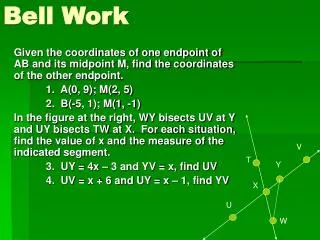
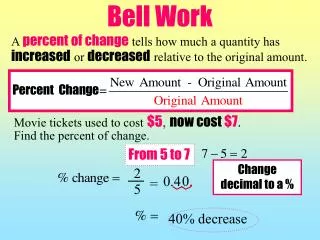
BELL WORK :
210 likes | 468 Vues
BELL WORK :. Take out your homework so I can check it. Turn in your Organ Trail Project (poster AND packet!!) Turn in your vocabulary project if you didn’t turn it in yesterday!! Get ready for your homework quiz!.

BELL WORK :
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BELL WORK: • Take out your homework so I can check it. • Turn in your Organ Trail Project (poster AND packet!!) • Turn in your vocabulary project if you didn’t turn it in yesterday!! • Get ready for your homework quiz!
CO: I will describe the interactions between the immune and integumentary systems. LO: I will write notes. I will draw and write how the immune system works.
Why do we have an immune system? • Attack from outside • animals must defend themselves against invaders (pathogens) • viruses • HIV, flu, cold, measles, chicken pox • bacteria • pneumonia, meningitis, tuberculosisLyme disease • fungi • yeast (“Athlete’s foot”…) • protists • amoeba, malaria • Attack from inside • cancers = abnormal body cells Mmmmm, What’s in your lunchbox?
Avenues of pathogen attack • Possible points of entry • digestive system • respiratory system • Genitals • Urinary tract • break in skin
Lines of defense • 1st line: Non-specific barriers • broad, external defense • “walls & moats” • skin & mucous membranes • 2nd line: Non-specific patrols • broad, internal defense • “patrolling soldiers” • leukocytes = phagocytic WBC • 3rd line: True immune system • specific, acquired immunity • “elite trained units” • lymphocytes & antibodies • B cells & T cells Bacteria & insectsinherit resistance. Vertebratesacquire immunity.
1st line:General Defense • Barrier • Skin (Integumentary System) • Traps • mucous membranes, cilia,hair, earwax • Elimination • coughing, sneezing, urination, diarrhea, throwing up • Unfavorable pH • stomach acid, sweat, saliva, urine • Lysozymeenzyme • digests bacterial cell walls • tears, sweat Lining of trachea: ciliated cells & mucus secreting cells
Integumentary System: Functions • Protection • First line of defense against • Bacteria • Viruses • Protects underlying structures from • Ultraviolet (UV) radiation • Dehydration • Body temperature regulation • If too hot • Dermal blood vessels dilate • Vessels carry more blood to surface so heat can escape • If too cold • Dermal blood vessels constrict • Prevents heat from escaping
Integumentary System: Functions • Vitamin D production • Needed for calcium absorption • Sensation • Sensory receptors (nerves) • Excretion • Small amounts of waste products are lost through perspiration (sweat)
2nd line: Non-specific Responses bacteria • Patrolling cells & proteins • attack pathogens, but don’t “remember” for next time • leukocytes • phagocytic white blood cells • macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells • Proteins that destroy cells macrophage yeast
2. Inflammatory response • Damage to tissue triggers local non-specific inflammatory response • release chemical signals • capillaries dilate, becomemore permeable (leaky) • increases temperature • Feveroccurs when local inflammatory response is not enough • High body temperature helps defend body
3rd line: Acquired (active) Immunity B cell • Specific defense with memory • lymphocytes • B cells • T cells • antibodies • immunoglobulins • Responds to… • antigens • cellular name tags • specific pathogens • specific toxins • abnormal body cells (cancer)
Lymphocytes bone marrow • B cells • mature in bone marrow • humoral response system • “humors” = body fluids • attack pathogens still circulating in blood & lymph • produce antibodies • T cells • mature in thymus • cellular response system • attack invaded cells
Vaccinations • Immune system exposed to harmless version of pathogen • stimulates B cell system to produce antibodies to pathogen • “active immunity” • rapid response on future exposure • creates immunity without getting disease! • Most successful against viruses
Passive immunity • Obtaining antibodies from another individual • maternal immunity (passed while in the womb or during breastfeeding) • Injection • injection of antibodies • short-term immunity
T What if the attacker gets past the B cells in the blood & actually infects (hides in) some of your cells? Attackof the Killer T cells! You need trained assassins to recognize & kill off these infected cells! But how do T cellsknow someone ishiding in there?
T cells • Attack, learn & remember pathogens hiding in infected cells • recognize antigen fragments • also defend against “non-self” body cells • cancer & transplant cells • Types of T cells • helper T cells • alerts rest of immune system • killer (cytotoxic) T cells • attack infected body cells • memory T cells • long term immunity T cell attacking cancer cell
HIV & AIDS • Human Immunodeficiency Virus • virus infects helper T cells • helper T cells don’t activate rest of immune system: killer T cells & B cells • also destroys helper T cells • AIDS: AcquiredImmunoDeficiency Syndrome • death usually from “opportunistic” infections • pneumonia, cancers HIV infected T cell
Immune system malfunctions • Auto-immune diseases • immune system attacks ownmolecules & cells • lupus • antibodies against many molecules released by normal breakdown of cells • rheumatoid arthritis • antibodies causing damage to cartilage & bone • diabetes • beta-islet cells of pancreas attacked & destroyed • multiple sclerosis • T cells attack myelin sheath of brain & spinal cord nerves • Allergies • over-reaction to environmental antigens • allergens = proteins on pollen, dust mites, in animal saliva • stimulates release of histamine
The rest of class… • Create an Immune System Comic: • Must have at least 4 boxes in your story • Explain ONE of the levels of defense in the immune system • Use “word bubbles” (like the ones shown) to explain what is happening