Understanding DNA to Protein: A Comprehensive Guide to Molecular Biology Processes
270 likes | 405 Vues
Dive into the intricate processes of DNA replication and gene expression in this detailed chapter on molecular biology. Explore key terminology such as genome, chromosome, alleles, and the central dogma of molecular biology, which illustrates the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. Learn about the enzymatic roles in DNA replication, including the leading and lagging strands, and the significance of transcription and translation in gene expression. Gain insights on the mechanisms of bacterial replication, RNA modifications, and the structure of ribosomes, crucial for synthesizing proteins.

Understanding DNA to Protein: A Comprehensive Guide to Molecular Biology Processes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
From DNA to Protein Chapter 8
Terminology • Genetics • Genome • Chromosome • Gene • Locus • Alleles • Genotype/Phenotype • Heredity
Living cells must accomplish two general tasks to multiply and survive • DNA replication • Gene expression • Expression involves two process • Transcription • Translation • Flow of information from DNA to RNA to protein
DNA • Polymer of nucleotides • Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases • AT and CG • Antiparallel • New nucleotides can only be added to the “free” 3’ end
DNA synthesis involves anabolic polymerization Monomers (Triphosphate deoxyribonucleotides) provide required energy for DNA synthesis
One DNA double helix. • Replication produces two DNA double helixes • Each contains one original strand and one new strand Semi-conservative DNA replication Two identical DNA double helixes, each with one parental strand (blue) and one new strand (pink).
DNA replication in bacteria is bi-directional • due to closed circular chromosome • replication forks eventually meet and two complete loops are separated
Bacterial DNA is attached at several points to the cell membrane • Enzymes need for replication are membrane proteins
Topoisomerase (DNA gyrase) • Helicase • Primase • DNA polymerases • DNA Ligase
Bacteria replication involves methylation of daughter stands • Methylase • Adds methyl group (-CH3) to nitrogenous bases (typically adenine) • Methylation functions: • Initiation of DNA repliction • Control of genetic expression • Protection from viral infection • Repair of DNA
DNA Replication • As DNA unwinds, it creates a replication fork • As nucleotides are added, the replication fork moves down the parental strand
Leading strand • Is synthesized CONTINUOUSLY as the DNA polymerase moves towards the replication fork • Lagging strand • Is synthesized DISCONTINUOUSLY in pieces as DNA polymerase moves away from the replication fork • Okazaki fragments
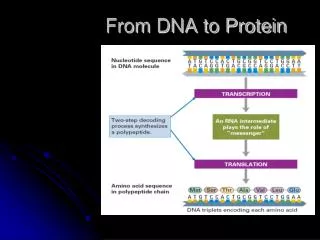
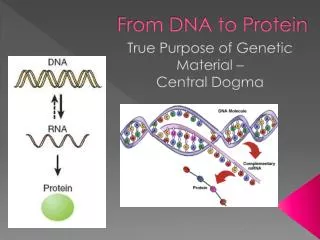
DNA contains the instructions for protein synthesis • Genes • RNA carries out the instructions • Genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology • DNA Transcribed RNA • RNA Translated Protein
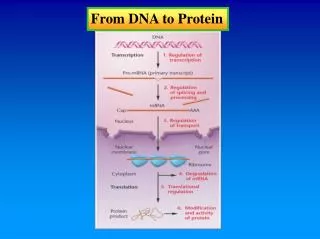
Gene Expression • Transcription • RNA polymerase synthesizes complementary mRNA from DNA template • Cytoplasm of prokaryotes and the nucleus of eukaryotes
Concurrent RNA transcription Multiple copies of RNA can be transcribed simultaneously
Eukaryotic DNA is more complex • Requires post-transcriptional modifications • Spliceosome • Cap and tail
Translation • The language of mRNA is in the form of codons • Three nucleotides situated next to each other on DNA • Sequence of codons determines sequence of amino acids in the protein • 64 codons make up the “alphabet” • 61 are sense codons • 3 “stop codons”
tRNA brings appropriate amino acid to site of translation • Each tRNA has an anticodon • complementary sequence to the mRNA codon
In a prokaryotes, many molecules of mRNA can by transcribed simultaneously • Why can translation begin before transcription is completed in a prokaryote but not in a eukaryote?
gene DNA complementary DNA strand template DNA strand codons mRNA anticodons tRNA amino acids protein methionine glycine valine