Genetic Code and Translation
440 likes | 672 Vues
Genetic Code and Translation. Outline. The Breaking of the Genetic Code Examples of two experimental approaches Concepts and Terms related to genetic code Wobble Degeneracy isoaccepting Translation prokaryote eukaryotes. The Genetic Code and Translation.

Genetic Code and Translation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Outline • The Breaking of the Genetic Code • Examples of two experimental approaches • Concepts and Terms related to genetic code • Wobble • Degeneracy • isoaccepting • Translation • prokaryote • eukaryotes
Experiments that “broke the genetic code” • 1. Cell Free experiments • Applied to the Homopolymer experiment • 2. Known RNA sequences and ribosomal bound tRNA
1. Overview 3 2 1 All these experiments used a cell free system. 4 5 ppt. protein
Application of experimental design 1 hot amino acid translation + 19 cold amino acids Cell free system 20X each a different “hot amino acid
2. Known mRNA sequences + Ribosomal bound tRNA Amino acid This is transfer RNA Now link this idea to The genetic code table Anti-codon
Amino Acid Transfer RNA ribosome
Mix with Codon of mRNA 2. EXPERIMENT Isolate ribosome bound tRNA Analyze amino acid
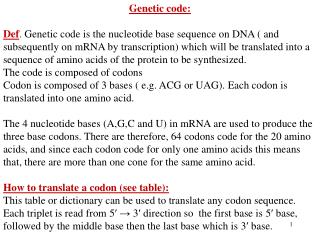
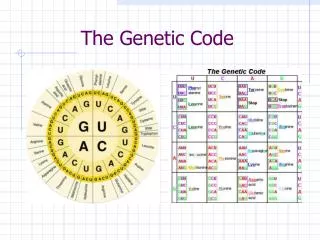
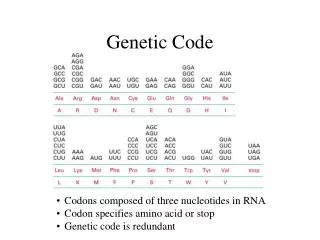
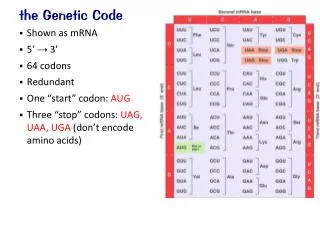
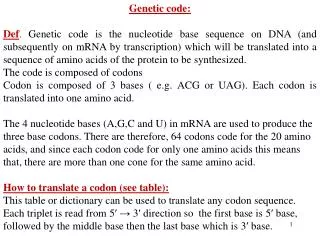
Genetic Code Table 1968 Wobble Degeneracy & mRNA
Isoaccepting & tRNAs Different tRNAs accept same amino acid!
We will approach our discussion of translation as a “Nonoverlapping Code” mRNA sequences
Steps of Translation • 1. Binding of amino acids to tRNA • 2. Initiation • 3. Elongation • 4. Termination • 5. Peptide Release • 6. Protein modification
It takes two steps to “charge” the tRNA Aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase Amino acid+ATP tRNA is charged
Bacterial Initiation Step 2: Initiation of Translation IF3
Note 3 ribosomal sites P A E 70S E A
Kozak Eukaryotic Initiation key differences
Peptidyl transferase 3. ELONGATION: look at the “EPA” sites
UAA UAG UGA Steps 4 and 5: Termination and Release
Animation of Translation http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter14/animations.html See chapter 15
6. Lipoprotein Glycoprotein
Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Streptoymycin Erythromycin Bind and block bacterial ribosomes “A” site Binds to large subunit; blocks peptide formation Blocks initiation step Blocks translocation step Antibiotics and Translation
Amino Acids-R groups • Nonpolar, aliphatic • Polar, uncharged • Aromatic • Positively charged • Negatively charged
For your review: Summary of important steps involved in translation
1. 2.
Eukaryotic translation is very similar except: • More IF’s • Kozak sequence • 5’CAP • 3’poly-A tail