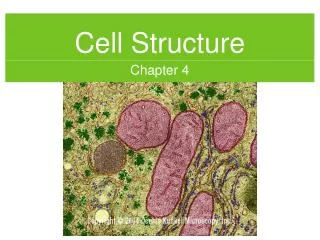
Cell Structure
430 likes | 620 Vues
nobelprize.org. Cell Structure. LECTURE #6. Identifying cells… 1600 ’ s. Hooke’s 1665 book was the origin of the word “ cell .”. inventors.about.com. Galileo and then Robert Hooke improved upon the microscope in the 1600s. Wikipedia.org. Microscopes. Light microscope (LM).

Cell Structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
nobelprize.org Cell Structure LECTURE #6
Identifying cells… 1600’s Hooke’s 1665 book was the origin of the word “cell.” inventors.about.com Galileo and then Robert Hooke improved upon the microscope in the 1600s. Wikipedia.org
Microscopes Light microscope (LM) Scanning electronmicroscope (SEM)
Size of cells One cell Most cells are less than 50 µm Trillions of cells
Size of cells blog.makezine.com Larger organisms don’t have bigger cells per se… … just more cells!
Size of cells 1m = 103 mm millimeter one-thousandth of a meter 1m = 106 µm micrometer one-millionth a meter 1 µm = small cell 1m = 109 nm nanometer one-billionth a meter 1 nm = amino acid
µm µm µm
Size of cells Q. Why are cells so small? A. Volume increasesfaster than surface area Q. How can a cell increase its surface area without increasing its volume? Microvilli of human intestine
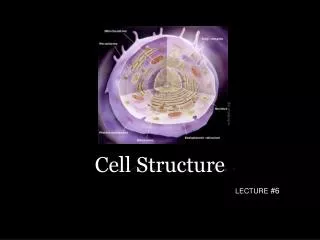
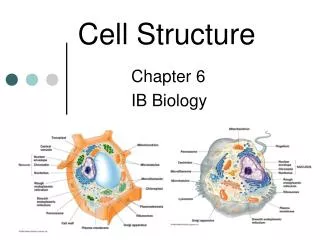
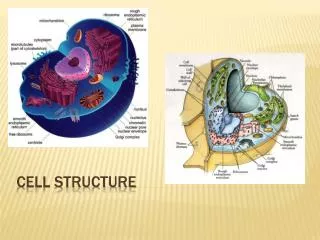
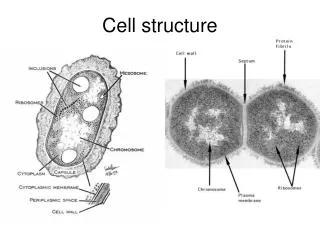
All cells have… Chromosomes that contain genes formed from DNA A plasma membrane binding their contents Cytosol – the semifluid substance within the membrane Ribosomes that make proteins
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! The cell is like a factory… … a factory that makes proteins.
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Plasma membrane security guard - Monitors movement of substancesinto and out of the cell
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Nucleus Control center - Contains blueprints (DNA) - Nucleolus is where ribosomes synthesized - Info (RNA) leaves through “doors” (nuclear pores) in the nuclear envelope
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Ribosomes work bench - Binds to and reads mRNA to synthesize polypeptides - After a short period of synthesis, ribosome docks on ER
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Rough endoplasmic reticulum assembly line - Where most protein synthesis occurs and proteins fold • Rough ER = protein synthesis (has ribosomes)
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Transport vesicles forklifts - Pieces of ER “bud off” into vesicles that carry proteins to golgi complex
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Golgi complex distribution/mailing center • Sorts, modifies and tags proteins for distribution to other parts of the cell • EX: 90210 (lysosome)
Be familiar with the protein pathway! p. 62 in book … and now more organelles (that aren’t part of the protein pathway)…
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) • Network of membranes next to RER • No ribosomes, so “smooth” • Synthesis of lipids (fats and steroids) and carbs • Detoxification by liver cells
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Lysosome Recycling center • Break down old/foreign material inside/outside cell • Membrane-bound sacs w/ digestive enzymes (ACIDIC!) • Formed in the golgi complex
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Mitochondria Energy source • Provides energy to carry outthe functions of the cell • Oxidizes food to release chemical energy in the form of ATP • One to several thousand in a cell • Endosymbiotic origin
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Cytoskeleton Support beams - Network of protein fibers that maintain shape of cell, location of organelles and cell movement.
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Microfilaments: -Send out pseudopodia Intermediate filaments: -Cytoskeleton structure Microtubules: -Hair-like extensions make cilia, flagella -Big monorail for proteins(vesicles ride from RER to golgi)
Cilia = profuse collections of hair-like projections that beat rapidly, forming currents that can propel a cell or move material around it. Flagellum on this sperm cell is enabling it to seek entry into an egg. Usually only one or two flagella (long and whip-like)
Plant cells possess unique structures • Cell wall • Chloroplasts • Central vacuole
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Vacuole Storage area • Stores toxins, nutrients, pigments… • May make up 90% of volume • Balances pH of cell
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Cell wall External wall • Outside of cell membrane • Provides support to cell (cellulose) • Regulates water intake, maintains turgor
A tour of the eukaryotic cell! Chloroplasts solar panels • Site of photosynthesis • Uses sun’s energy to convert CO2 into usable energy (sugar) • O2 is the byproduct