Cell Cycle
300 likes | 731 Vues
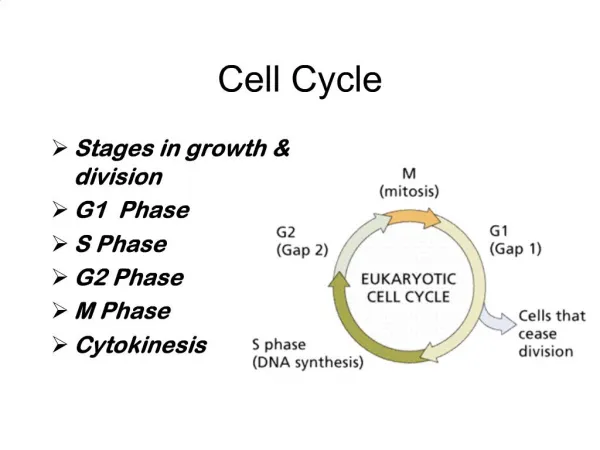
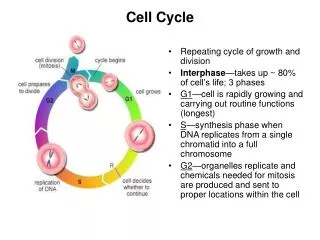
Cell Cycle. The cell cycle begins when the cell is formed and ends when the cell divides and forms new cells. DNA. Before a cell divides, DNA is copied DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes DNA is in the nucleus. Cell Cycle ( Prokaryotic ) BACTERIA.

Cell Cycle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell Cycle The cell cycle begins when the cell is formed and ends when the cell divides and forms new cells.
DNA • Before a cell divides, DNA is copied • DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes • DNA is in the nucleus
Cell Cycle (Prokaryotic) BACTERIA • Bacteria are not complex • Bacteria contain ribosomes and a single circular molecule of DNA • Bacteria have no membrane bound organelles, making cell division simple • Cell division is called binary fission- splitting into two parts • They make a copy of the DNA and split with each cell containing a copy
Binary Fission in Bacteria • Bacteria
Binary Fission • Bacteria
Eukaryotic Cell DivisionCHROMOSOMES • Chromosomes contain lots of DNA and proteins • Number of chromosomes is different in each organism-humans=46, potatoes=48, and fruit flies=8 • Chromosomes can line up in pairs containing similar information (homologous chromosomes)
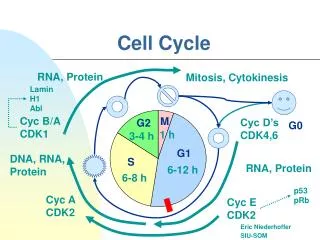
Making More Eukaryotic CellsINTERPHASE STAGE 1 • Three stages, Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis • Stage 1(INTERPHASE)=Cell grows and copies organelles, centriole, and chromosomes • Strands of DNA and proteins are like loosely coiled thread • After chromosomes are duplicated, the copies are now called chromatids • Chromatids are held together by a centromere
Making More Eukaryotic Cells MITOSIS STAGE 2 • Three stages, Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis • Stage 2 (Mitosis)Chromosome Separation • 4 Phases OF MITOSIS = Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase
Mitosis STAGE 2Separation – PHASE1 • Phase 1(Prophase) Mitosis begins • Nuclear membranes break apart • Chromosomes condense into rod like structures • Two pair of centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell • Fibers form between the centrioles and attach to the centromeres
Mitosis STAGE 2Separation – PHASE 2 • Phase 2 (Metaphase) • Chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell • Remember M for Middle
Mitosis – STAGE 2Separation – PHASE 3 • Phase 3 (Anaphase) • Chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite sides of the cell by fibers that are attached to the centrioles • Remember A for Apart
Mitosis – STAGE 2Separation – PHASE 4 • Phase 4 (Telophase) • Nuclear membrane forms around two sets of chromosomes and they unwind • Fibers disappear • Mitosis is completed • Remember T for Two • The kindergarten teacher said “Do not p on the mat! (PMAT)
Stage 3 CYTOKINESIS-Animal Cell • After mitosis, the cytoplasm splits in two, (Cytokinesis) • Result is two identical cells, identical to the original cell they came from • After cytokinesis, cell cycle is complete and will start over again
Stage 3 CYTOKINESIS-Plant Cell • When plant cells divide, a cell plate forms and the cell is split in two • Cell plate becomes the new cellmembrane that will separate the two cells • After split, new cell wall forms