Circuits
230 likes | 684 Vues
Circuits. What is electricity and how can you transfer it through circuits ? What are the differences between parallel and series circuits? What are the advantages and disadvantages of using serial and parallel circuits? . - Electric Current. Flow of Electric Charges.

Circuits
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Circuits • What is electricity and how can you transfer it through circuits? • What are the differences between parallel and series circuits? • What are the advantages and disadvantages of using serial and parallel circuits?
- Electric Current Flow of Electric Charges • Electric current is the continuous flow of electric charges through a material. Measured in amps.
Review Questions An electric current either transfers charges well or not very well. • What is something called that transfers energy well? (Ex. Metals) • What is something called that does NOT transfer energy well? (Ex. Non-metals)
Electric Charges • A conductor transfers electric charge well. • Metals are good conductors. Silver, copper, aluminum, and iron are metals. • An insulator does not transfer electric charges well. • Rubber, glass, plastic, and wood are good insulators. The rubber coating on an electric cord is an insulator.
- Electric Current Electric Circuit • An electric circuit is a complete, unbroken path through which electric charges can flow.
- Electric Circuits Parts of a Circuit
Parts of a circuit Energy source Resistor Wires Switch Load
Comprehension Check • What is a circuit? • What is an example of a circuit?
- Electric Circuits Series Circuits • In a series circuit, there is only one path for the current to take.
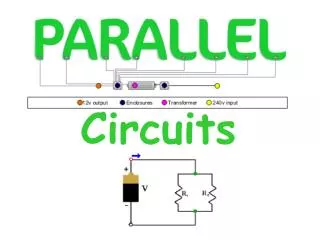
- Electric Circuits Parallel Circuits • In a parallel circuit, there are several paths for the current to take.
- Electric Circuits Series and Parallel Circuits Activity • Click the Active Art button to open a browser window and access Active Art about series and parallel circuits.
Complex Circuit • a circuit that has more than one parallel or series circuit linked together
Comprehension Check • What is an electrical circuit? • What are the 3 types of circuits?
- Electric Power Electric Power • The rate at which energy is transformed from one form to another is known as power. Power is measured in watts (W).
Voltage • Voltagecauses a current in an electric circuit. • Voltageis the difference in electrical potential energy between two places in a circuit. The unit of measure of voltage is the volt (V). • The energy that makes charges flow through a circuit is called electrical potential energy. • An electric circuit needs a source of energy to have voltage. Voltage sources: a battery, a generator
A household light bulb has about 0.5 amps of current in it. Since the standard household voltage is 120 volts, what is the power for this bulb? What are you trying to calculate? The power of the light bulb = ? What is the formula? Power = Voltage X Current Calculate. Power = 120 V X 0.5 A Power = 60 W - Electric Power Calculating Power
- Electric Power Comprehension Check Question Answer Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transformed into another form of energy. What is electric power?
The percentage of fires caused by a certain type of electrical equipment Reading Graphs: What determines the size of each wedge in the graph? - Electrical Safety Electrical Equipment and Fires
15% Reading Graphs: What percentage of fires are caused by appliances? Electrical Equipment and Fires
Cooking equipment is responsible for the most fires. Heating and cooling equipment is responsible for the fewest fires. Interpreting Data: Which category of equipment is responsible for the most fires? Which category is responsible for the fewest fires? - Electrical Safety Electrical Equipment and Fires
Summary • Identify pictures of circuits as parallel or series.
- Electric Circuits Thursday Warm Up Compare and contrast series circuits and parallel circuits in a Venn diagram. Series Circuit Parallel Circuit Only one path for current to take Unbroken path that has a current Several paths for current to take