The Scientific Method
170 likes | 340 Vues
The Scientific Method. The Scientific Method. The Scientific Method. The Scientific Method. Identify the Problem What do you want to solve? What question will you try to answer? Collect Information Research about your problem or question Make a Hypothesis

The Scientific Method
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Scientific Method The Scientific Method
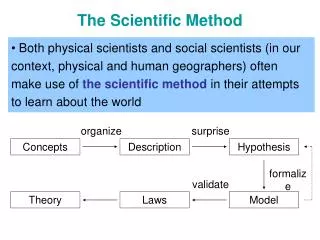
The Scientific Method • Identify the Problem • What do you want to solve? What question will you try to answer? • Collect Information • Research about your problem or question • Make a Hypothesis • Come up with an educated guess about the results of the experiment and give a reason why. • Do Experiment • Conduct a test of your hypothesis • Record Data • Record all results of the experiment • Conclusion • Use your data to help solve your problem
Hypothesis Formation • Each will have 3 parts • If – the condition to be tested • Then – the predicted results • Because – the explanation • If animals have long hair, then they will survive better in cold climates, because the hair keeps their body warm.
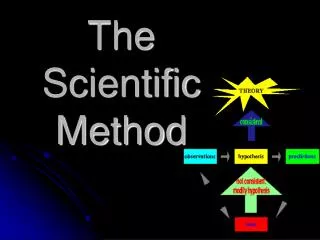
Hypothesis • When a hypothesis is continually supported by evidence it may become a THEORY • A theory is a carefully thought out explanation, based on well founded ideas • When a theory is continually supported by evidence it may become a law • A LAW is an idea or concept almost equal to a fact
Parts of an Experiment • Control • Factors in an experiment that are kept the same for all tests • Independent Variable • The factor of the experiment that is being tested • Dependent Variable • Factors of the experiment that will change because of the independent variable
A statement is made: “Fruit trees that grow in Florida produce more fruit than those grown in Maine”. Write a hypothesis based on this statement. What are the control and variables of this experiment? Control: Independent Variable: Dependent Variable: Experiment Example
Measurement The Metric System
Measuring Volume • Liters (L) • Milliliters (ml) • Graduated Cylinder • Meniscus
Measuring Mass • Grams (g) • Triple Beam Balance • Equal Arm Balance
Weight vs. Mass • Weight – the measure of the force of gravity pulling on an object • Mass – the amount of matter in an object
Converting Units in the Metric System: Length • Done by powers of 10 • Uses decimals instead of fractions • Less error
Converting Units in the Metric System: Volume • Done by powers of 10 • Same as length
Temperature • Fahrenheit • 32°-212° • Celsius • 0°-100° • Kelvin • Absolute Zero • 0°K = -273°C
Density • Mass per volume • D = m/v