Denormalizing the Surface Water Bodies Database for Enhanced Data Visualization
100 likes | 212 Vues
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of denormalizing the Surface Water Bodies (SWB) database. It covers understanding the database structure, compiling various views, and utilizing FME Workbench to streamline data processes. Key steps include removing relationships between main and child tables, mapping indexed fields from Lists of Values (LOVs), and adding unique attributes to shapes. Finally, the creation of a complete geodatabase enables efficient data exploitation and visualization using ArcMap, facilitating better management and analysis of surface water bodies.

Denormalizing the Surface Water Bodies Database for Enhanced Data Visualization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
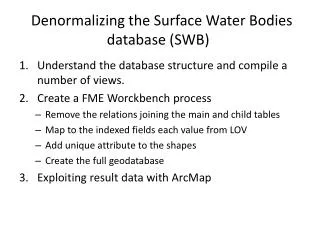
Denormalizingthe Surface Water Bodies database (SWB) • Understand the database structure and compile a number of views. • Create a FME Worckbench process • Remove the relations joining the main and child tables • Map to the indexed fields each value from LOV • Add unique attribute to the shapes • Create the full geodatabase • Exploiting result data with ArcMap
Denormalizingthe Surface Water Bodies database (SWB) • Understand the database structure and compile a number of views. • Create a FME Worckbench process • Remove the relations joining the main and child tables • Map to the indexed fields each value from LOV • Add unique attribute to the shapes • Create the full geodatabase • Exploiting result data with ArcMap
Surface Water Bodies database (SWB) 1 Understand the database structure
Denormalization of the SWB database LOV LOV LOV LOV 1 Understand the database structure
Denormalization of the SWB database Protected Area Status Surface Water Bodies LOV Ecological Status LOV Chemical Status LOV LOV 1 Understand the database structure
Denormalization of the SWB database Protected Area Status Surface Water Bodies LOV Ecological Status LOV Chemical Status LOV LOV 1 Understand the database structure
Denormalization of the SWB database Ecological Status Surface Water Bodies Protected Area Status Chemical Status 1 Understand the database structure
First approach of the SWB DB Ecological Status Surface Water Bodies Protected Area Status Chemical Status 1 Understand the database structure
Denormalizingthe Surface Water Bodies database (SWB) • Understand the database structure and compile a number of views. • Create a FME Worckbench process • Remove the relations joining the main and child tables • Map to the indexed fields each value from LOV • Add unique attribute to the shapes • Create the full geodatabase • Exploiting result data with ArcMap
Denormalizingthe Surface Water Bodies database (SWB) • Understand the database structure and compile a number of views. • Create a FME Worckbench process • Remove the relations joining the main and child tables • Map to the indexed fields each value from LOV • Add unique attribute to the shapes • Create the full geodatabase • Exploiting result data with ArcMap