Genetic Code
40 likes | 177 Vues
This chapter delves into the genetic code, which contains the instructions for protein synthesis in living organisms. It explains that RNA acts as the intermediary language between DNA and proteins, utilizing only four nitrogen bases: uracil (U), adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases are grouped into codons, with each codon consisting of three nucleotides that specify an amino acid. The significance of start and stop signals in translation, as well as the relationship between mRNA and tRNA in assembling amino acids into polypeptides, is also covered.

Genetic Code
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Genetic Code Chapter 10-3
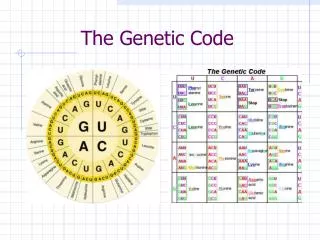
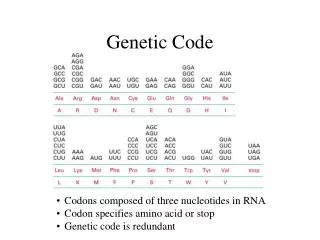
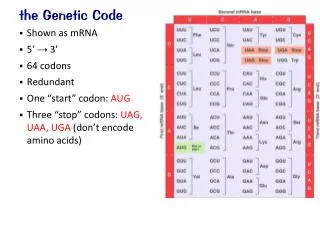
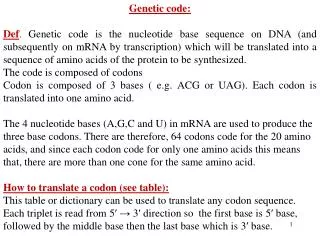
4 Letters • DNA contains instructions; RNA is the understood language • RNA has only 4 nitrogen bases (nucleotides): U, A, C, G • The nucleotides are read in groups of three
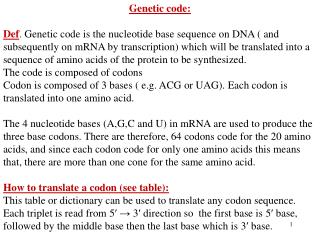
Codons • Codon: a group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid • Example: AAACACGGU AAA – CAC - GGU lysine – histidine - glycine • Start signal: AUG • Stop signal: UAA, UAG, UGA
Translation • Nucleotides in mRNA are decoded into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide • Floating in cytoplasm are amino acids and tRNA • mRNA (codon) has a complimentary tRNA (anticodon) bound with a specific amino acid