EKG - Dysrhythmia Workshop
4.67k likes | 4.92k Vues
EKG - Dysrhythmia Workshop. Wayne E. Ellis, Ph.D., CRNA . Overview. Anatomy Fundamental Concepts Myocardial Injury Modified Chest Leads Dysrhythmias S inus Atrial AV node Junctional Ventricular Practice Strips. Preop Predictors Periop Cardiac Morbidity “high risk patients”.

EKG - Dysrhythmia Workshop
E N D
Presentation Transcript
EKG - Dysrhythmia Workshop Wayne E. Ellis, Ph.D., CRNA
Overview AnatomyFundamental ConceptsMyocardial InjuryModified Chest LeadsDysrhythmias Sinus Atrial AV node Junctional VentricularPractice Strips
Preop Predictors Periop Cardiac Morbidity “high risk patients” Recent MI Current CHF
Let’s consider the following uninterpreted EKG : Lap-chole on 55 yo black male Hx HTN ( Rx “BP pill” ) Per family member Poor historian Lab “normal” 160 / 96 , 92 , 12
Your diagnosis ? a. “ I think it’s OK ” b. Wait for cardiology to confirm ? How should it / might it affect your anesthetic plan? a. Delay case ? b. Cancel case ? c. Proceed based upon surgeon’s request ? d. Consult with other anesthesia team member (MDA) & proceed accordingly ? Where do you stand medico-legally ?
Left Coronary Artery Sinus Artery Right Coronary Artery Circumflex Left Anterior Descending
Circumflex Right Coronary Artery Posterior Descending Coronary Artery
Circumflex Right Coronary Artery Posterior Descending Right Dominant Coronary Circulation
Circumflex Lateral MI
Right Coronary Artery Posterior MI
Posterior Descending Inferior MI
Left Anterior Descending Anterior MI
Bundle of His S-A Node Left Bundle Branch Posterior Fascicle Anterior Fascicle A-V Node Purkinje Fibers Right Bundle Branch
Coronary Circulation Distribution to the Conduction System
Bundle of His S-A Node A-V Node RCA / Cx
Posterior Fascicle Anterior Fascicle LAD Purkinje Fibers Right Bundle Branch
CHB 10% (11%) 5% Inferior MI Anterior MI
CHB Asystole Death (CHB after ea MI) 10% (11%) 15% (13%) 35% (36%) 5% 80% (78%) 80% (81%) Inferior MI Anterior MI
Arrhythmias & Type of MI Inferior - narrow complex dysrhythmias Sinus dysrhythmias Junctional dysrhythmias 3rd degree A-V block with a junctional escape rhythm Anterior - wide complex dysrhythmias Mobitz II 3rd degree A-V block with a ventricular escape rhythm
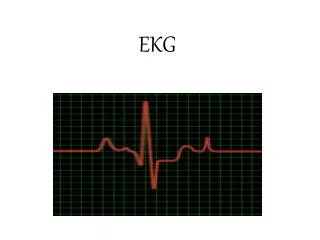
Fundamentals of Electrocardiographic Monitoring
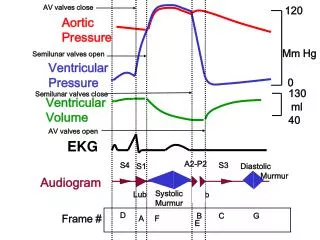
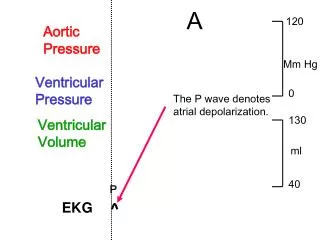
ventricular depolarization QRS = P = atrial depolarization ventricular repolarization T =
a v c CVP Tracing P QRS
1 2 0.16 0.08 0.04 0.12 0.20 3 4 5 3 1 2 4 calibration pulse 1 mV = 10 mm sweep speed 25 mm / sec vertical axis 1 mm = 0.1 mV each mm = 0.04 sec each square = 1 mm
Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification Isoelectric Line
Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification Isoelectric Line Positive Waveform Negative Waveform
Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification Isoelectric Line P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform
Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification Isoelectric Line P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform Q
Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification R Isoelectric Line P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform Q
Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification R Isoelectric Line P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform Q S
R Isoelectric Line T P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform Q S Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification
R Isoelectric Line T P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform U Q S Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification
U Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification R Isoelectric Line T P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform ST Q S
U Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification R Isoelectric Line T P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform ST PR interval Q S
U Waveform, Interval, and Segment Identification R Isoelectric Line T P Positive Waveform Negative Waveform ST PR interval Q S QT interval
QT Interval- Should be < 1/2 preceding R to R interval - QT interval
QT Interval- Should be < 1/2 preceding R to R interval - QT interval
R R QT Interval- Should be < 1/2 preceding R to R interval - QT interval
R R QT Interval- Should be < 1/2 preceding R to R interval - QT interval
R R QT Interval- Should be < 1/2 preceding R to R interval - QT interval
R R QT Interval- Should be < 1/2 preceding R to R interval - 65 - 90 bpm QT interval
R R QT Interval- Should be < 1/2 preceding R to R interval - 65 - 90 bpm QT interval Normal QTc = 0.46 sec
D A C B
D A C B No Q waves RS complex