Cell Cycle
210 likes | 885 Vues
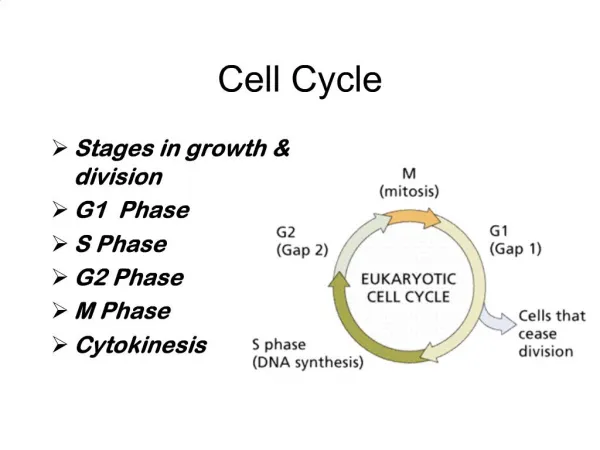
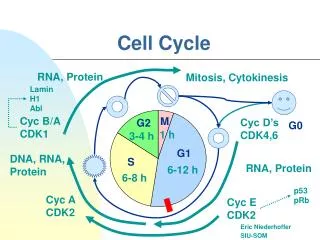
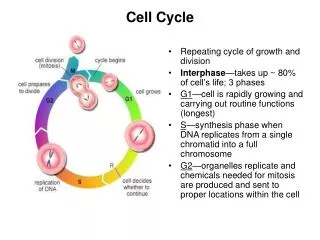
Cell Cycle . The repeating set of events in the life of a cell. Includes Interphase 3 phases Cell Division Mitosis Cytokinesis . Interphase. Period between cell divisions, 3 stages- 1. G 1 phase- Gap 1- Cells grow to mature size. 2. S phase- Synthesis - DNA replication.

Cell Cycle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell Cycle • The repeating set of events in the life of a cell. • Includes • Interphase • 3 phases • Cell Division • Mitosis • Cytokinesis
Interphase • Period between cell divisions, 3 stages- • 1. G1 phase- Gap 1- Cells grow to mature size. • 2. S phase- Synthesis- DNA replication. • 3. G2 phase- Gap 2- Cell prepares for cell division. • GO phase- Cell exits the cell cycle (usually after G1) Cells do not copy DNA or prepare to divide. Ex. CNS cells stop dividing at maturity and never divide again.
Mitosis • Division of the nucleus. • Distributes the cells copied DNA to offspring cells. • New cells get the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent cell • 4 phases
Prophase (p 156) • Chromosomes shorten, thicken and become visible • Chromatids (replicated chromosomes) lie side by side, attached by a centromere • Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell (animal cells) • Nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase (pp 156, 157) • Paired chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell • Centromeres attach to the spindle
Anaphase (156, 157) • Centromeres split • Chromatids separate, becoming individual chromosomes • Chromosomes move to opposite poles along spindle
Telophase (p 156, 157) • Chromosomes uncoil into tangle of chromatin • Nuclear envelope reforms around the chromatin
Cytokinesis (p 157) • The division of the cytoplasm into two cells • Animal cells- cell membrane pinches the cytoplasm into two equal parts • Plant cells- cell plate forms midway between divided nuclei, plate becomes cell wall