Perception is…
200 likes | 464 Vues
Perception is…. Awareness of things (aka reality) through our 5 senses Sight Smell Touch Hearing Taste. Perception…. Plays a key role in almost all subject areas If you had to choose one, in which subject area is perception most valuable? Least valuable? Is the centerpiece of Empiricism

Perception is…
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Perception is… • Awareness of things (aka reality) through our 5 senses • Sight • Smell • Touch • Hearing • Taste
Perception… • Plays a key role in almost all subject areas • If you had to choose one, in which subject area is perception most valuable? Least valuable? • Is the centerpiece of Empiricism • School of philosophy that holds that allknowledge is ultimately based on perceptual experience • In your opinion, is this too extreme, or spot on?
Perception consists of… • Sensation, which is provided by the world • Interpretation, which is provided by our minds.
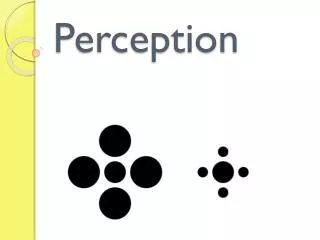
Perceptual Illusions • We can become aware of our interpretations of the world by examining visual illusions • Types of visual illusion include: • Context: we examine the overall context of an image to make a judgment about the size of an object • Figure and Ground: We tend to zero in on certain aspects (figure) and make other parts the background • Visual Grouping: We look for meaning in something and fill in the gaps (e.g. “dog” in the book) • Expectations: Our expectations will influence how we see things. (e.g. Paris in the the spring)
Selective Perception • We don’t process all the data that we’re presented with • We only notice some things and overlook others • Typically, there are two kind of stimuli we notice: • Intensity (a loud bang or sneeze) • Contrast (e.g. blood on a white carpet) • Mood and interest influences our perception as well; e.g. 3 friends hiking
Relationship between Belief and Sight • Our belief influences/taints/informs our sight • If we’re consciously looking for something, then we may see it even if it’s not really there • Vulcan • Virgin Mary in a church window; a face on Mars
Eye-witness testimony • Shown to be incredibly unreliable • The eye is not a camera and visual memories are not photographs • Even possible to say that every time we remember something we reconstruct it • For HW, please read 105 to 107 and take double column notes (5 entries)
Perception… • …can be an important source of knowledge. BUT, why do we need to treat it with caution?
Confirmation by another sense • One sense alone will not always provide us with an accurate idea of reality • Why privilege touch over the other senses?
Coherence • Also featured in determining whether a knowledge claim is reasonable or not • In the context of sensory perception, if something doesn’t fit in, then most likely you are mistaken
Independent Testimony • Credibility of evidence increases with each additional witness • Such testimony pushes credibility of evidence into the realm of “beyond a reasonable doubt”
Ultimate reality • Can we ever have knowledge of ultimate reality? • If so, how? If not, why not?
Experiencing reality • Pain, taste and color are simply the subjective experience that results from the interaction of you and your environment • e.g. Grass is not green, it’s just that you see green grass • Is reality colorless as the book says?
Experiencing reality • If a tree falls… • Is sound physical? Or experienced? What difference does it make? • Can we say that colors, sounds, and tastes exist out there independent of our experience of them?
Experiencing reality • If a tree falls… • Is sound physical? Or experienced? What difference does it make? • Can we say that colors, sounds, and tastes exist out there independent of our experience of them?
Experiencing reality • Does it matter whether things behave as expected when we’re not around? • Does it really only matter if we’re there? • E.g. tables in the classroom
3 Theories about Reality • Common-sense realism • The way we perceive the world mirrors it as it is • What is a criticism of common-sense realism?
3 Theories about Reality • Scientific Realism • The world exists as an independent reality and is very different from how we perceive it • Physical table vs. scientific table • Ultra-zoom view
3 Theories about Reality • Phenomenalism • Matter is “the permanent possibility of sensation” and it makes not sense to say the world exists independent of our experience of it • Beyond our experience of reality, there is nothing to be said, despite the probable fact that the world may exist outside of our experience with it