Why predict RNA?
100 likes | 271 Vues
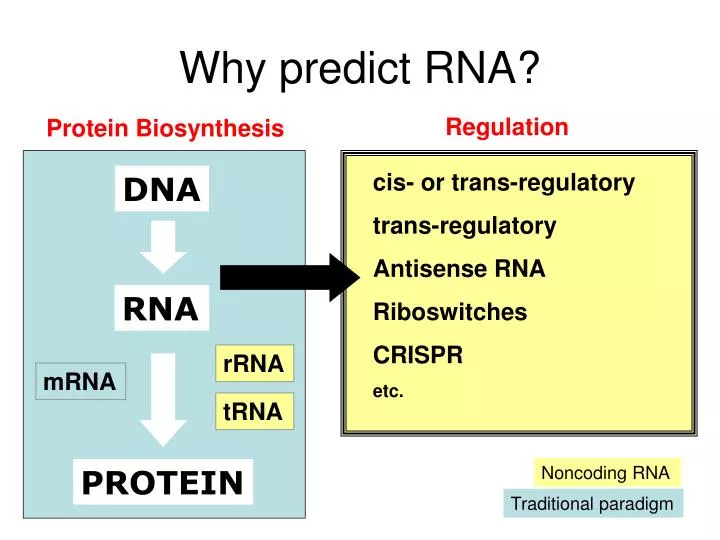
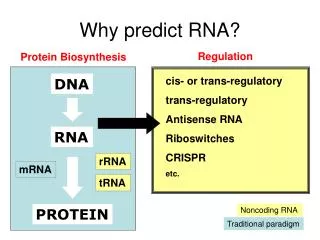
DNA. cis- or trans-regulatory trans-regulatory Antisense RNA Riboswitches CRISPR etc. RNA. rRNA. mRNA. tRNA. PROTEIN. Why predict RNA?. Regulation. Protein Biosynthesis. Noncoding RNA. Traditional paradigm. Regulatory sRNA.

Why predict RNA?
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DNA cis- or trans-regulatory trans-regulatory Antisense RNA Riboswitches CRISPR etc. RNA rRNA mRNA tRNA PROTEIN Why predict RNA? Regulation Protein Biosynthesis Noncoding RNA Traditional paradigm
Regulatory sRNA “Recent findings strongly suggest that sRNAs regulate the virulence of the gram-negative diarrheal pathogen V. cholera.*” Hypothesis: Virulence in N. Meningitiditis is associated with regulation of virulence genes *Jonathan Livny et al. Nucleic Acids Res. (2005) 33:4096
sRNA Challenges Methods to predict coding, tRNA and rRNA genes are much more mature than those for sRNA. • less information • small • sequence-acting • misleading information • dual purpose • boundaries not obvious
Fundamental Methodology • Comparative • Analogous to protein comparative models • Scoring is tailored for RNA • Sequence-based weight matrices (RFAM) • Profile HMM • Structure-enhanced (Covariance Model) • Noncomparative • Search for transcriptional signals
RFAM • RNA database • Each RNA sequence classified in a Family • Families determined by Covariance Model (CM) • CM extends Profile HMM to include Covariance • Annotation of Families with Wikipedia
What is Covariance? Christian Weile et al. BMC Genomics (2007) 8:244
Noncomparative Prediction Seek transcription signals: Limited utility… James A. Goodrich & Jennifer F. Kugel, Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. (2006) 7:612
Noncomparative Prediction • Cis: • Signals may dual-code for peptides • Trans: • Unknown nc-RNA termination signals • *Non-enterobacteria lack information on • Promoter consensus sequences • Transcription factor binding sites *Rolf Backofen & Wolfgang R. Hess, RNA Biol. (2010) 7:1
Comparative + Noncomparative • Effective sRNA prediction in V. cholerae • Non-enterobacteria • sRNAPredict2 • 32 novel sRNAs predicted • 9 tested • 6 confirmed *Jonathan Livny et al. Nucleic Acids Res. (2005) 33:4096
BLAST (NCBI, WU) ParAlign SSEARCH HMMer SAM ERPIN Infernal RaveNnA RSEARCH RSmatch RFAM NcDNAlign eQRNA ALIFOLDZ RNAz MultiZ Evofold FASTA ParAlign RNAMotif sRNAPredict2 sRNAFinder SIPHT Software *Rolf Backofen & Wolfgang R. Hess, RNA Biol. (2010) 7:1 Eva K. Freyhult et al. Genome Res. (2007) 17:117