Chapter 2: Measurement
110 likes | 367 Vues
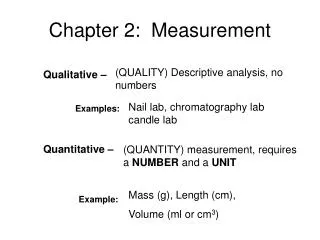
Chapter 2: Measurement. Qualitative – Examples: Quantitative – Example:. (QUALITY) Descriptive analysis, no numbers. Nail lab, chromatography lab candle lab. (QUANTITY) measurement, requires a NUMBER and a UNIT. Mass (g), Length (cm), Volume (ml or cm 3 ) . Precision and Accuracy.

Chapter 2: Measurement
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 2: Measurement Qualitative – Examples: Quantitative – Example: (QUALITY) Descriptive analysis, no numbers Nail lab, chromatography lab candle lab (QUANTITY) measurement, requires a NUMBER and a UNIT Mass (g), Length (cm), Volume (ml or cm3)
Precision and Accuracy Precision- Accuracy – Dart throwing examples: How close lab measurements of the same item are to each other How close a lab measurement is to the true value. Precise but not accurate Accurate & Precise Not Accurate or Precise
Metric System Based on the number _______ The International System of Units - _____ 10 SI
Metric System Increments (symbol) (Value) Mega ---- ---- Kilo Hecto Deka Base Units deci centi mili ---- ---- micro M 1,000,000; 1,000,000 bigger --- --- --- --- 1000; 1000 times bigger K 100; 100 times bigger H 10; 10 times bigger D gram (g), meter (m), liter (l) d 0.1; 1/10; 10 times smaller c 0.01; 1/100; 100 times smaller m 0.001; 1/1000; 1000 times smaller --- --- --- --- u 0.000001; 1/1000000; 1000000 times smaller
Metric Conversions • M - - King Henry Drinks Basically delicious chocolate milk - - u • Examples: • 50.0g = _______ mg 4) 2359ug = _________g • 250L = ________KL 5) 5ML = _________L • 3) 0.0462Km = _______m 6) 87dm = ________Km • (Worksheet and activity on the Metric System) e k a e c i e n t i i l i i c r o e g a e c t o a s e i l o 50,000 0.002359 0.250 5,000,000 46.2 0.0087
Place value QuantityUnitSymbolInstrumentread to Length Volume Mass Temperature Instruments used for measuring 0.01cm ruler meter m, cm 0.01cm ruler cm3 = L x W x H 10ml = 0.01ml liter Graduated cylinder L, ml 100ml = 0.1ml grams g balance 0.01g C Celsius thermometer 0.5 C
Distance Length – Area – (Length Experiment and Area and Volume Calculations) Direct measurement. (ruler) Calculated measurement Area = Length x width = cm2 Example: Find the area of your desk. L = ________; W = ________ ________ x ________ = _________
Volume Direct Measurement – Meniscus – Calculated Volume – Example: Using a graduated cylinder Used to measure liquids. Used to measure granular solids like sugar. Lowest point of the curve where you read the volume of a liquid in a graduated cylinder 3 meniscus 2 Volume = 2.2ml 1 Using a ruler. Length x width x height Used for regularly shaped objects: cubes, etc. Units = meters cubed Calculate the volume of your desk top. L = _______; W = _________; H = ________
Volume continued Water displacement – Example: Amount of water + object = ________ml Amount of water before = - ________ml Volume of object = ________ml Used to measure irregularly shaped objects 50.5 20.5 30.0 Interesting Fact: 1mL = 1cm3 = 1g H2O
Density Story of the king’s crown – was it gold or was it fake? Problem: I have a lump of yellowish, metallic looking stuff; how do I figure out what it is? 1. 2. 3. 4. Mass 10.00g Weight it 100.0ml Volume Water displacement 10g/100ml = 0.1g/ml D = M/V Density Look it up mass volume Density is a ratio of the ________ to the ________ of an object.
ratio mass Density is the __________ of the __________ to the ____________of an object. Units for density: or Density is a _________________ _______________ that does not change for any one element. volume g/cm3 g/ml physical property Density = mass/ volume Formula for density: To use the triangle cover up what you are solving for and the formula is what is left. M D V (Density worksheet and lab)