Westward Expansion
370 likes | 548 Vues
Westward Expansion. America’s “Manifest Destiny”. Do Now. Why do people move? List at least 5 reasons in your binder. Push and Pull. Why do people move? There are both push factors and pull factors: Push factors = conditions that force people to leave a certain area

Westward Expansion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Westward Expansion America’s “Manifest Destiny”
Do Now • Why do people move? • List at least 5 reasons in your binder.
Push and Pull • Why do people move? • There are both push factors and pull factors: • Push factors = conditions that force people to leave a certain area • Pull factors = conditions that draw people to a certain area
African American Migration • After the Civil War, many African Americans moved: • to towns and cities • to the North • to the West • What factors may have “pushed” African Americans to leave the South? • What might factors may have “pulled” African Americans to the city? To the North? To the West?
“Expansion” can have many meanings: • Expansion of territory (purchase of land, treaties, conquest). • Expansion of settler population (through migration).
“Manifest Destiny” • A phrase coined in the 1840s by an American journalist • First used to justify American expansioninto western territories. • Later used to justify American economic and cultural domination around the world John L. O'Sullivan
Manifest Destiny • Refers to the widely held belief that • The anglo-American way of life is better than any other (best type of government, economy, culture, etc.) • Therefore, the U.S. had both a right and a duty to spread out across the entire continent. • American expansion was inevitable, necessary, and had been ordained by God!
Manifest Destiny • Although the phrase was new, the idea was not: • even as British colonists, settlers pushed farther and farther west. • thousands of colonists, for example, ignored the Proclamation of 1763, which forbid settlement of the Ohio River Valley. Famous frontiersman Daniel Boone Escorts settlers through the Cumberland Gap
The Argument • Fulfilling this “destiny,” many argued, would benefit everyone involved: • American settlerswould gain access to much needed land (U.S. population was growing very quickly at this time) • others would have the opportunity to learn the (superior) American way of life.
Underlying Assumptions • Through farming and construction, it was believed that American settlers actually improved the land (made it more productive). • Anyone who did not build permanent homes and who did not farm on a large scale were simply wasting the land. Ethnocentrism?
Ethnocentrism • the belief that your own group or culture is better or more important than others.
How does this painting explain the attitude of Americans in the mid-1800s? Spirit of the Frontier (American Progress), 1872 by John Gast
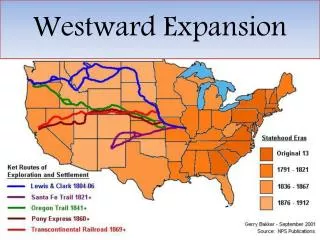
Events and Inventions that helped America fulfill its “Manifest Destiny” 1787 1803 • Northwest Ordinance – establishes a procedure for dividing land into territories and encourages settlement of the Ohio River Valley. • Louisiana Purchase - doubles the size of the U.S.
Events and Inventions that helped America fulfill its “Manifest Destiny” 1804 1836 • Lewis and Clark Expedition– to gather information about plants, animals, and Native American tribes of the West(pg. 200) • The Whitman family reaches the Oregon Territory – proves that wooden-wheeled wagons can travel the Oregon Trail; thousands of American pioneers would follow their lead(pgs. 283 and 286 - 287)
Events and Inventions that helped America fulfill its “Manifest Destiny” 1837 1846 • John Deere Invents the Steel Plow – slices through heavy soil much more easily than existing plows. • Texas Joins the Union – Mexican government is furious • U.S. War with Mexico Begins
Events and Inventions that helped America fulfill its “Manifest Destiny” 1848 1850 • Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo – ends war with Mexico • Gold is Discovered at Sutter’s Mill – migration to California skyrockets • Railroads Open the West – thefederal government begins making huge land grants to railroad companies.
Events and Inventions that helped America fulfill its “Manifest Destiny” 1862 1869 • President Lincoln signs the Homestead Act, the Pacific Railways Act, and the Morrill Actinto law. • Transcontinental Railroad Completed – Central Pacific and Union Pacific Railroads meet at Promontory Point, Utah.
Why might the information gathered by Lewis and Clarke be valuable to future settlers?
What were some of the obstacles settlers faced on western trails?
What lands did the US gain as a result of the war with Mexico (pg. 297)?
Promontory Point, Utah In what ways did the US government encourage the construction of railroads?
Do Now, 4/28/14 • Use the Excerpt provided to answer Homestead Act Do Now question #1
Do Now, 4/28/14 • According to section 2 of the Homestead Act, what did settlers have to DO before they could receive a patent (deed of ownership) for the land they were claiming? • Submit an application; • Pay a $10 application fee; • Live on the land for 5 years; • Cultivate (farm) a portion of the land (1/4 or less of the 160 acres); Document A
Do Now, 4/28/14 • According to section 2 of the Homestead Act, what did settlers have to DO before they could receive a patent (deed of ownership) for the land they were claiming? • Swear in writing that they met all of the qualifications (head of household, citizenship, etc.) and that they were not claiming the property for someone else; • Make other “improvements” such as building a home, barn, etc.; • Provide proof: Two “credible” witnesses had to swear in writing that the applicant had met all of the requirements. Document B
Homestead Document Analysis Document A: The Application Document B: The Proof Submitted 1863 Submitted 1868
Settling the Great Plains Film Clip
Settling the Great Plains: Part A Directions: Read pages 420 – 423 and note how each of the factors listed below (Causes) helped to settle the West and turned the eastern Great Plains into the nation’s “breadbasket” (Effects). • Land grants given to railroads. • The Homestead Act and related laws passed in the 1870s. • Inventions and improvements in farm technology. • Morrill Act and Hatch Act.
Settling the Great Plains: Model Cause Effect Homestead Act offered 160 acres of free land to anyone who would farm it for 5 years; similar acts offering cheap (or free) land in states such as Kansas and Oklahoma were later passed . • The Homestead Act and related laws passed in the 1870s
Settling the Great Plains: Part A Cause Effect Railroad companies sold frontier land to farmers at low prices; recruited Europeans to buy and farm frontier land. Homestead Act offered 160 acres of free land to anyone who would farm it for 5 years; similar acts offering cheap (or free) land in states such as Kansas and Oklahoma were later passed. • Land Grants given to the railroads. • The Homestead Act and related laws passed in the 1870s
Settling the Great Plains: Part A Cause Effect Increased farm productivity by decreasing the amount of effort and time required to produce farm goods; led to profitable industry – manufacturers of farm equipment multiply • Inventions and improvements in farm technology
Settling the Great Plains: Part A Cause Effect Supported farmers by financing agricultural education and research in farm technology and methodology • Morrill Act and Hatch Act
Exit Slip • Explain at least two ways in which the government encouraged the settlement of the Great Plains. Homework: Answer questions 5 – 10 in complete sentences on a sheet of lined paper.
Themes in History • Human-Environment Interaction: • Throughout history, humans have changed and have been changed by their environment. As you learn about our continuous interaction with the environment, keep these questions in mind: • How do humans adjust to the climate and terrain where they live? • What positive and negative changes have people made to their environment?
Human-Environment Interaction on the Plains • Use information from your completed “Settling the Great Plains” chart and guided reading questions to respond to the following: • How did settlers adjust to the climate and terrain of the Great Plains? • What positive and negative changes did settlers make to the environment of the Great Plains?