Understanding Dual Prices in Linear Programming
60 likes | 163 Vues
Learn about dual prices in linear programming and their significance in optimization problems. Explore how dual prices are calculated, their interpretation, and their role in duality theory. Gain insights into the primal-dual relationship and its implications in LP.

Understanding Dual Prices in Linear Programming
E N D
Presentation Transcript
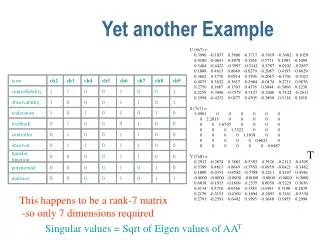
Another example • Max z=5x1+12x2+4x3-MR • S.t. • x1+2x2+x3+x4=10 • 2x1-x2+3x3+R=8 • X1,x2,x3,x4,R >=0. • The optimum table is in next slide, find the dual problem and its optimal solution
Dual Price Z=W Z is the dollars and W should also be the dollars. W= ∑bi yi bi represents the number of units available of resource i. Therefore Dollars= unit of resource i X yi Hence yi= dollars/unit of resource I So yi or dual price or shadow price of a resource I is the worth per unit of resource i.
Dual Price • Each dual price is associated with a constraint. It is the amount of improvement in the objective function value that is caused by a one-unit increase in the RHS of the constraint. • It is also called Shadow Price.
More on Dual Price: • A dual price can be negative, which shows a negative ( or worse off) contribution to the objective function value by an additional unit of RHS increase of the constraint.
Primal and Dual in LP • Each linear program has another associated with it. They are called a pair of primal and dual. • Primal and dual have equal optimal objective function values. • The solution of the dual is the dual prices of the primal, and vice versa.