Cell Cycle
200 likes | 485 Vues
Cell Cycle. Ovum (egg). Sperm. Cell Division. Cell division is the process where a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. There are two types of cell division: Mitosis occurs in somatic cells. Meiosis occurs in the sex organs and produces sex cells (gametes).

Cell Cycle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ovum (egg) Sperm Cell Division • Cell division is the process where a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. • There are two types of cell division: • Mitosis occurs in somatic cells. • Meiosis occurs in the sex organs and produces sex cells (gametes).
Introduction to Mitosis • During mitosis, an existing parent cell divides into two new daughter cells (right). • The cells are genetically identical. • There is no change in chromosomal number. • Cells are diploid, containing two setsof chromosomes. • In humans the diploid number is 46 • Mitosis is associated with the growth and repair of somatic cells in the body.
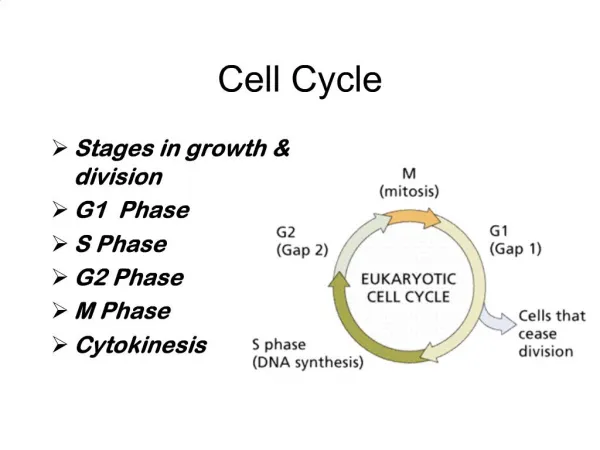
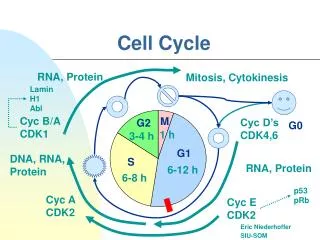
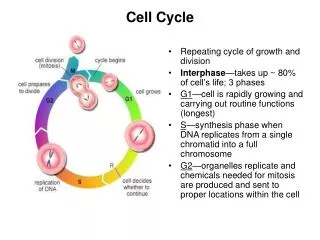
C Mitosis Interphase Cytokinesis The cell cycle Mitosis and the Cell Cycle • Mitosis is just one phase of the cell cycle. • There are three main phases in the cell cycle: • Interphase(three stages) • Mitosis (nuclear division) • Cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm)
Centrosome is replicated Nucleolus Chromosome Interphase G2 S • Interphase accounts for 90% of the cell cycle. • It is the longest phase of the cell cycle. • Interphase consists of three stages: • Growth 1: G1The cell grows and develops • Synthesis (S)The cell duplicates its geneticmaterial (chromosomes). • Growth 2: G2 Further growth G0 Nondividing state M The cell cycle C G1 Nuclear membrane
Early Prophase Late Anaphase Telophase Late Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Mitosis • The mitotic cycle is broken down into six phases.
Nucleolus disappears Nuclear membrane disintegrates Mitosis: Early Prophase • Prophase is the first stage of mitosis. In early prophase: • the nuclear membrane disintegrates • the nucleolus disappears • the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. Replicated centrosomes
Centromere Centrosome Chromatids Mitosis: Prophase • In late prophase: • the chromosomes continue to coiland appear as double chromatids. • the chromatids are each joined by a centromere. • the centrosomes (including centrioles in animal cells) move to opposite ends of the cell. As they do so, they form the mitotic spindle between the poles.
Mitotic spindle Chromosomes Mitosis: Metaphase • Duringmetaphase the chromosomes become aligned at the equator of the cell.
Mitosis: Early Anaphase • In anaphase, the sister chromatids split and the chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes Spindle Anaphase is the shortest mitotic phase
Mitosis: Late Anaphase • Bylateanaphase, the chromosomes have moved to opposite poles. • By the end of anaphase, the two poles of the cell have equivalent, and complete, collections of chromosomes. Centrosome Mitotic spindle Chromosomes
Mitosis: Telophase • Telophaseis characterized by the formation of two new nuclei. • The nucleoli reappear and the chromatin becomes less tightly coiled (less condensed). In plant cells, the cell plate forms where the new cell wall will form.
Two cells are formed Cytokinesis Cell wall • The division of the cytoplasm is termed cytokinesis. • Cytokinesis begins towards the end of telophase. • In plant cells, thecell plateforms where the newcell wall will form. • Inanimal cells, acleavage furrow pinches the cell in two. Nucleus
Cell enters mitosis Two independent cells. Cell elongates Nuclei reform. Early Prophase Chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate. Chromosomes separate to opposite poles. Cell plate forms (plants) Centrosomes move to opposite poles. Chromosomes appear as chromatids. Mitotic spindle forms. Nuclear membrane disintegrates. Nucleolus disintegrates. DNA continues condensing. Late Anaphase DNA replicated. Nucleus still well defined. Centrosome replicated. Interphase Anaphase Metaphase Cytokinesis Telophase Late Prophase Mitosis: Review
Mitosis animation • Mitosis Animation
Meristematic tissue (area of cell division) Zone of cell division Zone of elongation Zone of specialization Mitosis in the Root Tip • Mitosis in plant cells occurs only in regions of meristematictissue. • The meristematic tissue is located at the tip of every stem and every root. • In contrast, mitosis can occur throughout the body of a growing animal. Root tip growing in this direction Root cap