English Settlements
160 likes | 178 Vues
This article examines the impact of Puritan settlements on colonial literature from 1607 to 1750, exploring the beliefs, characteristics, and writings of the Puritans. It also introduces the Age of Reason and its influence on literature in the American colonies.

English Settlements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
English Settlements Colonial Literature 1607 - 1750
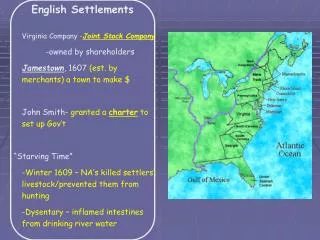
3 Groups – also establish location • New England – the Puritans – 1620 landed at Cape Cod • The Southern Colonies – farmers (cash crops) • The Middle Colonies – Quakers – Ethnic and culturally diverse
Puritans • A broad term referring to a number of Protestant groups. • Desired a simpler form of worship • Religion was a personal inner experience • Clergy/government not an intermediary between individual and God • Persecuted in England
Puritan theology – mixture of certainty and doubt • “Elect” = Saved • “Unregenerate” = one of the damned • Definite separation between church and state • How do you know which category you fall into? • You don’t
Puritans valued… • Self-reliance – • Industriousness – • Temperance – • Simplicity – plain, black/white clothing
Amer. Lit shaped by Puritans • American Literature was shaped by Puritans and their • Morals • Ethics • Religious Convictions
Characteristics of Puritan Writing • Bible provided a model for Puritan writing • Concept that each life was a journey to salvation • Used writing to explore their inner and outer lives for signs of the workings of God
Puritan characteristics con’t. • Diaries and histories were the most common forms • Puritans favored a plain style – stressing clarity of expression and avoiding figures of speech
Rationalism • The belief that human beings can arrive at truth by using reason, rather than by relying on past authorities, religious faith, or intuition. • Started in Europe and made its way to the American Colonies
Scientific Progress • Cotton Mather, a Puritan minister is also interested in natural science and medicine. • He implemented inoculations for the Smallpox disease in 1721.
Deism • In contrast to Puritans – Deists believed: • God was available at all times • People were inherently good • Individuals had the gift to reason
Literature • Age of pamphlets • Literature was intended to serve a purpose of practical or political ends.
Types of Colonial Lit. • New England Primer – textbook • The Day of Doom – poem about sinners who would experience the torment of hell. • The Selling of Joseph – anti-slavery tract • Bay Psalm Book – new translation of the Psalms • The History of Plymouth Plantation • Common Sense – Thomas Paine
Writers • Cotton Mather – witchcraft trials • Jonathan Edwards – puritan theologian • Anne Bradstreet – Poetry • Phillis Wheatley – slave poet • Philip Freneau – patriotic poet • Benjamin Franklin – autobiography • Thomas Jefferson – Dec. Independence • Poor Richard’s Almanack
Historical Narratives • Determine the purpose of each work • Consult the biographies to determine the various backgrounds of writers. • Use the graphic aids. • Try to distinguish fact from opinion. • Understand that these narrative lay the groundwork for later Amer. Lit. • Look for parallels to modern life.