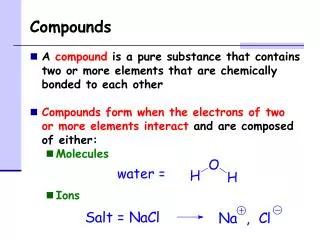
Compounds
710 likes | 1.15k Vues
Compounds. Binary Compounds. Binary compounds that contain a metal of fixed oxidation number (group 1, group 2, Al, Zn, Ag, etc.), and a non-metal. To name these compounds, give the name of metal followed by the name of the non-metal, with the ending replaced by the suffix – ide. Examples:.

Compounds
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Binary Compounds Binary compounds that contain a metal of fixed oxidation number (group 1, group 2, Al, Zn, Ag, etc.), and a non-metal. To name these compounds, give the name of metal followed by the name of the non-metal, with the ending replaced by the suffix –ide. Examples: NaCl sodium chloride (Na1+ Cl1-) CaS calcium sulfide (Ca2+ S2-) AlI3 aluminum iodide (Al3+ I1-)
Cations and Anions Common Simple Cations and Anions Cation Name Anion Name* H 1+ hydrogen H 1-hydride Li 1+ lithium F 1-fluoride Na 1+ sodium Cl 1-chloride K 1+ potassium Br 1-bromide Cs 1+ cesium I 1-iodide Be 2+ beryllium O 2-oxide Mg 2+ magnesium S 2-sulfide Al 3+ aluminum Ag 1+ silver *The root is given in color. Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry2002, page 86
Step 4: AlCl 3 Example: Aluminum Chloride Criss-Cross Rule Step 1: write out name with space Al Cl 3+ 1- Step 2: write symbols & charge of elements Al Cl Step 3: 1 3 criss-cross charges as subsrcipts combine as formula unit (“1” is never shown)
Example: Aluminum Chloride Criss-Cross Rule Step 1: Aluminum Chloride Step 2: Al3+ Cl1- Step 3: Al Cl 1 3 Step 4: AlCl 3
Example: Aluminum Oxide Criss-Cross Rule Step 1: Aluminum Oxide Step 2: Al3+ O2- Step 3: Al O 2 3 Step 4: Al2O3
Example: Magnesium Oxide Criss-Cross Rule Step 1: Magnesium Oxide Step 2: Mg2+ O2- Step 3: Mg O 2 2 Step 4: Mg2O2 Step 5: MgO
Naming Binary Compounds Formula Name barium oxide • BaO ____________________ • ________________ sodium bromide • MgI2 ____________________ • KCl ____________________ • ________________ strontium fluoride • ________________ cesium fluoride NaBr magnesium iodide potassium chloride SrF2 CsF
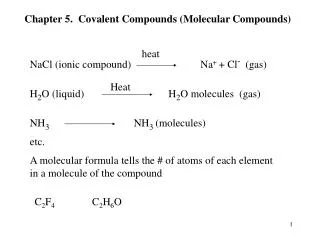
Ternary Compounds Ternary compounds are those containing three different elements. (NaNO3, NH4Cl, etc.). The naming of ternary compounds involves the memorization of several positive and negative polyatomic ions, (two or more atoms per ion), and adding these names to the element with which they combine. i.e., Sodium ion, Na1+ added to the nitrate ion, NO31-, to give the compound, NaNO3, sodium nitrate. Binary rules for indicating the oxidation number of metals and for indicating the numbers of atoms present are followed. The polyatomic ions that should be learned are listed in a separate handout.
