of a File • Text editor, such as Notepad • Visual Studio's IDE • In the Solution Explorer1. Select the Project name2. Click Show All Files button to display the bin folder3. Select the file to display in the editor window
Viewing the Contents of a File (continued) Select project name Show All Files button Contents of Data File New File bin folder
Reading Data from a File • Declare an object of the StreamReader class • Also declares the name of the data file • Opens the file • Use StreamReader's ReadLine method • May need a loop to retrieve multiple records • Call StreamReader's Closemethod
Reading Data from a File (continued) • The file must exist in the specified location or an exception occurs • Declare the StreamReader object in a procedure and enclose it in a Try/Catch block
Instantiating a StreamReader Object • General Form • Example Dim ObjectName As New StreamReader("FileName") Try Dim namesStreamReader As New StreamReader("C:\MyFiles\Names.txt") Catch MessageBox.Show("File does not exist") End Try
Using the ReadLine Method • Use to read previously saved data • Each time it executes, it reads the next line of data • Assign the value from the read to the desired location, such as a label, text box, or string variable
Using the ReadLine Method -Example nameLabel.Text = phoneStreamReader.ReadLine( )
Using the File Common Dialog Box • The previous data file examples included hard-coded file names (and paths) • May allow the user to browse and enter the file name at run time • Use the OpenFileDialogcommon dialog component to display the dialog box • Then use the object's FileNameproperty to open the selected file
OpenFileDialog Component Properties • Name – Can use default name • CheckFileExists • CheckPathExists • FileName (will be set by user's selection at run time) • Filter • InitialDirectory (set this property in code) • Title
The Form_Closing Procedure • Form’s Closing event procedure is best location to ask user to save the file • Closing event executes before the form closes no matter how user exits program or even Windows
Serialization • Save an object and the current value of all of its properties using Serialization • Serialization refers to a series or stream of bits • Object's state is converted to a series of bits that can be saved and later used to recreate the object • Deserialization is reading the saved data back and recreating the object
Serialization (continued) • To save an object • Class must be declared as Serializable • Must have a Formatter • Two types of Formatters • Binary, stores data in a binary form • SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol), stores data in an XML format