Respiratory system
100 likes | 241 Vues
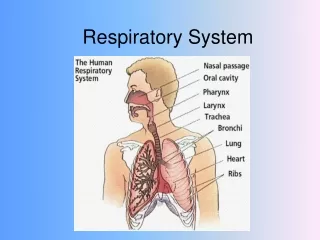
The respiratory system is vital for gas exchange, protecting the body from pathogens and extreme conditions. Its structure includes a series of air-conducting pathways, starting from the external nares and nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and bronchi. Alveoli, the functional units of the lungs, facilitate gas exchange with the bloodstream. Key functions include sound production and assisting with the sense of smell. This overview also touches on pulmonary ventilation, lung volumes, and the Heimlich maneuver, which is crucial for addressing choking emergencies.

Respiratory system
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Respiratory system Aka: what’s the heimlich manuever?
Why the respiratory system? • Large surface area for gas exchange • Move air to gas exchange area • Protect gas exchange area from pathogens, dehydration, extreme temperatures • Make noise! • Assist smelling ( who cut the cheese?).
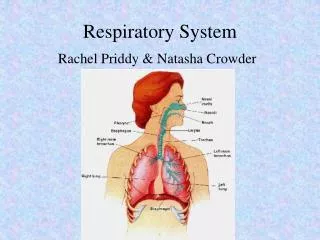
Air conducting (moving) path • External nares • Nasal cavity • guard hairs • Air warmed and moistened • Nasal septum
More path • Oral cavity • Separated from nasal by palatine/maxillary bones called “hard palate” • Soft palate- fleshy part beyond hard palate • Oropharynx- contains tonsils for protection from foreign bodies • Glottis- hole at start of trachea • Epiglottis- covers trachea • Larynx- contains vocal cords or “voice box”
Cont. • Coughing reflex- triggered when “stuff” hits vocal cords, • “cough”-glottis is closed and pressure built up in lungs until glottis is suddenly released • Tension on vocal cords determines pitch • Trachea- extends from larynx to branching of bronchi, includes rings of cartilage for support
More • Tracheostomy- inserting a tube through anterior tracheal wall. “Stoma” • Bronchi- branching of trachea into primary, secondary and tertiary branches • Bronchioles- when cartilage is no longer present ( less than 0.04 inch in diameter)
Alveola • Sack where gas exchange occurs • Trivia- 150 million alveola / lung • Gives spongy appearance to lung • Simple squamous epithelium • Dust cells- macrophages that roam around eating up dust and debri • Moist alveoli- why? • Surfactant- oily secretion that reduces surface tension of moist alveoli
Air movement • Hypoxia- hypo- low, oxia-? • Anoxia-? • Pulmonary ventilation depends on • Pressure gradient-? • Diaphragm- 75% of pulmonary vent. • Rib cage- 25% of pulmonary vent.
Lung volume/ capacity • Tidal volume- amount of air moved during a single respiratory cycle, normal breath • Expiratory reserve volume- ( forced exhalation volume) amount voluntarily expelled after a regular exhalation • Inspiratory reserve volume- (forced inhalation volume) amount voluntarily inhaled after a regular inhalation • Vital capacity= tidal volume+ERV+IRV, max air you can move
Residual volume- air left in lung even after forceful exhalation