Ternary Compounds NaNO2 sodium nitrite KClO3 potassium chlorate Ca3(PO4)2 calcium phosphate Fe(OH)3 iron (III) hydroxide NaHCO3 sodium bicarbonate ‘sodium hydrogen carbonate’
Common Polyatomic Ions Names of Common Polyatomic Ions Ion Name Ion Name NH41+ ammonium CO3 2- carbonate NO21- nitrite HCO31- hydrogen carbonate NO31- nitrate (“bicarbonate” is a widely SO32- sulfite used common name) SO42- sulfate ClO 1- hypochlorite HSO41- hydrogen sulfate ClO21- chlorite (“bisulfate” is a widely ClO31- chlorate used common name) ClO41- perchlorate OH 1- hydroxide C2H3O22- acetate CN 1- cyanide MnO41- permanganate PO43- phosphate Cr2O72- dichromate HPO42- hydrogen phosphate CrO42- chromate H2PO41- dihydrogen phosphate O22- peroxide Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry2002, page 100
Ternary Compounds Ca3(PO4) 2 • ________________ calcium phosphate • ________________ ammonium carbonate • ________________ aluminum sulfate • Na2SO4 ____________________ • LiCN ____________________ • Ba(ClO3)2 ____________________ • ________________ copper (II) hydroxide (NH4)2CO3 Al2(SO4)3 sodium sulfate lithium cyanide barium chlorate Cu(OH)2
Magnesium Phosphate Step 1: Magnesium Phosphate Step 2: Mg2+ PO43- Step 3: Mg (PO4) 3 2 Step 4: Mg3(PO4)2
NH41+ …………… OH1- …………… CN1- ………….. ammonium hydroxide cyanide Polyatomic Ions - Memorize Eight “-ATE’s” PO43- …………… SO42- …………… CO32- ………….. ClO31- ………….. NO31- ………..…. phosphate sulfate carbonate chlorate nitrate phosphATE sulfATE carbonATE chlorATE nitrATE Exceptions:
Polyatomic Ion: a group of atoms that stay together and have a single, overall charge.
Polyatomic Ion: a group of atoms that stay together and have a single, overall charge.
Write the compound formed by the following ions: • 1) Al3+ S2- • 2) Mg2+ PO43- • When a formula is given…write the proper name. • When a name is given…write the proper formula. • 3) BaO • 4) lithium bromide • 5) Ni2S3 • 6) triphosphorous heptaoxide • 7) N2O5 • 8) molybdenum (VI) nitride • 9) trinitrotoluene (TNT)… CH3C6H2(NO2)3 • 10) phosphoric acid H3PO4 Write the total number of atoms that make up each compound. Extra credit: What is the formula for plumbic iodide?(Hint: lead is Pb2+ or Pb4+)
POP QUIZ • Write the compound formed by the following ions: • 1) Al3+ S2- • 2) Mg2+ PO43- • When a formula is given…write the proper name. • When a name is given…write the proper formula. • 3) BaO • 4) lithium bromide • 5) Ni2S3 • 6) triphosphorous heptaoxide • 7) N2O5 • 8) molybdenum (VI) nitride • 9) trinitrotoluene (TNT)… CH3C6H2(NO2)3 • 10) phosphoric acid H3PO4 Write the total number of atoms that make up each compound. Extra credit: What is the formula for plumbic iodide?(Hint: lead is Pb2+ or Pb4+)
