Gantt Chart
190 likes | 676 Vues
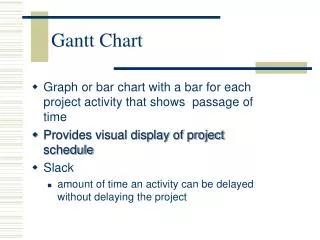
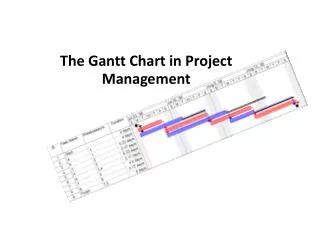
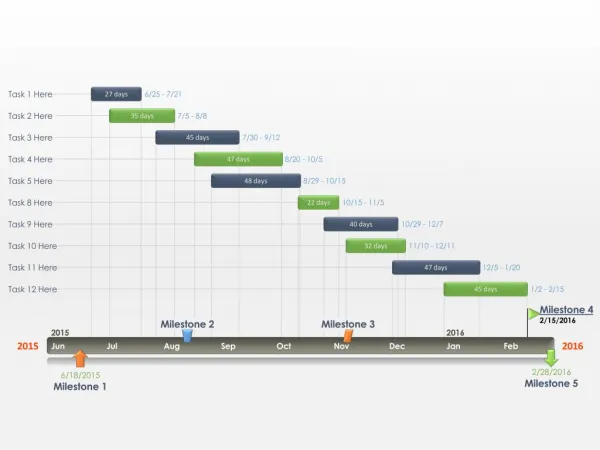
Graph or bar chart with a bar for each project activity that shows passage of time Provides visual display of project schedule Slack amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project. Gantt Chart. Month. 0 2 4 6 8 10. | | | | |. Activity

Gantt Chart
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Graph or bar chart with a bar for each project activity that shows passage of time Provides visual display of project schedule Slack amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project Gantt Chart
Month 0 2 4 6 8 10 | | | | | Activity Design house and obtain financing Lay foundation Order and receive materials Build house Select paint Select carpet Finish work 1 3 5 7 9 Month Example of Gantt Chart
The Project Network • Use of nodes and arrows Arrows An arrow leads from tail to head directionally • Indicate ACTIVITY, a time consuming effort that is required to perform a part of the work. Nodes A node is represented by a circle - Indicate EVENT, a point in time where one or more activities start and/or finish.
CPM/PERT • Critical Path Method (CPM) • DuPont & Remington-Rand (1956) • Deterministic task times • Activity-on-node network construction • Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) • US Navy, Booz, Allen & Hamilton • Multiple task time estimates • Activity-on-arrow network construction
Activity-on-node (AON) nodes represent activities, and arrows show precedence relationships Activity-on-arrow (AOA) arrows represent activities and nodes are events for points in time Event completion or beginning of an activity in a project Node 1 2 3 Branch/Activity Project Network
Lay foundations Build house Finish work 7 5 3 6 4 2 1 3 1 3 2 1 1 1 Start Design house and obtain financing Select carpet Order and receive materials Select paint AON Network for House Building Project
1 7 6 3 5 2 4 1 3 1 2 1 3 1 Start Critical Path A: 1-2-4-73 + 2 + 3 + 1 = 9 months B: 1-2-5-6-73 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 8 months C: 1-3-4-73 + 1 + 3 + 1 = 8 months D: 1-3-5-6-73 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 7 months • Critical path • Longest path through a network • Minimum project completion time
Start at 5 months Finish at 9 months 1 2 4 3 5 6 7 1 1 1 3 2 1 3 Finish Start Start at 6 months Start at 3 months Activity Start Times
Calculation of Required Time (Te) t0 + 4tm + tp • Te= 6 te=weighted arithmetic average time to= Optimistic Time tm= most likely time tp= pessimistic time
Networking 2 15 13 5 2 1 2 12 8 3 4
Activity Slack Each event has two important times associated with it : • Earliest time , Te , which is a calendar time when a event can occur when all the predecessor events completed at the earliest possible times • Latest time , TL , which is the latest time the event can occur with out delaying the subsequent events and completion of project. • Difference between the latest time and the earliest time of an event is the slack time for that event Slack=LF-EF, LS-ES Positive slack : Slack is the amount of time an event can be delayed without delaying the project completion
1 0 3 3 0 3 Mode Configuration Activity number Earliest start Earliest finish Latest finish Activity duration Latest start
Forward Pass • Start at the beginning of CPM/PERT network to determine the earliest activity times • Earliest Start Time (ES) • earliest time an activity can start • ES = maximum EF of immediate predecessors • Earliest finish time (EF) • earliest time an activity can finish • earliest start time plus activity time EF= ES + t
Lay foundations Build house 7 1 6 2 4 3 5 0 3 3 6 5 8 5 3 7 8 5 6 4 9 Start 2 1 1 3 1 3 1 Design house and obtain financing Finish work Select carpet Order and receive materials Select paint Earliest Activity Start and Finish Times
Lay foundations Build house 4 6 5 3 7 2 1 0 5 3 6 8 3 5 4 9 3 7 8 5 6 Start 1 2 1 3 3 1 1 Design house and obtain financing Finish work Select carpet Order and receive materials Select paint Earliest Activity Start and Finish Times * 0+3 3+1 * For forward pass maximum EF time would be taken in calculating ES time
Backward Pass • Determines latest activity times by starting at the end of CPM/PERT network and working forward • Latest Start Time (LS) • Latest time an activity can start without delaying critical path time LS= LF - t • Latest finish time (LF) • latest time an activity can be completed without delaying critical path time • LS = minimum LS of immediate predecessors
Lay foundations Build house 4 1 7 2 5 6 3 0 3 3 6 5 5 8 4 7 9 5 6 3 8 Start 1 2 1 1 3 3 1 7 8 6 5 4 3 0 8 3 9 7 5 8 5 Design house and obtain financing Finish work Select carpet Order and receive materials Select pain Latest Activity Start and Finish Times
Activity LS ES LF EF Slack S *1 0 0 3 3 0 *2 3 3 5 5 0 3 4 3 5 4 1 *4 5 5 8 8 0 5 6 5 7 6 1 6 7 6 8 7 1 *7 8 8 9 9 0 * Critical Path Activity Slack