CELL STRUCTURE
260 likes | 475 Vues
CELL STRUCTURE. Dannye DiNizo Lillian Cherry Will Granberry. Cell Structure. http://training.seer.cancer.gov/module_anatomy/unit2_1_cell_functions_1.html. Nucleus.

CELL STRUCTURE
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CELL STRUCTURE Dannye DiNizo Lillian Cherry Will Granberry
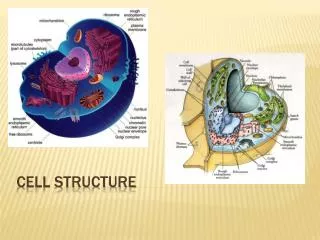
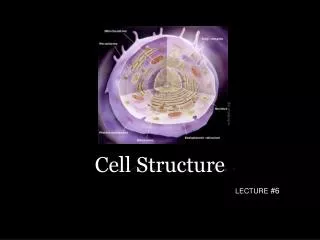
Cell Structure http://training.seer.cancer.gov/module_anatomy/unit2_1_cell_functions_1.html
Nucleus The positively charged, center of an atom. The nucleus contains the DNA and RNA of the cell. It’s responsible for growth and reproduction. The nucleus contains the nuclear membrane, chromatin, and the nucleolis http://www.uga.edu/caur/temimage.htm
Centriole Nine triplets of microtubules form one centriole. Two centrioles form one centrosome. The centriole forms spindle fibers to separate chromosomes during cell division. http://online-media.uni-marburg.de/histologie/introhis/HIS/txt/tacsem/tac06_sem.htm
Lysosome A sac-like organelle of a cell that contains enzymes for breaking down waste http://www.healthvalue.net/audeladesproteines.html
Peroxisome A cell organelle that contains enzymes that start the production and breakdown of hydrogen peroxide http://www.peroxisome.org/Scientist/scientist.html
Plasma Membrane It’s composed of proteins and lipids (fat molecules). It is the outer membrane of a cell. The membrane acts as a boundary to contain the cytoplasm. It is also selectively permeable, to choose which chemicals enter and leave the cell. http://sst.nsu.edu/bio110/exams/Plasma_Membrane_Quiz.jpg
Mitochondrion An organelle located in the cytoplasm containing genetic material and enzymes important for cell metabolism http://tidepool.st.usm.edu/crswr/110respiration.html
Vacuole A single layer of unit membrane enclosing fluid in a sac. It stores water and various chemicals. http://sun.menloschool.org/~cweaver/cells/c/vacuole/
Chromatin It is composed of long thin strands of DNA. The chromatin contains instructions that control cell metabolism and heredity. http://www.uni-mainz.de/FB/Medizin/Anatomie/workshop/EM/EMKern.html
Nucleolus Within the nucleus is the nucleolus. The nucleolus is like a “knot” of chromatin. The nucleolus is where ribosomes are manufactures. http://www.rockefeller.edu/rucal/journey/journey.html
Nuclear Membrane Two unit membranes with a fluid-filled space. It is electively permeable to control movement in and out of the nucleus. http://www.uni-mainz.de/FB/Medizin/Anatomie/workshop/EM/EMZelle.html
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Sheets of the unit membrane with ribosomes on the outside (rough). It forms a tubular network throughout the cell. It transports chemicals between and within cells. It Provides a large surface area for the organization of chemical reactions and synthesis http://www.kcl.ac.uk/kis/schools/life_sciences/biomed/bscb/softcell/er.html
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum The rough ER specializes in protein synthesis, production of steroids, the storage and production of glycogen, and the insertion of membrane proteins. http://trc.ucdavis.edu/mjguinan/apc100/modules/TermsCells&Tissues/structures/ER.html
Ribosomes Small cellular components composed of specialized ribosomal RNA and protein. It is the site of protein synthesis. http://www.rockefeller.edu/rucal/journey/journey.html
Golgi Apparatus A group of combined membranous vesicles present in animal cells that work for the formation of secretions within the cell. http://web.mit.edu/esgbio/www/cb/org/organelles.html
Microtubules (Cytoskeleton) Tubular structures that provide structural support to the cell http://www.noble.org/Press_Release/PlantBio/BlancaflorNASA/
Cytosol The cytosol is a semi-fluid component of the cell’s cytoplasm. The cytosol is also where most of the cell’s metabolism takes place. http://www014.upp.so-net.ne.jp/cytosol/
Microvilli Microvilli are hair-like pieces of microfilaments that out pouch from the nuclear membrane in extra cellular space. They are often used to help move the cell. http://www.cytochemistry.net/Cell-biology/actin_filaments.htm
Microfilament (Cytoskeleton) • A transport system for the cell, but it also makes lipids, processes carbohydrates, and detoxifies substances, such as poisons and alcohol. http://www.bi.umist.ac.uk/users/mjfssjm4/2MCD/default.htm