Answer Key • Write the compound formed by the following ions: • 1) Al3+ S2- • 2) Mg2+ PO43- • When a formula is given…write the proper name. • When a name is given…write the proper formula. • 3) BaO • 4) lithium bromide • 5) Ni2S3 • 6) triphosphorous heptaoxide • 7) N2O5 • 8) molybdenum (VI) nitride • 9) trinitrotoluene (TNT)… CH3C6H2(NO2)3 • 10) phosphoric acid H3PO4 Al2S3 Mg3(PO4)2 barium oxide LiBr nickel (III) sulfide P3O7 dinitrogenpentaoxide MoN2 Write the total number of atoms that make up each compound. 21 8 Extra credit: What is the formula for plumbic iodide?(Hint: lead is Pb2+ or Pb4+) PbI4
Polyatomic Ions - Quiz C2O42- …………… CrO42- …………… Cr2O72- ………….. MnO41- ………….. CH3COO1- ……. oxalate chromate dichromate permanganate acetate
Exceptions! Two exceptions to the simple –ide ending are the diatomic oxide ions, O22- and O21-. O22- is called peroxide O21- is called superoxide. Note the differences. BaO BaO2 barium oxide __________ barium peroxide __________ Ba2+ Na2O Na2O2 sodium oxide __________ sodium peroxide __________ Na1+ Do Not Reduceto lowest terms! K2O KO2 potassium oxide __________ potassium superoxide __________ K1+
Ionic Compounds:Polyatomic Ions Ionic Compounds: Polyatomic Ions Ionic Compounds: Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic Ions Grid to Memorize Chart of the Ions and Polyatomic Ions Keys
Ionic Binary Compounds:Multiple-Charge Cations Ionic Binary Compounds: Multiple-Charge Cations Ionic Binary Compounds: Multiple-Charge Cations Keys
Naming Chemical Compounds Binary Compound? No Yes Polyatomic ions present? Use the strategy summarized earlier No Yes This is a compound for which naming procedures have not yet been considered. Name the compound using procedures similar to those for naming binary ionic compounds. Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry2002, page 102
Oxidation Numbers and Ionic Compounds Oxidation Numbers and Ionic Compounds Oxidation Numbers and Ionic Compounds Keys
Names and Formulas of Compounds Names and Formulas of Compounds Names and Formulas of Compounds Keys
H 2.1 Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 N 3.0 O 3.5 F 4.0 Na 0.9 Mg 1.2 Al 1.5 Si 1.8 P 2.1 S 2.5 Cl 3.0 K 0.8 Ca 1.0 Sc 1.3 Ti 1.5 V 1.6 Cr 1.6 Mn 1.5 Fe 1.8 Co 1.8 Ni 1.8 Cu 1.9 Zn 1.7 Ga 1.6 Ge 1.8 As 2.0 Se 2.4 Br 2.8 Rb 0.8 Sr 1.0 Y 1.2 Zr 1.4 Nb 1.6 Mo 1.8 Tc 1.9 Ru 2.2 Rh 2.2 Pd 2.2 Ag 1.9 Cd 1.7 In 1.7 Sn 1.8 Sb 1.9 Te 2.1 I 2.5 * Cs 0.7 Ba 0.9 La 1.1 Hf 1.3 Ta 1.5 W 1.7 Re 1.9 Os 2.2 Ir 2.2 Pt 2.2 Au 2.4 Hg 1.9 Tl 1.8 Pb 1.8 Bi 1.9 Po 2.0 At 2.2 y Fr 0.7 Ra 0.9 Ac 1.1 * Lanthanides: 1.1 - 1.3 y Actinides: 1.3 - 1.5 Below 1.0 2.0 - 2.4 1.0 - 1.4 2.5 - 2.9 1.5 - 1.9 3.0 - 4.0 Electronegativities 1A 8A 1 1 3A 5A 7A 2A 4A 6A 2 2 3 3 2B 4B 6B 8B 1B 3B 5B 7B Period 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 Hill, Petrucci, General Chemistry An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition, page 373
O O S O O H H Interpretation of a Chemical Formula Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Two atoms of hydrogen One atom of sulfur Four atoms of oxygen
Chemical Formulas C8H18 Subscript indicates that there are 8 carbon atoms in a molecule of octane. Subscript indicates that there are 18 hydrogen atoms In a molecule of octane. Davis, Metcalfe, Williams, Castka, Modern Chemistry, 1999, page 203
