Understanding Static Charges & Magnetism Interaction
100 likes | 187 Vues
Learn about static charges, magnetism, and their interaction in this comprehensive guide. Discover how charged particles in atoms create static electricity and the forces of attraction and repulsion between them. Explore the similarities and differences between electric and magnetic fields, as well as methods of charge transfer. Enhance your knowledge of conservation of charges, visibility of charges, and static discharge phenomena. Get insights into friction, conduction, and induction processes related to static charges. Delve into the fascinating world of electromagnetism!

Understanding Static Charges & Magnetism Interaction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Magnetism Force of attraction/repulsion Unlike = attract Like = repel http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/science/images/sci_dia_74.gif
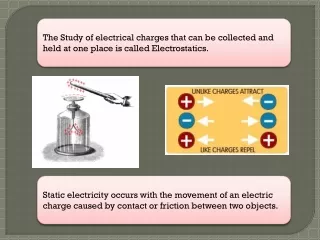
Charged Particles Found in atom Proton (positive) Electron (negative) Unlike charges = attract Like charges = repel Ben Franklin gave names positive and negative to the charges! http://www.geocities.com/CapeCanaveral/Hall/1410/charges.gif
Similarities/Differences Same two ends (pos/neg; north/south), field around them, like repel, opposite attract Different Magnetic poles = pairs Electric charges = alone
Electric Field Where electric force (attract/repel) around charged particle felt Lines = direction and strength Closer together lines… stronger the electric field http://www.rwc.uc.edu/koehler/biophys.2ed/images/fields2.gif
Field Lines http://buphy.bu.edu/~duffy/PY106/2e.GIF http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/electrical_charges.htm
Neutral? Protons = electrons
Static Electricity Static = stationary Temporary partial charge Charges build up – do not continue to flow http://www.esdsystems.com/images/carpet.gif
Transfer Conservation of Charges: Not created or destroyed; Transferred Electrons flow Lose electrons positive Gain electrons negative Friction – rubbing of uncharged objects Conduction – touching of a charged object to another object Induction – no touching, caused by electric field of charged object
Visibility Charges not seen Detected by electroscope Static Discharge – transfer until equal charges Can cause a spark (like lightning)! http://www.science.uwaterloo.ca/~cchieh/cact/nuctek/interact.html http://weathereye.kgan.com/cadet/lightning/electricity.html