Stock System of Nomenclature CuCl2 Name of Roman cation numeral indicating charge Name of anion + copper (II) chloride
Chemical Formulas Al2(SO4)3 Subscript 2 refers to 2 aluminum atoms. Subscript 4 refers to 4 oxygen atoms in sulfate ion. Subscript 3 refers to everything inside parentheses. Here there are 3 sulfate ions, with a total of 3 sulfur atoms and 12 oxygen atoms. Davis, Metcalfe, Williams, Castka, Modern Chemistry, 1999, page 204
Naming Binary Ionic Compounds Al2O3 Name of cation Name of anion aluminum oxide Davis, Metcalfe, Williams, Castka, Modern Chemistry, 1999, page 207
The Stock System of Nomenclature CuCl2 Name of Name of anion cation Roman numeral indicating charge + Copper (II) chloride Davis, Metcalfe, Williams, Castka, Modern Chemistry, 1999, page 208
Br1- Br1- Br Br K e- e- Br1- Br1- bromine atom potassium atom e- O2- potassium ion bromide ion Mg2+ K1+ K1+ K1+ K1+ K bromine atom potassium atom bromide ion potassium ion potassium bromide KBr magnesium bromide potassium oxide MgBr2 K2O
Br1- Br1- Br1- PO43- O2- N3- Al3+ Ca2+ Pb4+ Mg2+ S2- K1+ K1+ K1+ OH1- OH1- NH41+ NO31- ? Cu2+
OH1- OH1- Na1+ OH1- N3- N3- N3- N3- Pb4+ Pb4+ Pb4+ (metal) N2- N3- N3- Al3+ (metal) (metal) Ca2+ Pb4+ M2+ Mg2+ ? M1+ M1+ Chemical Bonding Activity (metal) (nonmetal) Pb4+ N3- Pb3N4 lead (IV) nitride or plumbic nitride
Chemical Bonding Activity Chemical Bonding Activity (pink/blue) Chemical Bonding Activity Pieces Chemical Bonding Activity (pink/blue) Chemical Bonding Activity Pieces Keys
Br1- Br1- Br1- N3- N3- N3- N3- Pb4+ Pb4+ Pb4+ O2- N3- Al3+ Mg2+ K1+ K1+ K1+ NH41+ NO31- Key http://www.unit5.org/christjs/4bondingact.doc 4. 5. 1. KBr 2. AlN 6. OH1- Cu2+ K2O OH1- 3. Cu(OH)2 7. Pb3N4 MgBr2 NH4NO3
Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ PO43- PO43- PO43- O2- O2- O2- O2- Al3+ Al3+ Fe2+ NH41+ NH41+ NH41+ Key 8. 9. 10. (NH4)3PO4 11. Ca3(PO4)2 Al2O3 FeO
13. Fe3+ Fe3+ S2- S2- S2- S2- O2- O2- O2- O2- O2- S2- Pb4+ Pb4+ Cu2+ Pb2+ Cu1+ Cu1+ Key 14. 12. PbS 15. CuO 16. Fe2O3 Cu2O Pb2S4 PbS2 Pb2S3
Molecular Models Activity Molecular Model's Activity Molecular Model's Activity Keys
Molecular Models Activity carbon tetrachloride methane water ethane ethyne dihydrogen monosulfide carbon dioxide ammonia hydrogen monochloride trichloromethane urea propane butane nitrogen triiodide (video) supplies
B : N : : O Bonding and Shape of Molecules Number of Bonds Number of Unshared Pairs Covalent Structure Shape Examples -Be- 0 0 0 1 2 2 3 4 3 2 Linear Trigonal planar Tetrahedral Pyramidal Bent BeCl2 BF3 CH4, SiCl4 NH3, PCl3 H2O, H2S, SCl2 C
Cl Cl Cl C Cl C Cl Cl Cl 109.5o Cl Carbon tetrachloride Tetrahedral geometry CCl4 Carbon tetrachloride – “carbon tet” had been used as dry cleaning solvent because of its extreme non-polarity.
H H C H H C H H H 109.5o H Methane Tetrahedral geometry Methane –The first member of the paraffin (alkane) hydrocarbons series. a.k.a. (marsh gas, CH4).